Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
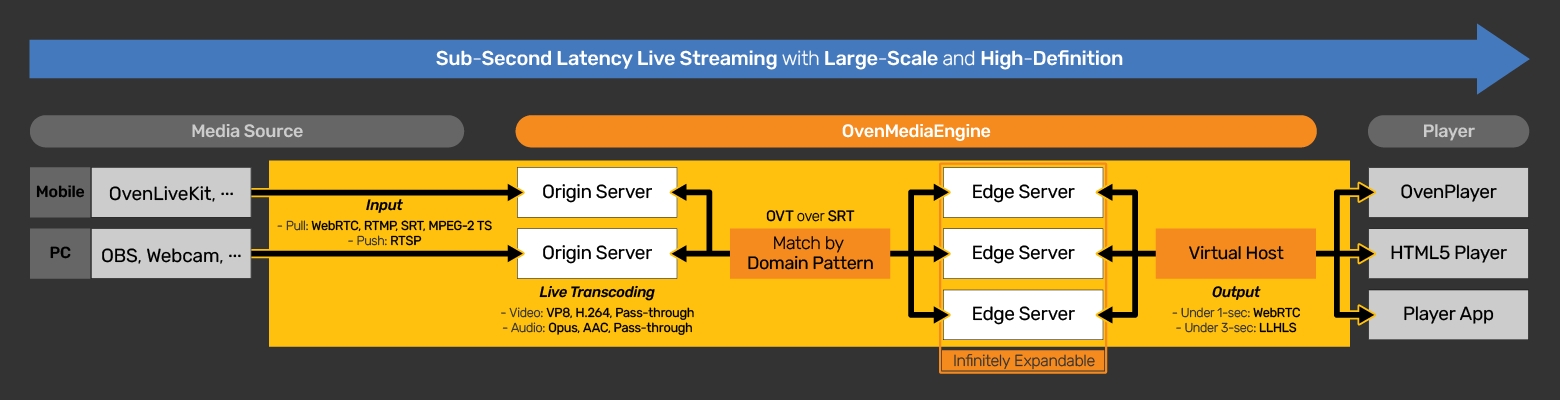
OvenMediaEngine supports multiple protocols for input from various live sources, without compromising basic usability. This allows you to publish a variety of live sources with sub-second latency. See the sub-page for more information.
We provide online demos of OvenPlayer(WebRTC/LLHLS Player) and OvenLiveKit(WebRTC Live Encoder) so that users can easily test out OvenMediaEngine.
To connect to your OvenMediaEngine in the online demo, you will need to install a certificate and use either the HTTPS or WSS protocol. Unsecured HTTP or WS protocols could not work in online demos due to browser security policies.
OvenSpace offers a fast and easy way to experience the powerful tools of OvenMediaEngine, OvenPlayer, and OvenLiveKit in action.
With OvenSpace, you can quickly and easily stream content with sub-second latency using WebRTC technology, or take advantage of Apple's LLHLS specification to deliver low-latency live streaming. The platform allows you to stream from various sources, including your webcam, microphone, screen, or an external live encoder that supports RTMP and SRT.
OvenSpace is available online, so you can try it out for yourself at . You'll get a hands-on experience of how OvenMediaEngine, OvenPlayer, and OvenLiveKit work together seamlessly to deliver top-quality streaming, whether you're a developer looking to build a media service or someone who wants to experience sub-second or low-latency streaming firsthand.
OvenSpace is also available on as open source. It will be a good reference when developing media services using OvenMediaEngine, OvenPlayer and OvenLiveKit.
From OvenMediaEngine v0.14.0, updates to legacy HLS, DASH, and LLDASH are now discontinued. These will be deprecated.
LLHLS, released from v0.14.0, is superior to Dash and LLDASH in all aspects of compatibility, performance and function, and also support legacy HLS players. Therefore, we decided not to update legacy HLS, DASH and LLDASH anymore. With the energy that was used to maintain these features, we will focus on more wonderful features in the future.
(OME) is a Sub-Second Latency Live Streaming Server with Large-Scale and High-Definition. With OME, you can create platforms/services/systems that transmit high-definition video to hundreds-thousand viewers with sub-second latency and be scalable, depending on the number of concurrent viewers.
OvenMediaEngine can receive a video/audio, video, or audio source from encoders and cameras such as , OBS, XSplit, and more, to WebRTC, SRT, RTMP, MPEG-2 TS, and RTSP as Input. Then, OME transmits this source using
In order to publish thumbnails, an encoding profile for thumbnails must be set. JPG and PNG are supported as codec. And framerate and resolution can be adjusted. Framerate is the number of thumbnails extracted per second. We recommend 1 as the thumbnail framerate. Thumbnail encoding uses a lot of resources. Therefore, if you increase this value excessively, it can cause a failure due to excessive use of system resources. The resolution can be set as desired by the user, and if the ratio is different from the input image, it is stretched. We plan to support various ratio modes in the future.
Declaring a thumbnail publisher. Cross-domain settings are available as a detailed option.
When the setting is made for the thumbnail and the stream is input, you can view the thumbnail through the following URL.
Method
URL Pattern
GET
http(s)://<ome_host>:<port>/<app_name>/<output_stream_name>/thumb.<jpg|png>
<Bind>
<Publishers>
...
<Thumbnail>
<Port>20080</Port>
<!-- If you need TLS support, please uncomment below:
<TLSPort>20081</TLSPort>
-->
</Thumbnail>
</Publishers>
</Bind><OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>default_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}_preview</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Image>
<Codec>jpeg</Codec>
<Framerate>1</Framerate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
</Image>
<Image>
<Codec>png</Codec>
<Framerate>1</Framerate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
</Image>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles><Publishers>
...
<Thumbnail>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</Thumbnail>
</Publishers>Our goal is to make it easier for you to build a stable broadcasting/streaming service with sub-second latency.
Ingest
Push: WebRTC, WHIP, SRT, RTMP, MPEG-2 TS
Pull: RTSP
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) for LLHLS and WebRTC
Low-Latency Streaming using LLHLS
DVR (Live Rewind)
Dump for VoD
ID3v2 timed metadata
Sub-Second Latency Streaming using WebRTC
WebRTC over TCP (with embedded TURN server)
Embedded WebRTC Signaling Server (WebSocket based)
Retransmission with NACK
Embedded Live Transcoder
Video: VP8, H.264, Pass-through
Audio: Opus, AAC, Pass-through
Clustering (Origin-Edge Structure)
Monitoring
Access Control
AdmissionWebhooks
SignedPolicy
File Recording
Push Publishing using RTMP and MPEG2-TS (Re-streaming)
Thumbnail
REST API
Experiment
P2P Traffic Distribution (Only WebRTC)
We have tested OvenMediaEngine on platforms, listed below. However, we think it can work with other Linux packages as well:
Ubuntu 18+
CentOS 7+
Fedora 28+
Please read Getting Started chapter in the tutorials.
Thank you so much for being so interested in OvenMediaEngine.
We need your help to keep and develop our open-source project, and we want to tell you that you can contribute in many ways. Please see our Guidelines, Rules, and Contribute.
We always hope that OvenMediaEngine will give you good inspiration.
Test Player
Without TLS:
With TLS:
OvenMediaEngine is licensed under the AGPL-3.0-only. However, if you need another license, please feel free to email us at [email protected].
You can check the docker container status with the following command:
$ docker ps -f name=ome
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c9dd9e56d7a0 airensoft/ovenmediaengine:latest "/opt/ovenmediaengin…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:1935->1935/tcp, :::1935->1935/tcp, 80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:3333->3333/tcp, :::3333->3333/tcp, 3334/tcp, 8080/tcp, 0.0.0.0:3478->3478/tcp, :::3478->3478/tcp, 4000-4005/udp, 8090/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, :::9000->9000/tcp, 10010/udp, 0.0.0.0:9999-10009->9999-10009/udp, :::9999-10009->9999-10009/udp omeYou can view the log with the command below. This is important because you can check the version of OvenMediaEngine that is running.
$ docker logs ome -f
[2023-03-06 08:01:24.810] I [OvenMediaEngine:1] Config | config_manager.cpp:239 | Trying to set logfile in directory... (/var/log/ovenmediaengine)
[2023-03-06 08:01:24.810] I [OvenMediaEngine:1] Config | config_manager.cpp:261 | Trying to load configurations... (origin_conf/Server.xml)
[2023-03-06 08:01:24.816] I [OvenMediaEngine:1] OvenMediaEngine | banner.cpp:23 | OvenMediaEngine v0.15.1 () is started on [ab3995acafd4] (Linux x86_64 - 5.13.0-44-generic, #49~20.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Wed May 18 18:44:28 UTC 2022)
...Publish your live stream to OvenMediaEngine using a live encoder like OBS.
The RTMP publishing address is :
Server rtmp://Your.Docker.Host.IP:1935/app
Stream Key stream
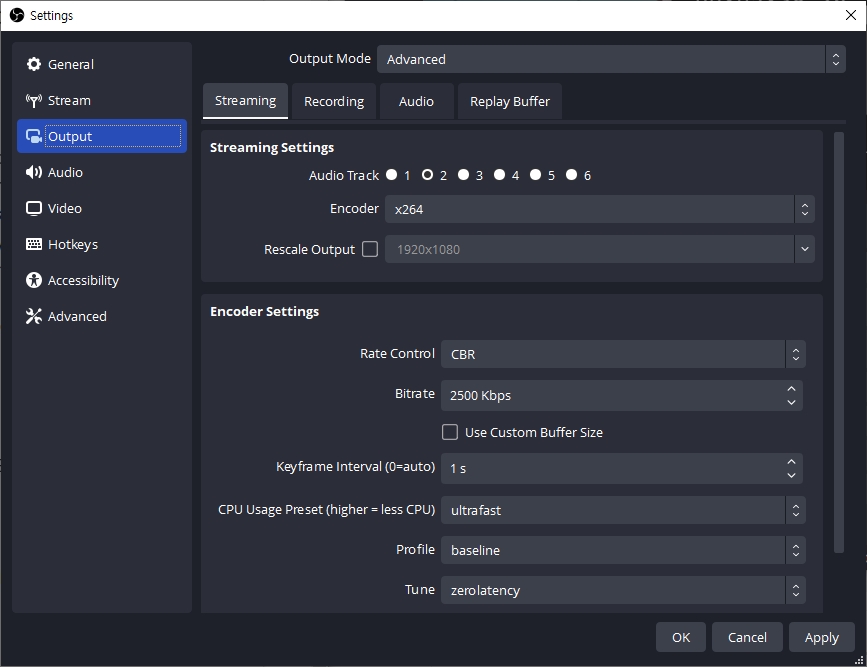
The settings below are recommended for ultra-low latency.
Keyframe Interval
1s (DO NOT set it to 0)
CPU Usage Preset
ultrafast
Profile
baseline
Tune
zerolatency
Open the installed OvenPlayer Demo page in your browser.
http://Your.Docker.Host.IP:8090/
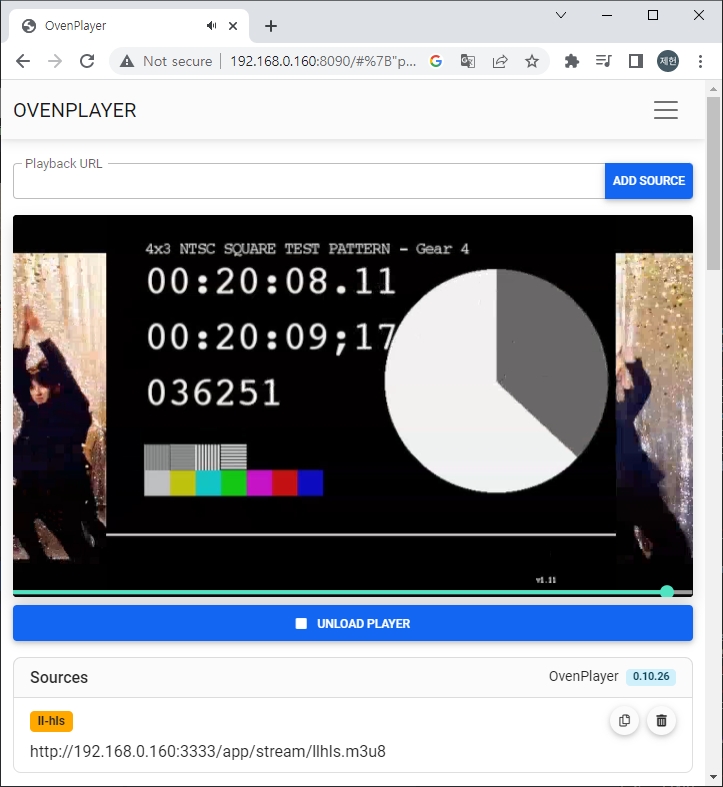
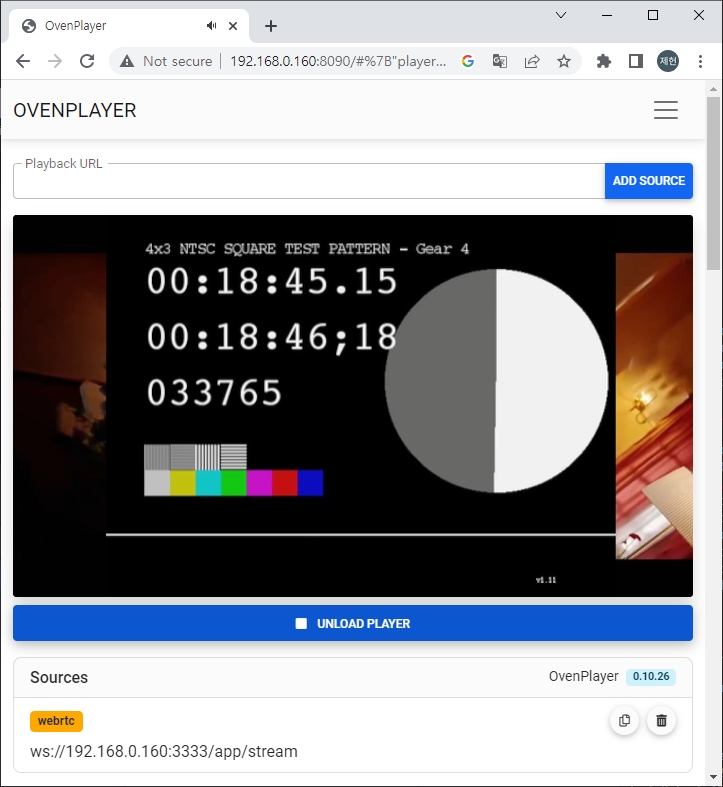
Add ws://Your.Docker.Host.IP:3333/app/stream to the Playback URL and click the ADD SOURCE and LOAD PLAYER button to play the live stream with WebRTC.
Add http://Your.Docker.Host.IP:3333/app/stream/llhls.m3u8 to the Playback URL and click the ADD SOURCE and LOAD PLAYER button to play the live stream with LLHLS.
Site URL
Description
OvenPlayer demo (TLS not enabled)
OvenPlayer demo
OvenLiveKit (WebRTC Live Encoder) demo
Most browsers can't load resources via HTTP and WS (WebSocket) from HTTPS web pages secured with TLS. Therefore, if the player is on an HTTPS page, the player must request streaming through "https" and "wss" URLs secured with TLS. In this case, you must apply the TLS certificate to the OvenMediaEngine.
You can set the port for TLS in TLSPort. Currently, LLHLS and WebRTC Signaling support TLS.
<Bind>
<!-- For API Server -->
<Managers>
<API>
<Port>8081</Port>
<TLSPort>8082</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</API>
</Managers>
<!-- For Providers -->
<Providers>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
...
</WebRTC>
</Providers>
<!- For Publishers -->
<Publishers>
<LLHLS>
<Port>80</Port>
<TLSPort>443</TLSPort>
</LLHLS>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
</Signalling>
...
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Bind>Add your certificate files to as follows:
To enable HTTP for HLS and WebRTC signaling servers, you must enable the TLS element and install the certificate file in PEM format. This involves indicating a server certificate through the CertPath, as well as a private key file through the KeyPath. These paths can be specified as either absolute or relative paths from the executable. However, if the server certificate was issued using an intermediate certificate, some browsers may raise concerns about the certificate's authenticity. To address this, a bundle of chained certificates provided by a Certificate Authority can be set in the ChainCertPath.
Assuming the certificate settings are correctly configured, WebRTC streaming can then be played via the wss://url protocol, while LLHLS streaming can be accessed via .
OvenMediaEngine supports Push Publishing function that can retransmit live streams to other systems. The protocol supported for retransmission uses SRT, RTMP or MPEGTS. Because, most services and products support this protocol. also, one output stream can be transmitted to multiple destinations at the same time. You can start and stop pushing the output stream through REST API. Note that the only codecs that can be retransmitted in RTMP and MPEGTS protocol are H264 and AAC.
To use RTMP Push Publishing, you need to declare the <RTMPPush> publisher in the configuration. There are no other detailed options.
To use MPEGTS Push Publishing, you need to declare the <MPEGTSPush> publisher in the configuration. There are no other detailed options.
To use SRT Push Publishing, you need to declare the <SRTPush> publisher in the configuration. There are no other detailed options.
For control of push, use the REST API. SRT, RTMP, MPEGTS push can be requested based on the output stream name (specified in the JSON body), and you can selectively transfer all/some tracks. In addition, you must specify the URL and Stream Key of the external server to be transmitted. It can send multiple Pushes simultaneously for the same stream. If transmission is interrupted due to network or other problems, it automatically reconnects.
For how to use the API, please refer to the link below.
Providers ingests streams that come from a media source. OvenMediaEngine supports RTMP protocol. You can set it in the configuration as follows:
When a live source inputs to the <Application>, a stream is automatically created in the <Application>. The created stream is passed to Encoder and Publisher.
Secure Reliable Transport (or SRT in short) is an open source video transport protocol and technology stack that optimizes streaming performance across unpredictable networks with secure streams and easy firewall traversal, bringing the best quality live video over the worst networks. We consider SRT to be one of the great alternatives to RTMP, and OvenMediaEngine can receive video streaming over SRT. For more information on SRT, please visit the .
SRT uses the MPEG-TS format when transmitting live streams. This means that unlike RTMP, it can support many codecs. Currently, OvenMediaEngine supports H.264, H.265, and AAC codecs received by SRT.
From version 0.10.4, MPEG-2 TS input is supported. The supported codecs are H.264, AAC(ADTS). Supported codecs will continue to be added. And the current version only supports basic MPEG-2 TS with 188 bytes packet size. Since the information about the input stream is obtained using PAT and PMT, the client must send this table information as required.
To enable MPEG-2 TS, you must bind the ports fist and map the bound ports and streams.
$ docker run --name ome -d -e OME_HOST_IP=Your.HOST.IP.Address \
-p 1935:1935 -p 9999:9999/udp -p 9000:9000 -p 3333:3333 -p 3478:3478 -p 10000-10009:10000-10009/udp \
airensoft/ovenmediaengine:0.16.3$ docker run -d -p 8090:80 airensoft/ovenplayerdemo:latest<!-- For API Server -->
<Managers>
<Host>
<Names>
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<TLS>
<CertPath>path/to/file.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>path/to/file.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>path/to/file.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
</Host>
...
</Managers>
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<!-- For Vitual Host -->
<Host>
<Names>
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<TLS>
<CertPath>/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.ca-bundle</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
</Host>Reload the certificate of the specified Virtual Hosts. In case of failure, the existing certificate will continue to be used.
To use multiple streams, it is necessary to bind multiple ports, so we provide a way to bind multiple ports as in the example below. You can use the dash to specify the port as a range, such as Start port-End port, and multiple ports using commas.
First, name the stream and map the port bound above. The macro ${Port} is provided to map multiple streams at once. Check out the example below.
This is an example of publishing using FFMPEG.
# Video / Audio
ffmpeg.exe -re -stream_loop -1 -i <file.ext> -c:v libx264 -bf 0 -x264-params keyint=30:scenecut=0 -acodec aac -pes_payload_size 0 -f mpegts udp://<IP>:4000?pkt_size=1316
# Video only
ffmpeg.exe -re -stream_loop -1 -i <file.ext> -c:v libx264 -bf 0 -x264-params keyint=30:scenecut=0 -an -f mpegts udp://<IP>:4000?pkt_size=1316
# Audio only
ffmpeg.exe -re -stream_loop -1 -i <file.ext> -vn -acodec aac -pes_payload_size 0 -f mpegts udp://<IP>:4000?pkt_size=1316Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code<Applications>
<Application>
...
<Publishers>
...
<RTMPPush>
</RTMPPush>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications><Applications>
<Application>
...
<Publishers>
...
<MPEGTSPush>
</MPEGTSPush>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications><Applications>
<Application>
...
<Publishers>
...
<SRTPush>
</SRTPush>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications><Server>
...
<Bind>
<Providers>
<MPEGTS>
<!--
Listen on port 4000,4001,4004,4005
This is just a demonstration to show that
you can configure the port in several ways
-->
<Port>4000-4001,4004,4005/udp</Port>
</MPEGTS>
</Providers>
</Bind>
...
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Application>
<Providers>
<MPEGTS>
<StreamMap>
<!--
Set the stream name of the client connected to the
port to "stream_${Port}"
For example, if a client connets to port 4000,
OME creates a "stream_4000" stream
-->
<Stream>
<Name>stream_${Port}</Name>
<Port>4000-4001,4004</Port>
</Stream>
<Stream>
<Name>stream_name_for_4005_port</Name>
<Port>4005</Port>
</Stream>
</StreamMap>
</MPEGTS>
</Providers>
<Application>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server>DRM (Widevine, Fairplay)
ULPFEC (Uneven Level Protection Forward Error Correction)
VP8, H.264
In-band FEC (Forward Error Correction)
Opus
OvenMediaEngine can work with a variety of open-sources and libraries. First, install them on your clean Linux machine as described below. We think that OME can support most Linux packages, but the tested platforms we use are Ubuntu 18+, Fedora 28+, and CentOS 7+.
You can build the OvenMediaEngine source using the following command:
sudo apt-get update
cd OvenMediaEngine-0.16.3/src
make release
sudo make install
systemctl start ovenmediaengine
# If you want automatically start on boot
systemctl enable ovenmediaengine.service sudo dnf update
cd OvenMediaEngine-0.16.3/src
make release
sudo make install
systemctl start ovenmediaengine
# If you want automatically start on boot
systemctl enable ovenmediaengine.servicesudo yum update
source scl_source enable devtoolset-7
cd OvenMediaEngine-0.16.3/src
make release
sudo make install
systemctl start ovenmediaengine
# If you want automatically start on boot
In addition, we recommend that you permanently set environment variables as follows.
$ echo 'source scl_source enable devtoolset-7' >> ~/.bashrc The default configuration uses the following ports, so you need to open it in your firewall settings.
1935/TCP
RTMP Input
9999/UDP
SRT Input
4000/UDP
MPEG-2 TS Input
9000/TCP
Origin Server (OVT)
3333/TCP 3334/TLS
LLHLS Streaming * Streaming over Non-TLS is not allowed with modern browsers.
To use TLS, you must set up a certificate. See TLS Encryption for more information.
You can open firewall ports as in the following example:
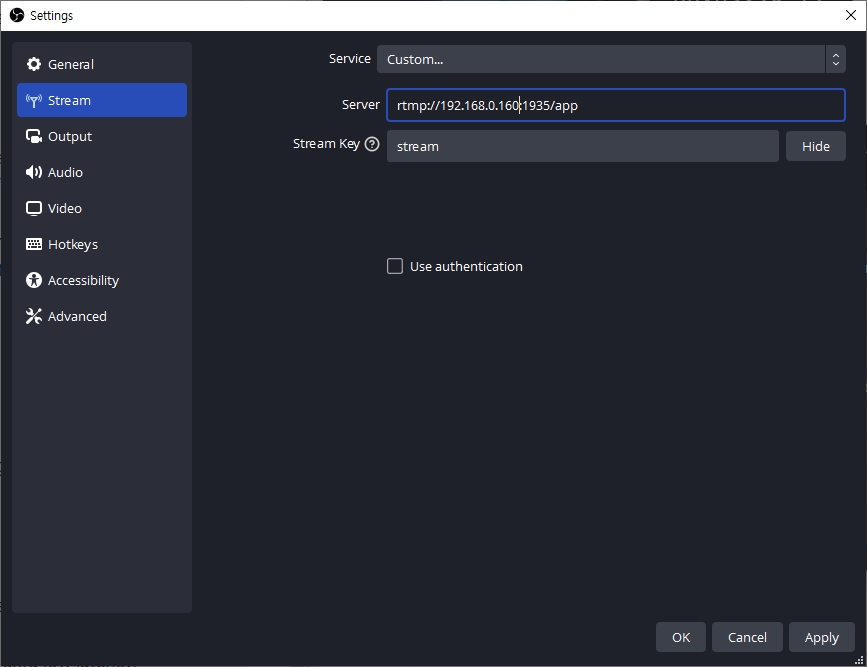
If you set up a live stream using an RTMP-based encoder, you need to set the following in Server.xml:
<BlockDuplicateStreamName> is a policy for streams that are inputted as overlaps.
<BlockDuplicateStreamName> works with the following rules:
true
Default Rejects the new stream inputted as overlap and maintains the existing stream.
false
Accepts a new stream inputted as overlap and disconnects the existing stream.
If you want to publish the source stream, you need to set the following in the Encoder:
URL RTMP://<OvenMediaEngine IP>[:<RTMP Listen Port>]/<App Name]>
Stream Key Stream Name
If you use the default configuration, the <RTMP><ListenPort> is 1935, which is the default port for RTMP. So it can be omitted. Also, since the Application named app is created by default in the default configuration, you can enter app in the [App Name]. You can define a Stream Key and use it in the Encoder, and the Streaming URL will change according to the Stream Key.
Moreover, some encoders can include a stream key in the URL, and if you use these encoders, you need to set it as follows:
URL RTMP://<OvenMediaEngine IP>[:<RTMP Listen Port>/<App Name>/<Stream Name>
If you are using the default configuration, press the URL button in the top right corner of OvenStreamEnoder, and enter the URL as shown below:
Also, <App name> and <Stream name> can be changed and used as desired in the configuration.
If you use the default configuration, set the OBS as follows:
You can set the Stream Key to any name you like at any time.
Set the SRT listen port as follows:
SRT input can be turned on/off for each application. As follows Setting enables the SRT input function of the application.
There are various encoders that support SRT such as FFMPEG, OBS Studio, and srt-live-transmit. Please check the specifications of each encoder on how to transmit streams through SRT from the encoder. We describe an example using OBS Studio.
OvenMediaEngine classifies each stream using SRT's streamid. This means that unlike MEPG-TS/udp, OvenMediaEngine can receive multiple SRT streams through one port. For more information on streamid, see Haivision's official documentation.
Therefore, in order for the SRT encoder to transmit a stream to OvenMediaEngine, the following information must be included in the streamid as percent encoded.
streamid = percent_encoding("srt://{host}[:port]/{app name}/{stream name}[?query=value]")
The streamid contains the URL format, so it must be percent encoded****
OBS Studio 25.0 or later supports SRT. Please refer to the OBS official documentation for more information. Enter the address of OvenMediaEngine in OBS Studio's Server as follows: When using SRT in OBS, you can leave the Stream Key blank.
srt://ip:port?streamid=srt%3A%2F%2F{domain or IP address}[%3APort]%2F{App name}%2F{Stream name}
You can configure SRT's socket options using <Options>. This is particularly useful when setting the encryption for SRT, and you can specify a passphrase by configuring as follows:
For more information on SRT socket options, please refer to https://github.com/Haivision/srt/blob/master/docs/API/API-socket-options.md#list-of-options.
User can send video/audio from web browser to OvenMediaEngine via WebRTC without plug-in. Of course, you can use any encoder that supports WebRTC transmission as well as a browser.
OvenMediaEngine supports self-defined signaling protocol and for WebRTC ingest.
You can set the port to use for signaling in <Bind><Provider><WebRTC><Signaling>. <Port> is for setting an unsecured HTTP port, and <TLSPort> is for setting a secured HTTP port that is encrypted with TLS.
For WebRTC ingest, you must set the ICE candidates of the OvenMediaEnigne server to <IceCandidates>. The candidates set in <IceCandate> are delivered to the WebRTC peer, and the peer requests communication with this candidate. Therefore, you must set the IP that the peer can access. If the IP is specified as *, OvenMediaEngine gathers all IPs of the server and delivers them to the peer.
<TcpRelay> means OvenMediaEngine's built-in TURN Server. When this is enabled, the address of this turn server is passed to the peer via self-defined signaling protocol or WHIP, and the peer communicates with this turn server over TCP. This allows OvenMediaEngine to support WebRTC/TCP itself. For more information on URL settings, check out .
WebRTC input can be turned on/off for each application. As follows Setting enables the WebRTC input function of the application. The <CrossDomains> setting is used in WebRTC signaling.
OvenMediaEnigne supports self-defined signaling protocol and WHIP for WebRTC ingest.
The signaling URL for WebRTC ingest uses the query string ?direction=send as follows to distinguish it from the url for WebRTC playback. Since the self-defined WebRTC signaling protocol is based on WebSocket, you must specify ws[s] as the scheme.
ws[s]://<host>[:signaling port]/<app name>/<stream name>?direction=send
For ingest from the WHIP client, put ?direction=whip in the query string in the signaling URL as in the example below. Since WHIP is based on HTTP, you must specify http[s] as the scheme.
http[s]://<host>[:signaling port]/<app name>/<stream name>?direction=whip
WebRTC transmission is sensitive to packet loss because it affects all players who access the stream. Therefore, it is recommended to provide WebRTC transmission over TCP. OvenMediaEngine has a built-in TURN server for WebRTC/TCP, and receives or transmits streams using the TCP session that the player's TURN client connects to the TURN server as it is. To use WebRTC/TCP, use transport=tcp query string as in WebRTC playback. See for more information.
ws[s]://<host>[:port]/<app name>/<stream name>?direction=send&transport=tcp
http[s]://<host>[:port]/<app name>/<stream name>?direction=whip&transport=tcp
To use WebRTC/tcp, <TcpRelay> must be turned on in <Bind> setting.
If <TcpForce> is set to true, it works over TCP even if you omit the ?transport=tcp query string from the URL.
We provide a demo page so you can easily test your WebRTC input. You can access the demo page at the URL below.
The getUserMedia API to access the local device only works in a . So, the WebRTC Input demo page can only work on the https site **** . This means that due to you have to install the certificate in OvenMediaEngine and use the signaling URL as wss to test this. If you can't install the certificate in OvenMediaEngine, you can temporarily test it by allowing the insecure content of the demo.ovenplayer.com URL in your browser.
To create a custom WebRTC Producer, you need to implement OvenMediaEngine's Self-defined Signaling Protocol or WHIP. Self-defined protocol is structured in a simple format and uses the.
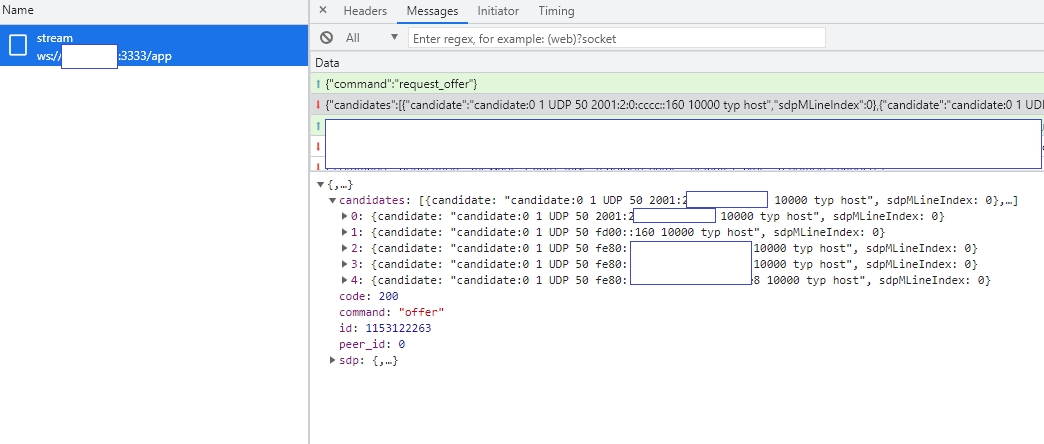
When the player connects to ws[s]://host:port/app/stream?direction=send through a web socket and sends a request offer command, the server responds to the offer sdp. If transport=tcp exists in the query string of the URL, information is included in offer sdp, which contains the information of OvenMediaEngine's built-in TURN server, so you need to set this in RTCPeerConnection to use WebRTC/TCP. The player then setsRemoteDescription and addIceCandidate offer sdp, generates an answer sdp, and responds to the server.
OvenMediaEngine can pull RTSP Stream in two ways. The first way is to use the Stream creation API, and the second way is to use OriginMap or OriginMapStore. The supported codecs are H.264, AAC(ADTS). Supported codecs will continue to be added.
You can create a stream by pulling an RTSP stream using the Stream Creation API. For more information on using the REST API, check out that chapter.
If OriginMapStore is configured and Redis Server provides an rtsp URL, OvenMediaEngine pulls the RTSP URL when a playback request comes in. Check out for more details.
RTSP Pull is provided through OriginMap configuration. OriginMap is the rule that the Edge server pulls the stream of the Origin server. Edge server can pull a stream of origin with RTSP and OVT (protocol defined by OvenMediaEngine for Origin-Edge) protocol. See the section for more information about OVT.
For example, in the above setup, when a player requests "ws://ome.com/app_name/rtsp_stream_name" to stream WebRTC, it pulls the stream from "rtsp://192.168.0.200:554" and publishes it to WebRTC.
If the app name set in Location isn't created, OvenMediaEngine creates the app with default settings. The default generated app doesn't have an OPUS encoding profile, so to use WebRTC streaming, you need to add the app to your configuration.
Pulling type providers are activated by streaming requests from publishers. And by default, the provider is automatically disabled after 30 seconds of no client playback. If you want to change this setting, check out the chapter.
When a playback request comes in from the following URL, RTSP pull starts working according to Origins settings.
OvenMediaEngine provides P2P Delivery to be able to distribute Edge Traffic to Player. This feature is currently the Preview version, and if you want to use it, you need only to use OvenPlayer. Moreover, we plan to perform more experiments in various real-world and then upgrade it to the full version in OvenMediaEngine.
First of all, we have rules. The peer that sends the Traffic in the P2P network is called a Host Peer, and the peer that receives the Traffic from the Host Peer is called a Client Peer. Also, P2P Delivery in OvenMediaEngine doesn't designate the Client Peer as the Host Peer again. In other words, it only operates as 1 Depth.
According to our experiments so far, P2P Delivery provides the best performance and stability when using 1 Depth to connect between Players and connecting up to two Players to one Player.
In other words, P2P Delivery has distributed two-thirds of existing Traffic. So, this means that it can expand the Capacity of the Edge Network by three times and reduce Traffic costs by two-thirds.
You can use the P2P function of OvenMediaEngine by adding the <P2P> element as the following settings:
Also, If you want to use P2P Delivery when your OvenMediaEngine is running in Origin-Edge Cluster-Mode, you need to apply this setting to all the Edges. You can instantly test P2P Delivery with OvenPlayer.
<MaxClientPeersPerHostPeer> sets the number of Client Peers connecting to one Host Peer.
When OvenMediaEngine receives a WebRTC connection request from a new player, it determines the Host Peer or Client Peer according to the following rules:
If you have a better idea, we hope that you improve our code and contribute to our project. Please visit .
curl -LOJ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine/archive/v0.16.3.tar.gz && \
tar xvfz OvenMediaEngine-0.16.3.tar.gz && \
OvenMediaEngine-0.16.3/misc/prerequisites.sh$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=3333/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=3334/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1935/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=9999/udp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=4000/udp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=3478/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=9000/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=10000-10009/udp<Server>
...
<Bind>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
</RTMP>
</Providers>
</Bind>
...
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Application>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
...
</RTMP>
...
</Providers>
<Application>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server><Application>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<BlockDuplicateStreamName>true</BlockDuplicateStreamName>
</RTMP>
</Providers>
<Application><Bind>
<Providers>
...
<SRT>
<Port>9999</Port>
<!-- <WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount> -->
</SRT>
</Providers><Applications>
<Application>
<Name>app</Name>
<Providers>
<SRT/><Server>
<Bind>
<Providers>
<SRT>
...
<Options>
<Option>
<Key>SRTO_PBKEYLEN</Key>
<Value>16</Value>
</Option>
<Option>
<Key>SRTO_PASSPHRASE</Key>
<Value>thisismypassphrase</Value>
</Option>
</Options>
</SRT>
...3333/TCP 3334/TLS
WebRTC Signaling (both ingest and streaming)
3478/TCP
WebRTC TCP relay (TURN Server, both ingest and streaming)
10000 - 10009/UDP
WebRTC Ice candidate (both ingest and streaming)
Protocol
URL
WebRTC
ws[s]:://host.com[:port]/app_name/rtsp_stream_name
LLHLS
http[s]://host.com[:port]/app_name/rtsp_stream_name/llhls.m3u8
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost include="VHost*.xml" />
<VirtualHost>
<Name>default</Name>
<Host>
<Names>
<!-- Host names
<Name>stream1.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>stream2.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>*.sub.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>192.168.0.1</Name>
-->
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<!--
<TLS>
<CertPath>path/to/file.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>path/to/file.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>path/to/file.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
-->
</Host>
<Origins>
<Origin>
<Location>/app_name/rtsp_stream_name</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>rtsp</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>192.168.0.200:554/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
</Origins>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>The device isn't Mobile
OS isn't Linux
Browser isn't MS Edge Browser
Browser isn't Unknown Browser
One of the Host Peers uses the same kind of browser
Host Peer is vacant
Starting from version OME v0.15.1, IPv6 is supported.
To use IPv6, you need to change the settings of the Server.xml file as follows:
You can use /Server/IP to support IPv6. In versions prior to v0.15.0, only one /Server/IP setting could be specified, but in versions after v0.15.1, multiple settings can be specified. That is, if you add an /Server/IP element for IPv6 to the existing configuration as follows, you can accept IPv6 requests from clients:
OME listens to the 1935 port for RTMP as follows:
OME listens to the 1935 port for RTMP as follows:
OME listens to the 1935 port for RTMP as follows:
IceCandidates (for WebRTC)When you specify IPv6 interface /Server/IP, most Providers/Publishers will work with IPv6, but WebRTC will not. While the WebSocket server used as the WebRTC Signalling server works well with the above setting, but more setting is required for ICE Candidates that actually transmit/receive data.
To use IPv6 ICE Candidate, you need to add an IPv6 IceCandidate to /Server/Bind/(Providers|Publishers)/WebRTC/IceCandidates.
By setting up as above, OME is ready to use ICE Candidates for IPv6 as well as IPv4. The ICE Candidate generated here can be viewed in the signaling step of the web browser.
<Origin>Now you can set up the OME edge to look at an origin with an IPv6 IP address. To do this, you can set /Server/VirtualHosts/VirtualHost/Origins/Origin/Pass/Urls/Url as follows:
This configuration creates a stream that refers an RTSP source provided on port 1234 of an origin which has an IPv6 address of 1:2:3:4:5:6:7:8.
<AdmissionWebhooks>You can also specify an IPv6 address for the server that AdmissionWebhooks is using. To do this, set the value of /Server/VirtualHosts/VirtualHost/AdmissionWebhooks/ControlServerUrl as follows:
The above configuration asks whether the client has the permission to publish or playback using http://[1:2:3:4:5:6:7:8]:7000/a/b/c.
{
"statusCode": 404,
"message": "Could not find the application: [default/non-exists] (404)"
}<Bind>
<Providers>
...
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<TcpForce>false</TcpForce>
<IceCandidate>*:10000-10005/udp</IceCandidate>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Providers><Applications>
<Application>
<Name>app</Name>
<Providers>
<WebRTC>
<Timeout>30000</Timeout>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</WebRTC><Server version="...">
...
<P2P>
<MaxClientPeersPerHostPeer>2</MaxClientPeersPerHostPeer>
</P2P>
...
</Server>{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"stream",
"stream2"
]
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Json array containing a list of stream names{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}
OvenMediaEngine supports GPU-based hardware decoding and encoding. Currently supported GPU acceleration devices are Intel's QuickSync and NVIDIA. This article explains how to install the drivers for OvenMediaEngine and set up the configuration to use your GPU.
If you are using an NVIDIA graphics card, please refer to the following guide to install the driver. The OS that supports installation with the provided script are CentOS 7/8 and Ubuntu 18/20 versions. If you want to install the driver in another OS, please refer to the manual installation guide document.
CentOS environment requires the process of uninstalling the nouveau driver. After uninstalling the driver, the first reboot is required, and a new NVIDIA driver must be installed and rebooted. Therefore, two install scripts must be executed.
How to check driver installation
After the driver installation is complete, check whether the driver is operating normally with the nvidia-smi command.
If you have finished installing the driver to use the GPU, you need to reinstall the open source library using Prerequisites.sh . The purpose is to allow external libraries to use the installed graphics driver.
If you are using an Intel CPU that supports QuickSync, please refer to the following guide to install the driver. The OSes that support installation using the provided scripts are CentOS 7/8 and Ubuntu 18/20 versions. If you want to install the driver on a different OS, please refer to the Manual Installation Guide document.
When the Intel QuickSync driver installation is complete, the OS must be rebooted for normal operation.
How to check driver installation
After the driver installation is complete, check whether the driver operates normally with the Matrix Monitor program.
Please refer to the link for how to build and run.
To use hardware acceleration, set the HardwareAcceleration option to true under OutputProfiles. If this option is enabled, a hardware codec is automatically used when creating a stream, and if it is unavailable due to insufficient hardware resources, it is replaced with a software codec.
The codecs available using hardware accelerators in OvenMediaEngine are as shown in the table below. Different GPUs support different codecs. If the hardware codec is not available, you should check if your GPU device supports the codec.
D : Decoding, E : Encoding
Quick Sync Video Format :
NVIDIA NVDEC Video Format :
NVIDIA NVENV Video Format :
CUDA Toolkit Installation Guide :
The REST APIs provided by OME allow you to query or change settings such as VirtualHost and Application/Stream.
There are some limitations/considerations.
If you add/change/delete the settings of the App/Output Profile by invoking the API, the app will be restarted. This means that all sessions connected to the app will be disconnected.
VirtualHost settings in Server.xml cannot be modified through API. This rule also applies to Application/OutputStream, etc. within that VirtualHost. So, if you call a POST/PUT/DELETE API for VirtualHost/Application/OutputProfile declared in Server.xml, it will not work with a 403 Forbidden error.
By default, OvenMediaEngine's API Server is disabled, so the following settings are required to use the API.
The API server's port can be set in <Bind><Managers><API>. <Port> is an unsecured port and <TLSPort> is a secured port. To use TLSPort, TLS certificate must be set in the .
In order to use the API server, you must configure <Managers> as well as port binding.
In <Names>, set the domain or IP that can access the API server. If * is set, any address is used. In order to access using the TLS Port, a certificate must be set in <TLS>.
API Server uses Basic HTTP Authentication Scheme to authenticate clients. An AccessToken is a plaintext credential string before base64 encoding. Setting the AccessToken to the form user-id:password per RFC7617 allows standard browsers to pass authentication, but it is not required.
For more information about HTTP Basic authentication, refer to the URL below.
To enable CORS on your API Server, you can add a setting. You can add * to allow all domains. If contains a scheme, such as https://, only that scheme can be allowed, or if the scheme is omitted, such as *.airensoft.com, all schemes can be accepted.
API endpoints are provided in the following format.
Method http://API.Server.Address[:Port]/v1/Resource
Method https://API.Server.Address[:TLSPort]/v1/Resource
OvenMediaEngine supports GET, POST, and DELETE methods, and sometimes supports PATCH depending on the type of resource. For detailed API specifications, please check the subdirectory of this chapter.
In OvenMediaEngine's REST API, action is provided in the following format.
POST http://host/v1/resource:{action name}
For example, an action to send an ID3 Timedmeta event to an LLHLS stream is provided by the endpoint below.
POST http://-/v1/vhosts/{vhost}/apps/{app}/streams/{stream}:sendEvent
In this API reference document, the API endpoint is described as follows. Note that scheme://Host[:Port] is omitted for all endpoints.
Responses from API endpoints are provided in the following format.
OvenMediaEngine can record live streams. You can start and stop recording the output stream through REST API. When the recording is complete, a recording information file is created together with the recorded file so that the user can perform various post-recording processing.
To enable recording, add the <FILE> publisher to the configuration file as shown below. <FilePath> and <InfoPath> are required and used as default values. <FilePath> is the setting for the file path and file name. <InfoPath>is the setting for the path and name of the XML file that contains information about the recorded files. If there is no file path value among parameters when requesting recording through API, recording is performed with the set default value. This may be necessary if for security reasons you do not want to specify the file path when calling the API to avoid exposing the server's internal path. <<RootPath> is an optional parameter. It is used when requesting with a relative path is required when requesting an API. also, it is applied to <FilePath> and <InfoPath> as in the example below.
You must specify .ts or .mp4 at the end of the FilePath string to select a container for the recording file. We recommend using .ts unless you have a special case. This is because vp8 and opus codecs are not recorded due to container limitations if you choose .mp4.
Various macro values are supported for file paths and names as shown below.
For control of recording, use the REST API. Recording can be requested based on the output stream name (specified in the JSON body), and all/some tracks can be selectively recorded. And, it is possible to simultaneously record multiple files for the same stream. When recording is complete, an XML file is created at the path specified in InfoPath. For a sample of the recorded file information XML, refer to Appendix A.
For how to use the API, please refer to the link below.
Split recording methods provide interval and schedule. The interval method splits files based on the accumulated recording time. The Schedule method then splits files according to scheduling options based on system time. The scheduling option is the same as the pattern used in crontab. However, only three options are used: seconds/minutes/hour.
The following is a sample of an XML file that expresses information on a recorded file.
<Server>
...
<IP>*</IP>
<!-- Listening the bind ports on IPv6 interfaces -->
<IP>::</IP>
...<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<Type>origin</Type>
<IP>*</IP>
<Bind>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
</RTMP>
</Providers>
</Bind>
</Server>$ sudo netstat -tulnp | grep "$(pgrep OvenMediaEngine)"
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1935 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN xxx/OvenMediaEn<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<Type>origin</Type>
<IP>::</IP>
<Bind>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
</RTMP>
</Providers>
</Bind>
</Server>$ sudo netstat -tulnp | grep "$(pgrep OvenMediaEngine)"
tcp6 0 0 :::1935 :::* LISTEN xxx/OvenMediaEn<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<Type>origin</Type>
<IP>*</IP>
<IP>::</IP>
<Bind>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
</RTMP>
</Providers>
</Bind>
</Server>
$ sudo netstat -tulnp | grep "$(pgrep OvenMediaEngine)"
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1935 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN xxx/OvenMediaEn
tcp6 0 0 :::1935 :::* LISTEN xxx/OvenMediaEn<Server version="8">
...
<Bind>
<Providers>
<WebRTC>
...
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000/udp</IceCandidate>
<IceCandidate>[::]:10000/udp</IceCandidate>
</IceCandidates>
...<Server version="8">
...
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Origins>
<Origin>
<Location>/rtsp/stream</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>rtsp</Scheme>
<Urls>
<Url>airen:airen@[1:2:3:4:5:6:7:8]:1234/app/stream</Url>
</Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
</Origins>
...<Server version="8">
...
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<AdmissionWebhooks>
<ControlServerUrl>http://[1:2:3:4:5:6:7:8]:7000/a/b/c</ControlServerUrl>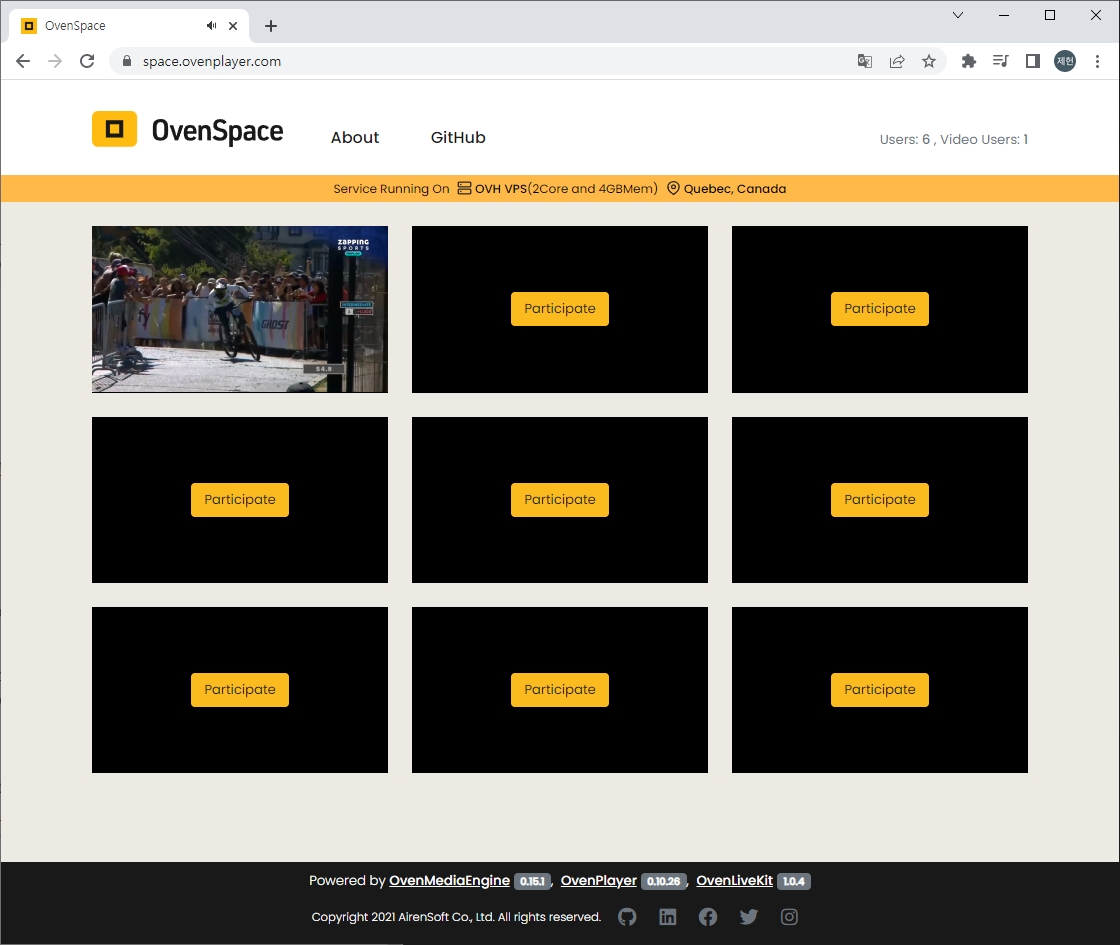
Application name
${SourceStream}
Source stream name
${Stream}
Output stream name
${Sequence}
Sequence value that increases when splitting a file in a single transaction
${TransactionId}
Unique ID for the recording transaction. It is automatically created when recording starts. and is released when recording is stopped. In case of split recording, it is distinguished that it is the same transaction.
${Id}
User-defined identification ID
${StartTime:YYYYMMDDhhmmss}
Recording start time
YYYY - Year
MM - Month
DD - Days
hh : Hours (023)
mm : Minutes (0059)
ss : Seconds (00~59)
${EndTime:YYYYMMDDhhmmss}
Recording end time
YYYY - Year
MM - Month
DD - Days
hh : Hours (023)
mm : Minutes (0059)
ss : Seconds (00~59)
${VirtualHost}
Virtual host name
${Application}
A Docker Image build script that supports NVIDIA GPU is provided separately. Please refer to the previous guide for how to build
If you have finished installing the driver to use the GPU, you need to reinstall the open source library using Prerequisites.sh . The purpose is to allow external libraries to use the installed graphics driver.
-
Docker on NVIDIA Container Toolkit
D / E
D / E
-
-
NVIDIA Container Toolkit : https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/arch-overview.html#arch-overview
Quick Sync Video format support: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_Quick_Sync_Video
QuickSync
D / E
D / E
-
-
NVIDIA
D / E
D / E
(curl -LOJ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine/archive/master.tar.gz && tar xvfz OvenMediaEngine-master.tar.gz)
OvenMediaEngine-master/misc/install_nvidia_driver.sh$ nvidia-smi
Thu Jun 17 10:20:23 2021
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 465.19.01 Driver Version: 465.19.01 CUDA Version: 11.3 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce ... Off | 00000000:01:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 20% 35C P8 N/A / 75W | 156MiB / 1997MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+-
Describe the request body content. The body of all APIs consists of Json content. Therefore, the Content-Type header value is always application/json, which can be omitted in the document.
Description the response body content. The body of all response consists of Json content. Therefore, the Content-Type header value is always application/json, which can be omitted in the document.
<Applications>
<Application>
...
<Publishers>
<FILE>
<RootPath>/mnt/shared_volumes</RootPath>
<FilePath>/${VirtualHost}/${Application}/${Stream}/
${StartTime:YYYYMMDDhhmmss}_${EndTime:YYYYMMDDhhmmss}.ts</FilePath>
<InfoPath>/${VirtualHost}/${Application}/${Stream}.xml</InfoPath>
</FILE>
</Publishers>
...<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<files>
<file>
<transactionId>bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3</transactionId>
<id>CTS_ID001</id>
<vhost>default</vhost>
<app>app</app>
<stream>stream_o</stream>
<filePath><![CDATA[/home/dev/OvenMediaEngine/records/bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3_default_app_stream_o_20201204005351_20201204005405.ts]]></filePath>
<recordBytes>8774737</recordBytes>
<recordTime>60011</recordTime>
<sequence>0</sequence>
<interval>60000</interval>
<lastSequence>true</lastSequence>
<createdTime>2020-12-04T12:53:51.455+0900</createdTime>
<startTime>2020-12-04T12:53:51.612+0900</startTime>
<finishTime>2020-12-04T12:54:51.473+0900</finishTime>
</file>
<file>
<transactionId>bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3</transactionId>
<id>CTS_ID001</id>
<vhost>default</vhost>
<app>app</app>
<stream>stream_o</stream>
<filePath><![CDATA[/home/dev/OvenMediaEngine/records/bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3_default_app_stream_o_20201204005408_20201204005412.ts]]></filePath>
<recordBytes>2285797</recordBytes>
<recordTime>60012</recordTime>
<sequence>0</sequence>
<schedule>0 */1 *</schedule>
<lastSequence>false</lastSequence>
<createdTime>2020-12-04T12:53:00.000+0900</createdTime>
<startTime>2020-12-04T12:53:00.000+0900</startTime>
<finishTime>2020-12-04T12:54:00.000+0900</finishTime>
</file>
<file>
<transactionId>bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3</transactionId>
<id>CTS_ID001</id>
<vhost>default</vhost>
<app>app</app>
<stream>stream_o</stream>
<filePath><![CDATA[/home/dev/OvenMediaEngine/records/bcUCyJeKuOGnsah3_default_app_stream_o_20201204005415_20201204005422.ts]]></filePath>
<recordBytes>4544626</recordBytes>
<recordTime>60000</recordTime>
<sequence>1</sequence>
<schedule>0 */1 *</schedule>
<lastSequence>true</lastSequence>
<createdTime>2020-12-04T12:54:00.000+0900</createdTime>
<startTime>2020-12-04T12:54:00.000+0900</startTime>
<finishTime>2020-12-04T12:55:00.000+0900</finishTime>
</file>
</files>OvenMediaEngine-master/misc/prerequisites.sh --enable-nvc(curl -LOJ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine/archive/master.tar.gz && tar xvfz OvenMediaEngine-master.tar.gz)
OvenMediaEngine-master/misc/install_intel_driver.shdocker run -d ... --gpus all airensoft/ovenmediaengine:dev<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Name>default</Name>
...
<!-- Settings for applications -->
<Applications>
<Application>
<Name>app</Name>
<Type>live</Type>
<OutputProfiles>
<!-- Settings to use hardware codecs -->
<HardwareAcceleration>true</HardwareAcceleration>
<OutputProfile>
...
</OutputProfile>
<OutputProfile>
...
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles>
<Providers>
...
</Providers>
<Publishers>
...
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>OvenMediaEngine-master/misc/install_nvidia_docker_container.shOvenMediaEngine-master/Dockerfile.cuda
OvenMediaEngine-master/Dockerfile.cuda.local# Use the samples provided in the Intel Media SDK
# Check the list of codecs supported by iGPU
/MediaSDK-intel-mediasdk-21.1.2/build/__bin/release/simple_7_codecOvenMediaEngine-master/misc/prerequisites.sh --enable-qsv<Server version="8">
...
<Bind>
<Managers>
<API>
<Port>8081</Port>
<TLSPort>8082</TLSPort>
</API>
</Managers>
...
</Bind>
...
</Server><Server version="8">
<Bind>
...
</Bind>
<Managers>
<Host>
<Names>
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<TLS>
<CertPath>airensoft_com.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>airensoft_com.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>airensoft_com_chain.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
</Host>
<API>
<AccessToken>your_access_token</AccessToken>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*.airensoft.com</Url>
<Url>http://*.sub-domain.airensoft.com</Url>
<Url>http?://airensoft.*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</API>
</Managers>
<VirtualHosts>
...
</VirtualHosts>
</Server>Header-Key: Value
# Header-Key
DescriptionHeader-Key: Value{
"requestId": "value"
}
# key (required)
The description of the key/value of the body content is provided like this.{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Response Contents
The LLHLS Dump feature can be controlled with this API.
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
The info file is continuously updated after the dump file is written. It is in XML format and is as follows. will continue to be added.
To monitor the OvenMediaEngine, you can view in real-time the log files generated by itself. You can configure a log type and level by creating the Logger.xml configuration file in the same location as Server.xml.
You can set up Logger.xml as shown in the following example: OvenMediaEngine prints logs separated by many tag names and levels. Set <Tag name=".*" level="debug"> to have OvenMediaEngine print all logs and read the logs. And then it's better to disable tags that you don't need.
OvenMediaEngine generates log files. If you start OvenMediaEngine by systemctl start ovenmediaengine, the log file is generated to the following path.
If you run it directly from the command line, it will be generated to the following location:
If you run it in the Docker container, the log file is in the following path:
Following is the example of real logs.
OvenMediaEngine collects the following metrics for each host, application, and stream.
Bytes in/out by protocol
Connections by protocol
Maximum connections and time
Time is taken to connect to origin
You can get the current statistics using the REST API. See for the statistics REST API.
Files such as webrtc_stat.log and hls_rtsp_xxxx.log that were previously output are deprecated in the current version. We are developing a formal stats file, which will be open in the future.
OvenMediaEngine supports clustering and ensures high availability (HA) and scalability. For this we provide the OriginMap and OriginMapStore features. is a method of configuring Origin server information in each Edge server, and is a method for Origin servers and Edge servers to dynamically share information through Redis Server.
The OvenMediaEngine running as edge pulls a stream from an external server when a user requests it. The external server could be another OvenMediaEngine with OVT enabled or another stream server that supports RTSP.
The OVT is a protocol defined by OvenMediaEngine to relay stream between Origin-Edge and OVT can be run over SRT and TCP. For more information on the SRT Protocol, please visit the
<Logger version="2">
<!-- Log file location -->
<Path>/var/log/ovenmediaengine</Path>
<!-- Disable some SRT internal logs -->
<Tag name="SRT" level="critical" />
<Tag name="Monitor" level="critical" />
<!-- Log level: [debug, info, warn, error, critical] -->
<Tag name=".*" level="info" />
</Logger>
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"connections": {
"dash": 0,
"file": 0,
"hls": 0,
"lldash": 0,
"llhls": 0,
"mpegtspush": 0,
"ovt": 0,
"rtmppush": 0,
"thumbnail": 0,
"webrtc": 0
},
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastRecvTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastSentTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastThroughputIn": 0,
"lastThroughputOut": 0,
"maxTotalConnectionTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"maxTotalConnections": 0,
"totalBytesIn": 0,
"totalBytesOut": 0,
"totalConnections": 0,
"avgThroughputIn": 0,
"avgThroughputOut": 0,
"maxThroughputIn": 0,
"maxThroughputOut": 0
}
}WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the virtual host: [default1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}/var/log/ovenmediaengineAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"connections": {
"dash": 0,
"file": 0,
"hls": 0,
"lldash": 0,
"llhls": 0,
"mpegtspush": 0,
"ovt": 0,
"rtmppush": 0,
"thumbnail": 0,
"webrtc": 0
},
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastRecvTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastSentTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastThroughputIn": 0,
"lastThroughputOut": 0,
"maxTotalConnectionTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"maxTotalConnections": 0,
"totalBytesIn": 0,
"totalBytesOut": 0,
"totalConnections": 0,
"avgThroughputIn": 0,
"avgThroughputOut": 0,
"maxThroughputIn": 0,
"maxThroughputOut": 0
}
}WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [default/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"connections": {
"dash": 0,
"file": 0,
"hls": 0,
"lldash": 0,
"llhls": 0,
"mpegtspush": 0,
"ovt": 0,
"rtmppush": 0,
"thumbnail": 0,
"webrtc": 0
},
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastRecvTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastSentTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"lastThroughputIn": 0,
"lastThroughputOut": 0,
"maxTotalConnectionTime": "2023-03-15T19:46:13.728+09:00",
"maxTotalConnections": 0,
"totalBytesIn": 0,
"totalBytesOut": 0,
"totalConnections": 0,
"avgThroughputIn": 0,
"avgThroughputOut": 0,
"maxThroughputIn": 0,
"maxThroughputOut": 0
}
}WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the stream: [default/#default#app/stream] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}/<OvenMediaEngine Binary Path>/log/# For Origin mode
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/log/
# For Edge mode
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/log/getroot@Jeheon-Main:/var/log/ovenmediaengine$ cat ovenmediaengine.log
[03-27 19:59:13.221] I 10996 Config | config_manager.cpp:144 | Trying to set logfile in directory... (/var/log/ovenmediaengine)
[03-27 19:59:13.221] I 10996 Config | config_manager.cpp:47 | Trying to load configurations... (origin_conf/Server.xml)
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:211 | OvenMediaEngine v0.9.5 (v0.9.1-422-g6e4b7ce) is started on [Jeheon-Main] (Linux x86_64 - 4.4.0-18362-Microsoft, #476-Microsoft Fri Nov 01 16:53:00 PST 2019)
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:213 | With modules:
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:214 | FFmpeg 3.4.2
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:215 | Configuration: --prefix=/opt/ovenmediaengine --enable-gpl --enable-nonfree --extra-cflags=-I/opt/ovenmediaengine/include --extra-ldflags='-L/opt/ovenmediaengine/lib -Wl,-rpath,/opt/ovenmediaengine/lib' --extra-libs=-ldl --enable-shared --disable-static --disable-debug --disable-doc --disable-programs --disable-avdevice --disable-dct --disable-dwt --disable-error-resilience --disable-lsp --disable-lzo --disable-rdft --disable-faan --disable-pixelutils --disable-everything --enable-zlib --enable-libopus --enable-libvpx --enable-libfdk_aac --enable-libx264 --enable-encoder='libvpx_vp8,libvpx_vp9,libopus,libfdk_aac,libx264' --enable-decoder='aac,aac_latm,aac_fixed,h264' --enable-parser='aac,aac_latm,aac_fixed,h264' --enable-network --enable-protocol=tcp --enable-protocol=udp --enable-protocol=rtp --enable-demuxer=rtsp --enable-filter='asetnsamples,aresample,aformat,channelmap,channelsplit,scale,transpose,fps,settb,asettb'
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:216 | libavformat: 57.83.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:217 | libavcodec: 57.107.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:218 | libavutil: 55.78.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:219 | libavfilter: 6.107.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:220 | libswresample: 2.9.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:221 | libswscale: 4.8.100
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:222 | SRT: 1.3.3
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:223 | SRTP: libsrtp2 2.2.0
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:224 | OpenSSL: OpenSSL 1.1.0g 2 Nov 2017
[03-27 19:59:13.235] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:225 | Configuration: compiler: gcc -DDSO_DLFCN -DHAVE_DLFCN_H -DNDEBUG -DOPENSSL_THREADS -DOPENSSL_NO_STATIC_ENGINE -DOPENSSL_PIC -DOPENSSL_IA32_SSE2 -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_MONT -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_MONT5 -DOPENSSL_BN_ASM_GF2m -DSHA1_ASM -DSHA256_ASM -DSHA512_ASM -DRC4_ASM -DMD5_ASM -DAES_ASM -DVPAES_ASM -DBSAES_ASM -DGHASH_ASM -DECP_NISTZ256_ASM -DPADLOCK_ASM -DPOLY1305_ASM -DOPENSSLDIR="\"/opt/ovenmediaengine\"" -DENGINESDIR="\"/opt/ovenmediaengine/lib/engines-1.1\"" -Wa,--noexecstack
[03-27 19:59:13.240] I 10996 Monitor | monitoring.cpp:35 | Create HostMetrics(default) for monitoring
[03-27 19:59:13.240] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:148 | Trying to create a module MediaRouter for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.240] I 10996 MediaRouter | media_router.cpp:40 | MediaRouter has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.240] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:151 | Trying to create a module RTMP Provider for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.244] I 10996 RtmpProvider | rtmp_provider.cpp:63 | RTMP Server has started listening on 0.0.0.0:1935...
[03-27 19:59:13.246] I 10996 Provider | provider.cpp:40 | RtmpProvider has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.246] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:152 | Trying to create a module OVT Provider for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.248] I 10996 Provider | provider.cpp:40 | OvtProvider has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.248] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:153 | Trying to create a module RTSPC Provider for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.250] I 10996 Provider | provider.cpp:40 | RtspcProvider has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.250] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:154 | Trying to create a module RTSP Provider for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.250] I 10996 RtspProvider | rtsp_provider.cpp:40 | RTSP is disabled in the configuration.
[03-27 19:59:13.251] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:157 | Trying to create a module Transcoder for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.251] I 10996 Transcoder | transcoder.cpp:38 | Transcoder has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.251] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:160 | Trying to create a module WebRTC Publisher for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.251] I 10996 Signalling | rtc_signalling_server.cpp:74 | P2P is disabled in the configuration
[03-27 19:59:13.258] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10000/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.260] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10001/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.261] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10002/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.263] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10003/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.264] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10004/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.266] I 10996 Ice | ice_port.cpp:89 | ICE port is bound to 0.0.0.0:10005/UDP
[03-27 19:59:13.266] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | WebRTC Publisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.266] I 10996 WebRTC | webrtc_publisher.cpp:89 | WebRTC Publisher has started listening on 0.0.0.0:3333...
[03-27 19:59:13.266] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | WebRTC Publisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.266] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:161 | Trying to create a module HLS Publisher for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.273] I 10996 Publisher | segment_publisher.cpp:65 | HLS Publisher has started listening on 0.0.0.0:8080...
[03-27 19:59:13.273] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | HLS Publisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.275] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:162 | Trying to create a module MPEG-DASH Publisher for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.281] I 10996 Publisher | segment_publisher.cpp:65 | DASH Publisher has started listening on 0.0.0.0:8080...
[03-27 19:59:13.281] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | DASH Publisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.282] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:163 | Trying to create a module Low-Latency MPEG-DASH Publisher for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.289] I 10996 Publisher | segment_publisher.cpp:65 | LLDASH Publisher has started listening on 0.0.0.0:8080...
[03-27 19:59:13.289] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | LLDASH Publisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.291] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:164 | Trying to create a module OVT Publisher for [default] host...
[03-27 19:59:13.294] I 10996 OVT | ovt_publisher.cpp:49 | Ovt Publisher has started listening on 0.0.0.0:9000
[03-27 19:59:13.294] I 10996 Publisher | publisher.cpp:15 | OVTPublisher has been started.
[03-27 19:59:13.294] I 10996 OvenMediaEngine | main.cpp:169 | All modules are initialized successfully
[03-27 19:59:13.294] I 10996 Orchestrator | orchestrator.cpp:856 | Trying to create an application: [#default#app]
[03-27 19:59:13.294] I 10996 Monitor | host_metrics.cpp:52 | Create ApplicationMetrics(#default#app) for monitoring
[03-27 19:59:13.297] I 10996 Provider | application.cpp:30 | [#default#app] RTMP Provider application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.297] I 10996 Provider | application.cpp:30 | [#default#app] OVT Provider application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.297] I 10996 Provider | application.cpp:30 | [#default#app] RTSP Pull Provider application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.297] I 10996 Provider | application.cpp:30 | [#default#app] RTSP Provider application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.298] I 10996 TranscodeApplication | transcode_application.cpp:36 | [#default#app] Transcoder Application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.300] I 10996 Publisher | application.cpp:26 | [#default#app] WebRTC Publisher application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.302] I 10996 Publisher | application.cpp:26 | [#default#app] HLS Publisher application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.304] I 10996 Publisher | application.cpp:26 | [#default#app] DASH Publisher application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.305] I 10996 Publisher | application.cpp:26 | [#default#app] LLDASH Publisher application has been started
[03-27 19:59:13.307] I 10996 Publisher | application.cpp:26 | [#default#app] OVT Publisher application has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.706] I 11002 RtmpProvider | rtmp_server.cpp:126 | A RTMP client has connected from <ClientSocket: 0x7fffd4000b70, #24, state: 4, TCP, 192.168.0.200:11031>
[03-27 19:59:14.835] I 11002 RtmpProvider | rtmp_server.cpp:226 | [#default#app/stream] RTMP Provider stream has been created: id(0/0) device(OBS) remote(<ClientSocket: 0x7fffd4000b70, #24, state: 4, TCP, 192.168.0.200:11031>)
[03-27 19:59:14.835] I 11002 MediaRouter.App | media_route_application.cpp:184 | Trying to create a stream: [#default#app/stream(2921228900)]
[03-27 19:59:14.836] I 11002 Monitor | stream.cpp:240 |
[Stream Info]
id(2921228900), name(stream), SourceType(Rtmp), Created Time (Fri Mar 27 19:59:14 2020)
Video Track #0: Bypass(false) Bitrate(2.50Mb) codec(1, avc) resolution(1280x720) framerate(30.00fps) timebase(1/90000)
Audio Track #1: Bypass(false) Bitrate(160.00Kb) codec(5, aac) samplerate(44.1K) format(s16, 16) channel(stereo, 2) timebase(1/44100)
[03-27 19:59:14.836] I 11002 Monitor | application_metrics.cpp:56 | Create StreamMetrics(stream) for monitoring
[03-27 19:59:14.836] I 11002 TranscodeStream | transcode_stream.cpp:353 | [#default#app/stream(2921228900)] -> [#default#app/stream_medium_o(3169746412)] Transcoder output stream has been created.
[03-27 19:59:14.839] I 11002 FFmpeg | third_parties.cpp:115 | [AVCodecContext] using SAR=1/1
[03-27 19:59:14.841] I 11002 FFmpeg | third_parties.cpp:115 | [AVCodecContext] using cpu capabilities: MMX2 SSE2Fast SSSE3 SSE4.2 AVX FMA3 BMI2 AVX2
[03-27 19:59:14.846] I 11002 FFmpeg | third_parties.cpp:115 | [AVCodecContext] profile Constrained Baseline, level 3.0, 4:2:0, 8-bit
[03-27 19:59:14.849] I 11002 FFmpeg | third_parties.cpp:115 | [AVCodecContext] v1.7.0
[03-27 19:59:14.864] I 11048 MediaRouter.App | media_route_application.cpp:184 | Trying to create a stream: [#default#app/stream_medium_o(3169746412)]
[03-27 19:59:14.864] I 11002 TranscodeStream | transcode_stream.cpp:108 | [#default#app/stream(2921228900)] Transcoder input stream has been started. Status : (2) Decoders, (4) Encoders
[03-27 19:59:14.865] I 11048 Monitor | stream.cpp:240 |
[Stream Info]
id(3169746412), name(stream_medium_o), SourceType(Transcoder), Created Time (Fri Mar 27 19:59:14 2020)
>> Origin Stream Info
id(2921228900), name(stream), SourceType(Rtmp), Created Time (Fri Mar 27 19:59:14 2020)
Video Track #0: Bypass(false) Bitrate(700.00Kb) codec(2, vp8) resolution(640x360) framerate(30.00fps) timebase(1/90000)
Video Track #1: Bypass(false) Bitrate(700.00Kb) codec(1, avc) resolution(640x360) framerate(30.00fps) timebase(1/90000)
Audio Track #2: Bypass(false) Bitrate(48.00Kb) codec(7, opus) samplerate(48.0K) format(s16, 16) channel(stereo, 2) timebase(1/48000)
Audio Track #3: Bypass(false) Bitrate(48.00Kb) codec(5, aac) samplerate(48.0K) format(s16, 16) channel(stereo, 2) timebase(1/48000)
[03-27 19:59:14.865] I 11048 Monitor | application_metrics.cpp:56 | Create StreamMetrics(stream_medium_o) for monitoring
[03-27 19:59:14.865] I 11048 WebRTC | rtc_stream.cpp:181 | Unsupported codec(Audio/AAC) is being input from media track
[03-27 19:59:14.880] I 11048 Publisher | stream.cpp:192 | [stream_medium_o(3169746412)] WebRTC Publisher stream has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.881] I 11048 Publisher | stream.cpp:192 | [stream_medium_o(3169746412)] HLS Publisher stream has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.881] I 11048 Publisher | stream.cpp:192 | [stream_medium_o(3169746412)] DASH Publisher stream has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.881] I 11048 Publisher | stream.cpp:192 | [stream_medium_o(3169746412)] LLDASH Publisher stream has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.897] I 11048 Publisher | stream.cpp:192 | [stream_medium_o(3169746412)] OVT Publisher stream has been started
[03-27 19:59:14.898] I 11048 TranscodeCodec | transcode_codec_dec_aac.cpp:49 | [#default#app/stream(2921228900)] input stream information: [audio] aac (LC), 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp, 154 kbps, timebase: 1/44100, frame_size: 1024
[03-27 19:59:14.985] I 11048 TranscodeCodec | transcode_codec_dec_avc.cpp:48 | [#default#app/stream(2921228900)] input stream information: [video] h264 (Constrained Baseline 3.1), yuv420p, 1280x720 [SAR 0:1 DAR 16:9], 30 fps, 195 kbps, timebase: 1/60, frame_size: 0Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
Content-Type: application/json
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"outputStreamName": "stream",
"id": "unique_dump_id",
"outputPath": "/tmp/",
"playlist" : ["llhls.m3u8", "abr.m3u8"],
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"stream",
"stream2"
]
}
{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}AdmissionWebhooks can be set up on VirtualHost, as shown below.
ControlServerUrl
The HTTP Server to receive the query. HTTP and HTTPS are available.
SecretKey
The secret key used when encrypting with HMAC-SHA1
For more information, see .
Timeout
Time to wait for a response after request (in milliseconds)
Enables
Enable Providers and Publishers to use AdmissionWebhooks
AdmissionWebhooks send HTTP/1.1 request message to the configured user's control server when an encoder requests publishing or a player requests playback. The request message format is as follows.
The message is sent in POST method and the payload is in application/json format. X-OME-Signature is a base64 url safe encoded value obtained by encrypting the payload with HMAC-SHA1 so that the ControlServer can validate this message. See the Security section for more information on X-OME-Signature.
Here is a detailed explanation of each element of Json payload:
client
Information of the client who requested the connection.
address
Client's IP address
port
Client's Port number
The control server may need to validate incoming http requests for security reasons. To do this, the AdmissionWebhooks module puts the X-OME-Signature value in the HTTP request header. X-OME-Signature is a base64 url safe encoded value obtained by encrypting the payload of an HTTP request with the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm using the secret key set in <AdmissionWebhooks><SecretKey> of the configuration.
As shown below, the trigger condition of request is different for each protocol.
WebRTC
When a client requests Offer SDP
RTMP
When a client sends a publish message
SRT
When a client send a
LLHLS
When a client requests a playlist (llhls.m3u8)
The engine in the closing state does not need any parameter in response. To the query just answer with empty json object.
ControlServer must respond with the following Json format. In particular, the "allowed" element is required.
allowed (required)
true or false
Allows or rejects the client's request.
new_url (optional)
Redirects the client to a new url. However, the scheme, port, and file cannot be different from the request. Only host, app, and stream can be changed. The host can only be changed to another virtual host on the same server.
lifetime (optional)
The amount of time (in milliseconds) that a client can maintain a connection (Publishing or Playback)
0 means infinity
HTTP based streaming (HLS, DASH, LLDASH) does not keep a connection, so this value does not apply.
reason (optional)
If allowed is false, it will be output to the log.
new_url redirects the original request to another app/stream. This can be used to hide the actual app/stream name from the user or to authenticate the user by inserting additional information instead of the app/stream name.
For example, you can issue a WebRTC streaming URL by inserting the user ID as follows: ws://domain.com:3333/user_id It will be more effective if you issue a URl with the encrypted value that contains the user ID, url expiration time, and other information.
After the Control Server checks whether the user is authorized to play using user_id, and responds with ws://domain.com:3333/app/sport-3 to new_url, the user can play app/sport-3.
If the user has only one hour of playback rights, the Control Server responds by putting 3600000 in the lifetime.
OvenMediaEngine provides OVT protocol for passing streams from the origin to the edge. To run OvenMediaEngine as Origin, OVT port, and OVT Publisher must be enabled as follows :
The role of the edge is to receive and distribute streams from an origin. You can configure hundreds of Edge to distribute traffic to your players. As a result of testing, a single edge can stream 4-5Gbps traffic by WebRTC based on AWS C5.2XLarge. If you need to stream to thousands of people, you can configure and use multiple edges.
The edge supports OVT and RTSP to pull stream from an origin. In the near future, we will support more protocols. The stream pulled through OVT is bypassed without being encoded.
To run OvenMediaEngine as Edge, you need to add Origins elements to the configuration file as follows:
The <Origin>is a rule about where to pull a stream from for what request.
The <Origin>has the ability to automatically create an application with that name if the application you set in <Location> doesn't exist on the server. If an application exists in the system, a stream will be created in the application.
NoInputFailoverTimeout (default 3000)
NoInputFailoverTimeout is the time (in milliseconds) to switch to the next URL if there is no input for the set time.
UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout (default 60000)
UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout is a function that deletes a stream created with OriginMap if there is no viewer for a set amount of time (milliseconds). This helps to save network traffic and system resources for Origin and Edge.
For a detailed description of Origin's elements, see:
Location
Origin is already filtered by domain because it belongs to VirtualHost. Therefore, in Location, set App, Stream, and File to match except domain area. If a request matches multiple Origins, the top of them runs.
Pass
Pass consists of Scheme and Url.
<Scheme> is the protocol that will use to pull from the Origin Stream. It currently can be configured as OVTor RTSP.
If the origin server is OvenMediaEngine, you have to set OVTinto the <Scheme>.
You can pull the stream from the RTSP server by setting RTSPinto the<Scheme>. In this case, the <RTSPPull> provider must be enabled. The application automatically generated by Origin doesn't need to worry because all providers are enabled.
Urls is the address of origin stream and can consist of multiple URLs.
ForwardQueryParams is an option to determine whether to pass the query string part to the server at the URL you requested to play.(Default : true) Some RTSP servers classify streams according to query strings, so you may want this option to be set to false. For example, if a user requests ws://host:port/app/stream?transport=tcp to play WebRTC, the ?transport=tcp may also be forwarded to the RTSP server, so the stream may not be found on the RTSP server. On the other hand, OVT does not affect anything, so you can use it as the default setting.
The final address to be requested by OvenMediaEngine is generated by combining the configured Url and user's request except for Location. For example, if the following is set
If a user requests http://edge.com/edge_app/stream, OvenMediaEngine makes an address to ovt: //origin.com: 9000/origin_app/stream.
OriginMapStore is designed to make it easier to support autoscaling within a cluster. All Origin Servers and Edge Servers in the cluster share stream information and origin OVT URLs through Redis. That is, when a stream is created on the Origin server, the Origin server sets the app/stream name and OVT url to access the stream to the Redis server. Edge gets the OVT url corresponding to the app/stream from the Redis server when the user's playback request comes in.
This means that existing settings do not need to be updated when extending Origin servers and Edge servers. Therefore, all Origins can be grouped into one domain, and all Edges can be bundled with one domain. OriginMapStore allows you to expand Origins or Edges within a cluster without any additional configuration.
OriginMapStore functionality has been tested with Redis Server 5.0.7. You can enable this feature by adding the following settings to Server.xml of Origin and Edge. Note that must be set in Server.xml of the Origin server. This is used when Origin registers its own OVT url, so you just need to set a domain name or IP address that can be accessed as an OVT publisher.
It is either impossible or very cumbersome for edge servers to pre-configure all applications. So OriginMap and OriginMapStore have the ability to dynamically create an application if the application does not exist when creating the stream. They create a new application by copying the application configuration with <Name>*</Name>. That is, the special application with the name * is a dynamic application template.
When you are configuring Load Balancer, you need to use third-party solutions such as L4 Switch, LVS, or GSLB, but we recommend using DNS Round Robin. Also, services such as cloud-based AWS Route53, Azure DNS, or Google Cloud DNS can be a good alternative.
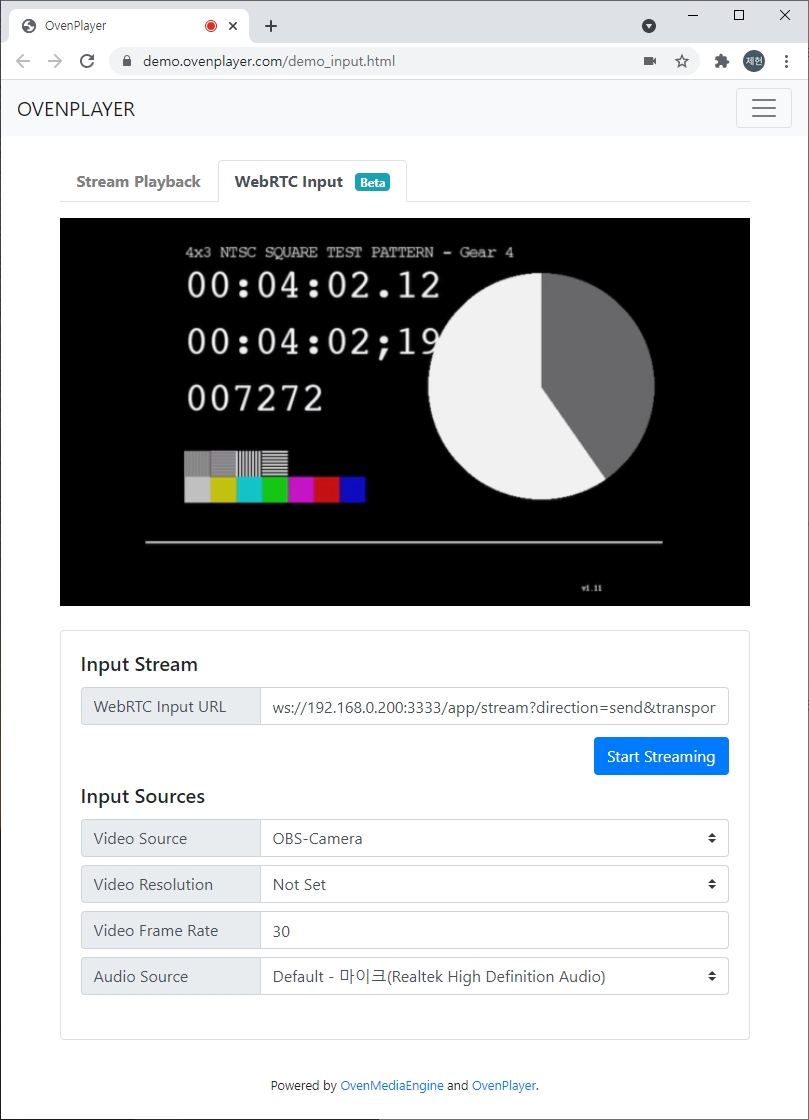
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
Content-Type: application/json
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”Content-Type: application/json<HLSDumpInfo>
<UserData>~~~</UserData>
<Stream>/default/app/stream</Stream>
<Status>Running | Completed | Error </Status>
<Items>
<Item>
<Seq>0</Seq>
<Time>~~~</Time>
<File>~~~</File>
</Item>
...
<Item>
<Seq>1</Seq>
<Time>~~~</Time>
<File>/tmp/abc/xxx/298182/chunklist_0_video_llhls.m3u8</File>
</Item>
...
<Item>
<Seq>2</Seq>
<Time>~~~</Time>
<File>chunklist_0_video_llhls.m3u8</File>
</Item>
</Items>
</HLSDumpInfo>{
"statusCode": 404,
"message": "Could not find the application: [default/non-exists] (404)"
}{
"outputStreamName": "stream",
"id": "dump_id"
}
# outputStreamName (required)
The name of the output stream created with OutputProfile.
# id (optional)
This is the id passed when calling the startHlsDump API.
If id is not passed, all dump in progress at outputStreamName is aborted.{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"stream",
"stream2"
]
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Json array containing a list of stream names{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"statusCode": 404,
"message": "Could not find the application: [default/non-exists] (404)"
}<VirtualHost>
<AdmissionWebhooks>
<ControlServerUrl>https://192.168.0.161:9595/v1/admission</ControlServerUrl>
<SecretKey>1234</SecretKey>
<Timeout>3000</Timeout>
<Enables>
<Providers>rtmp,webrtc,srt</Providers>
<Publishers>webrtc,llhls,thumbnail</Publishers>
</Enables>
</AdmissionWebhooks>
</VirtualHost>POST /configured/target/url/ HTTP/1.1
Content-Length: 325
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
X-OME-Signature: f871jd991jj1929jsjd91pqa0amm1
{
"client":
{
"address": "211.233.58.86",
"port": 29291,
"user_agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/110.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
},
"request":
{
"direction": "incoming | outgoing",
"protocol": "webrtc | rtmp | srt | llhls | thumbnail",
"status": "opening | closing",
"url": "scheme://host[:port]/app/stream/file?query=value&query2=value2",
"new_url": "scheme://host[:port]/app/new_stream/file?query=value&query2=value2",
"time": ""2021-05-12T13:45:00.000Z"
}
}HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 5
Content-Type: application/json
Connection: Closed
{
}HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 102
Content-Type: application/json
Connection: Closed
{
"allowed": true,
"new_url": "scheme://host[:port]/app/stream/file?query=value&query2=value2",
"lifetime": milliseconds,
"reason": "authorized"
}<Server version="5">
<Bind>
<Publishers>
<OVT>
<Port>9000</Port>
</OVT>
</Publishers>
</Bind>
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Applications>
<Application>
...
<Publishers>
<OVT />
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server><VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Origins>
<Properties>
<NoInputFailoverTimeout>3000</NoInputFailoverTimeout>
<UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout>60000</UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout>
</Properties>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/stream</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/stream_720p</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
<ForwardQueryParams>true</ForwardQueryParams>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>OVT</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>RTSP</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin2.com:9000/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
</Origins>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts><Location>/edge_app/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/origin_app/</Url></Urls>
</Pass><VirtualHost>
...
<OriginMapStore>
<!-- In order to use OriginMap, you must enable OVT Publisher in Origin and OVT Provider in Edge. -->
<RedisServer>
<Host>192.168.0.160:6379</Host>
<Auth>!@#ovenmediaengine</Auth>
</RedisServer>
<!-- This is only needed for the origin server and used to register the ovt address of the stream. -->
<OriginHostName>ome-dev.airensoft.com</OriginHostName>
</OriginMapStore>
...
</VirtualHost><Applications>
<Application>
<Name>*</Name>
<Type>live</Type>
<OutputProfiles>
...
</OutputProfiles>
<Providers>
<OVT />
</Providers>
<Publishers>
<AppWorkerCount>1</AppWorkerCount>
<StreamWorkerCount>8</StreamWorkerCount>
<WebRTC>
<Timeout>30000</Timeout>
<Rtx>false</Rtx>
<Ulpfec>false</Ulpfec>
<JitterBuffer>false</JitterBuffer>
</WebRTC>
<LLHLS>
<ChunkDuration>0.5</ChunkDuration>
<SegmentDuration>6</SegmentDuration>
<SegmentCount>10</SegmentCount>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</LLHLS>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>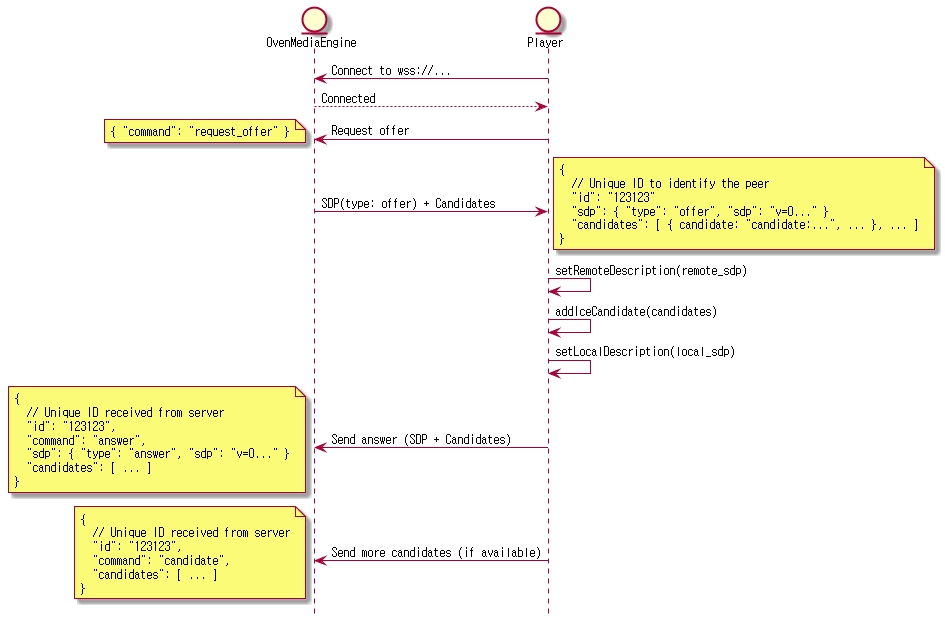
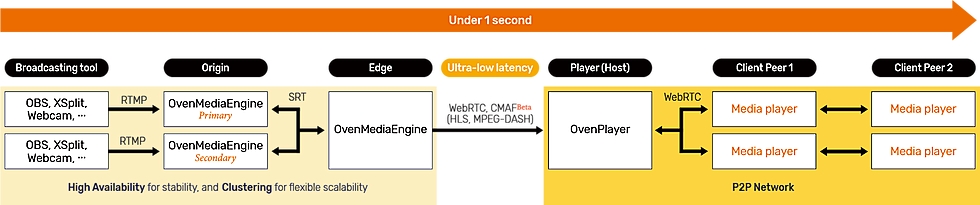
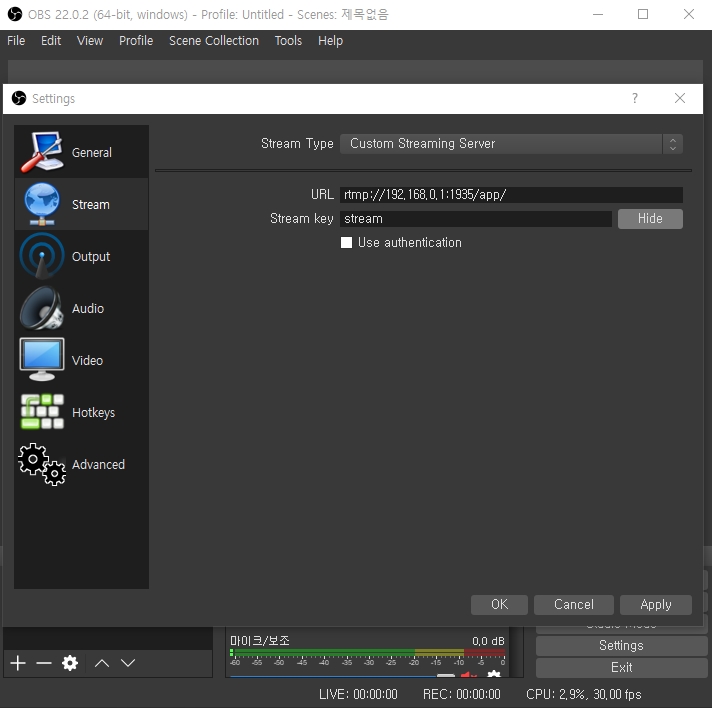
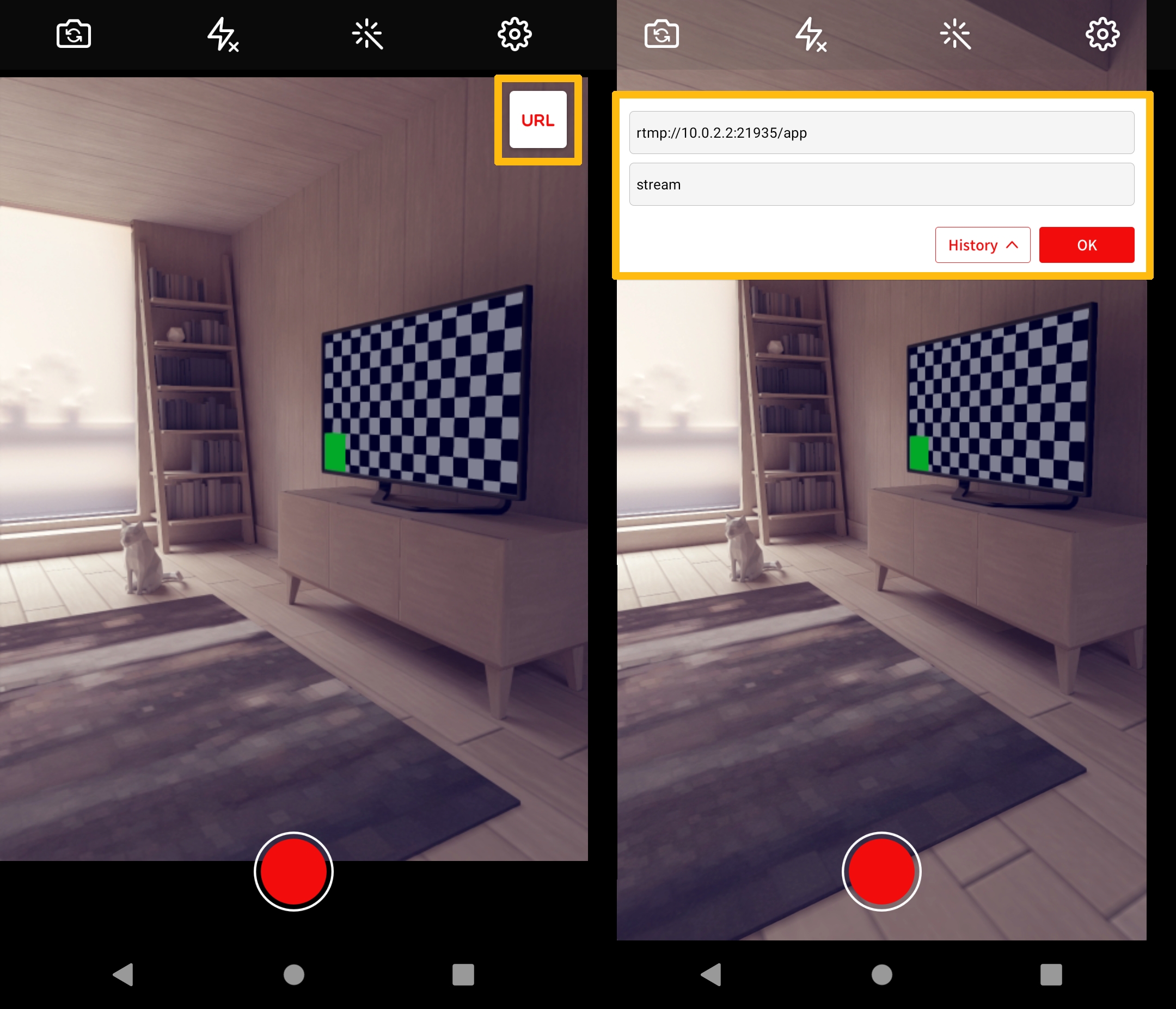
user_agent (optional)
Client's User_Agent
request
Information about the client's request
direction
incoming : A client requests to publish a stream
outgoing : A client requests to play a stream
protocol
webrtc, srt, rtmp, llhls, thumbnail
status
opening : A client requests to open a stream
closing : A client closed the stream
url
url requested by the client
new_url (optional)
url redirected from user's control server (status "closing" only)
time
time requested by the client (ISO8601 format)
Alert is a module that can detect anomalies and patterns of interest in a stream or system and send notifications to users. Anomalies and patterns of interest can be set through predefined , and when detected, the module sends an HTTP(S) request to the user's notification server.
Alert can be set up on <Server>, as shown below.
Here is a detailed explanation of each element of JSON payload:
The control server may need to validate incoming http requests for security reasons. To do this, the AdmissionWebhooks module puts the X-OME-Signature value in the HTTP request header. X-OME-Signature is a base64 url safe encoded value obtained by encrypting the payload of an HTTP request with the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm using the secret key set in <Alert><SecretKey> of the configuration.
The engine in the closing state does not need any parameter in response. To the query just answer with empty JSON object.
Apple supports Low-Latency HLS (LLHLS), which enables low-latency video streaming while maintaining scalability. LLHLS enables broadcasting with an end-to-end latency of about 2 to 5 seconds. OvenMediaEngine officially supports LLHLS as of v0.14.0.
LLHLS is an extension of HLS, so legacy HLS players can play LLHLS streams. However, the legacy HLS player plays the stream without using the low-latency function.
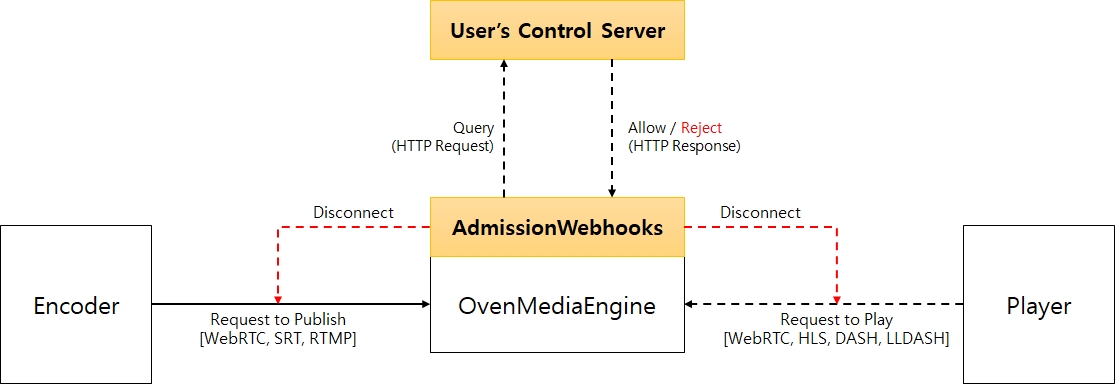
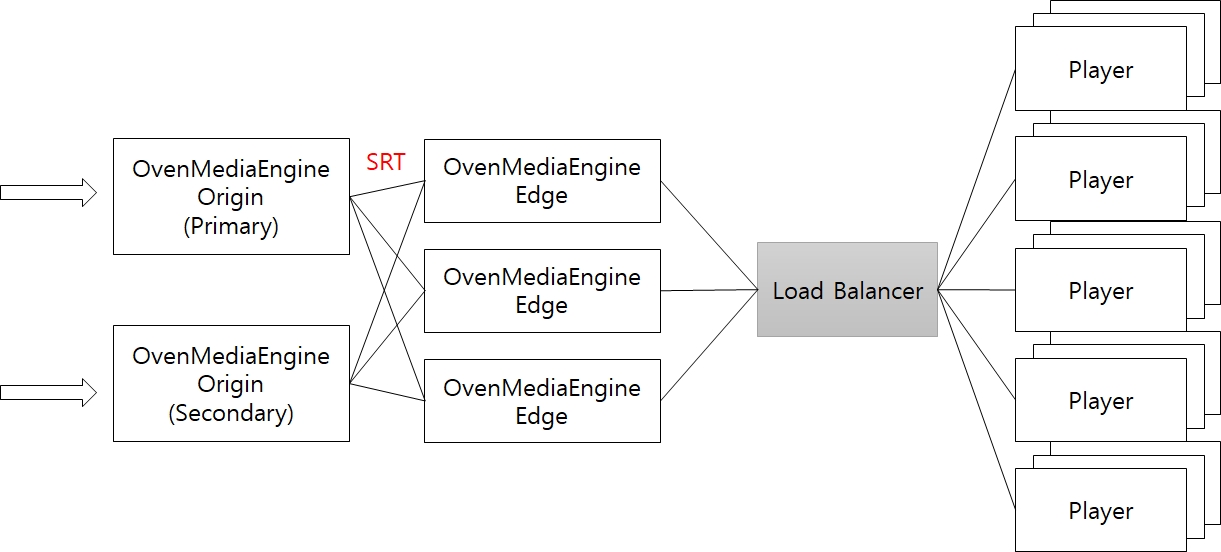
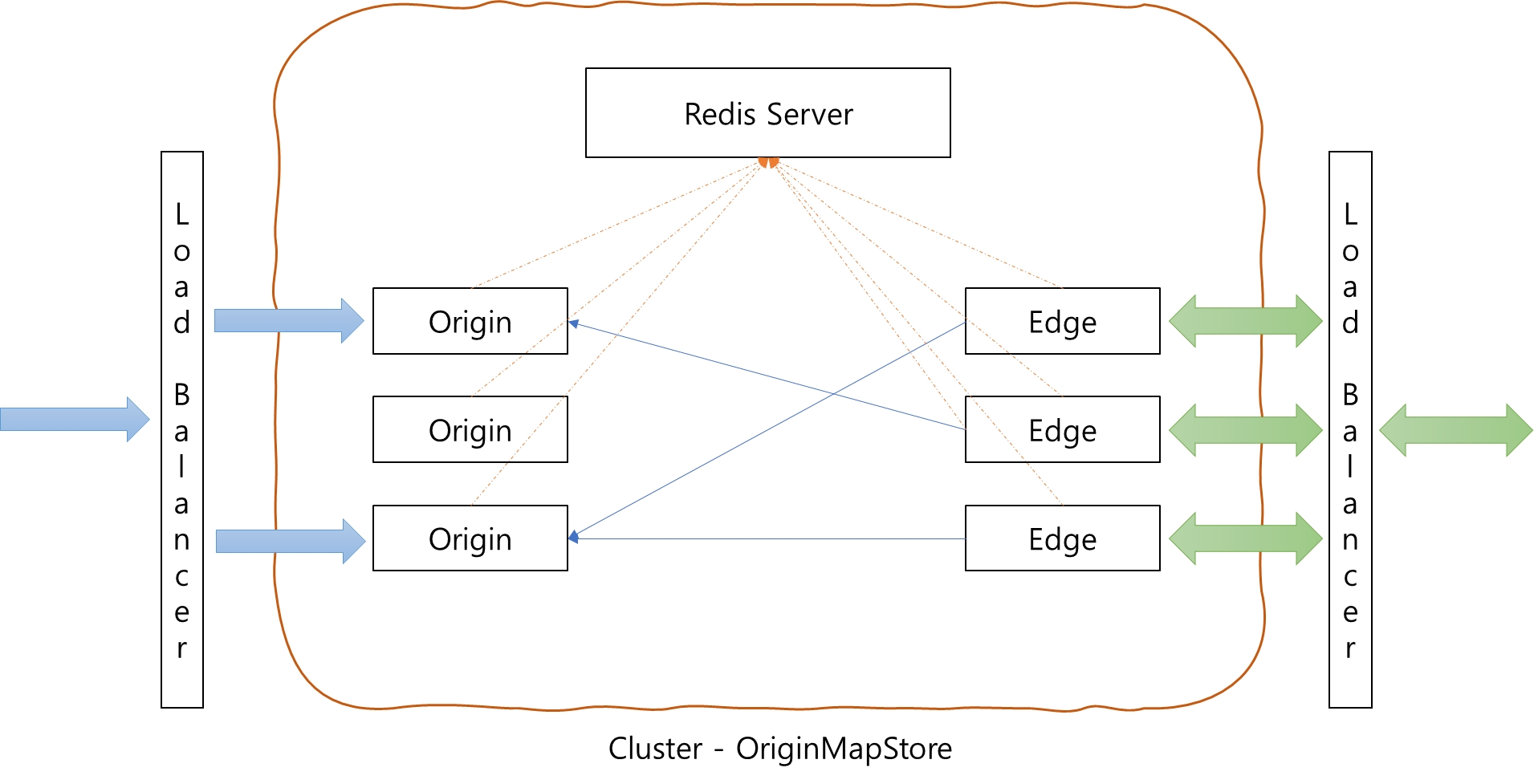
MaxFramerate
Detects when the input stream's framerate is greater than the set value.
MinWidth
Detects when the input stream's width is lower than the set value.
MaxWidth
Detects when the input stream's width is greater than the set value.
MinHeight
Detects when the input stream's height is lower than the set value.
MaxHeight
Detects when the input stream's height is greater than the set value.
MinSamplerate
Detects when the input stream's samplerate is lower than the set value.
MaxSamplerate
Detects when the input stream's samplerate is greater than the set value.
LongKeyFrameInterval
Detects when the input stream's keyframe interval is too long (exceeds 4 seconds).
HasBFrames
Detects when there are B-frames in the input stream.
The ingress stream's width (%d) is larger than the configured width (%d)
INGRESS_HEIGHT_SMALL
The ingress stream's height (%d) is smaller than the configured height (%d)
INGRESS_HEIGHT_LARGE
The ingress stream's height (%d) is larger than the configured height (%d)
INGRESS_SAMPLERATE_LOW
The ingress stream's current samplerate (%d) is lower than the configured samplerate (%d)
INGRESS_SAMPLERATE_HIGH
The ingress stream's current samplerate (%d) is higher than the configured samplerate (%d)
INGRESS_LONG_KEY_FRAME_INTERVAL
The ingress stream's current keyframe interval (%.1f seconds) is too long. Please use a keyframe interval of 4 seconds or less
INGRESS_HAS_BFRAME
There are B-Frames in the ingress stream
Url
The HTTP Server to receive the notification. HTTP and HTTPS are available.
Secretkey
The secret key used when encrypting with HMAC-SHA1
For more information, see Security.
Timeout
Time to wait for a response after request. (in milliseconds)
Rules
Anomalies and patterns of interest to be detected.
Ingress
MinBitrate
Detects when the input stream's bitrate is lower than the set value.
MaxBitrate
Detects when the input stream's bitrate is greater than the set value.
MinFramerate
Detects when the input stream's framerate is lower than the set value.
sourceUri
URI information of the detected source.
It consists of #<vhost>#<application>/<stream>.
messages
List of messages detected by the Rules.
sourceInfo
Detailed information about the source at the time of detection. It is identical to the response of the REST API's source information query for the detected source.
type
It represents the format of the JSON payload. The information of the JSON elements can vary depending on the value of the type.
Currently, the value is fixed as INGRESS.
INGRESS_BITRATE_LOW
The ingress stream's current bitrate (%d bps) is lower than the configured bitrate (%d bps)
INGRESS_BITRATE_HIGH
The ingress stream's current bitrate (%d bps) is higher than the configured bitrate (%d bps)
INGRESS_FRAMERATE_LOW
The ingress stream's current framerate (%.2f fps) is lower than the configured framerate (%.2f fps)
INGRESS_FRAMERATE_HIGH
The ingress stream's current framerate (%f fps) is higher than the configured framerate (%f fps)
INGRESS_WIDTH_SMALL
The ingress stream's width (%d) is smaller than the configured width (%d)
INGRESS_WIDTH_LARGE
<Server version="8">
<Alert>
<Url>http://192.168.0.161:9595/alert/notification</Url>
<SecretKey>1234</SecretKey>
<Timeout>3000</Timeout>
<Rules>
<Ingress>
<MinBitrate>2000000</MinBitrate>
<MaxBitrate>4000000</MaxBitrate>
<MinFramerate>15</MinFramerate>
<MaxFramerate>60</MaxFramerate>
<MinWidth>1280</MinWidth>
<MinHeight>720</MinHeight>
<MaxWidth>1920</MaxWidth>
<MaxHeight>1080</MaxHeight>
<MinSamplerate>16000</MinSamplerate>
<MaxSamplerate>50400</MaxSamplerate>
<LongKeyFrameInterval />
<HasBFrames />
</Ingress>
</Rules>
</Alert>
</Server>POST /configured/target/url/ HTTP/1.1
Content-Length: 1037
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
X-OME-Signature: f871jd991jj1929jsjd91pqa0amm1
{
"sourceUri":"#default#app/stream",
"messages":[
{
"code":"INGRESS_HAS_BFRAME",
"description":"There are B-Frames in the ingress stream."
},
{
"code":"INGRESS_BITRATE_LOW",
"description":"The ingress stream's current bitrate (316228 bps) is lower than the configured bitrate (2000000 bps)"
}
],
"sourceInfo":{
"createdTime":"2023-04-07T21:15:24.487+09:00",
"sourceType":"Rtmp",
"sourceUrl":"TCP://192.168.0.220:10639",
"tracks":[
{
"id":0,
"name":"Video",
"type":"Video",
"video":{
"bitrate":"300000",
"bypass":false,
"codec":"H264",
"framerate":30.0,
"hasBframes":true,
"height":1080,
"keyFrameInterval":0,
"width":1920
}
},
{
"audio":{
"bitrate":"160000",
"bypass":false,
"channel":1,
"codec":"AAC",
"samplerate":48000
},
"id":1,
"name":"Audio",
"type":"Audio"
},
{
"id":2,
"name":"Data",
"type":"Data"
}
]
},
"type":"INGRESS"
}HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 5
Content-Type: application/json
Connection: Closed
{
}fMP4
Codecs
H.264 AAC
To use LLHLS, you need to add the <LLHLS> elements to the <Publishers> in the configuration as shown in the following example.
Bind
Set the HTTP ports to provide LLHLS.
ChunkDuration
Set the partial segment length to fractional seconds. This value affects low-latency HLS player. We recommend 0.2 seconds for this value.
SegmentDuration
Set the length of the segment in seconds. Therefore, a shorter value allows the stream to start faster. However, a value that is too short will make legacy HLS players unstable. Apple recommends 6 seconds for this value.
SegmentCount
The number of segments listed in the playlist. This value has little effect on LLHLS players, so use 10 as recommended by Apple. 5 is recommended for legacy HLS players. Do not set below 3. It can only be used for experimentation.
CrossDomains
Control the domain in which the player works through <CorssDomain>. For more information, please refer to the section.
LLHLS can deliver adaptive bitrate streaming. OME encodes the same source with multiple renditions and delivers it to the players. And LLHLS Player, including OvenPlayer, selects the best quality rendition according to its network environment. Of course, these players also provide option for users to manually select rendition.
See the Adaptive Bitrates Streaming section for how to configure renditions.
Most browsers and players prohibit accessing other domain resources in the currently running domain. You can control this situation through Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) or Cross-Domain (CrossDomain). You can set CORS and Cross-Domain as <CrossDomains> element.
You can set it using the <Url> element as shown above, and you can use the following values:
*
Allows requests from all Domains
domain
Allows both HTTP and HTTPS requests from the specified Domain
http://domain
Allows HTTP requests from the specified Domain
https://domain
Allows HTTPS requests from the specified Domain
LLHLS is ready when a live source is inputted and a stream is created. Viewers can stream using OvenPlayer or other players.
If your input stream is already h.264/aac, you can use the input stream as is like below. If not, or if you want to change the encoding quality, you can do Transcoding.
When you create a stream, as shown above, you can play LLHLS with the following URL:
http[s]://domain[:port]/<app name>/<stream name>/llhls.m3u8
If you use the default configuration, you can start streaming with the following URL:
https://domain:3334/app/<stream name>/llhls.m3u8
We have prepared a test player that you can quickly see if OvenMediaEngine is working. Please refer to the Test Player for more information.
You can create as long a playlist as you want by setting <DVR> to the LLHLS publisher as shown below. This allows the player to rewind the live stream and play older segments. OvenMediaEngine stores and uses old segments in a file in <DVR><TempStoragePath> to prevent excessive memory usage. It stores as much as <DVR><MaxDuration> and the unit is seconds.
ID3 Timed metadata can be sent to the LLHLS stream through the Send Event API.
You can dump the LLHLS stream for VoD. You can enable it by setting the following in <Application><Publishers><LLHLS>. Dump function can also be controlled by Dump API.
TargetStreamName
The name of the stream to dump to. You can use * and ? to filter stream names.
Playlists
The name of the master playlist file to be dumped together.
OutputPath
The folder to output to. In the OutputPath you can use the macros shown in the table below. You must have write permission on the specified folder.
${VHostName}
Virtual Host Name
${AppName}
Application Name
${StreamName}
Stream Name
${YYYY}
Year
${MM}
Month
OvenMediaEngine supports Widevine and Fairplay in LLHLS with simple setup since version 0.16.0.
Currently, DRM is only supported for H.264 and AAC codecs. Support for H.265 will be added soon.
To include DRM information in your LLHLS Publisher configuration, follow these steps. You can set the InfoFile path as either a relative path, starting from the directory where Server.xml is located, or as an absolute path.
The separation of the DRMInfoFile is designed to allow dynamic changes to the file. Any modifications to the DRMInfoFile will take effect when a new stream is generated.
Here's how you should structure your DRM Info File:
Multiple <DRM> can be set. Specify the VirtualHost, Application, and StreamName where DRM should be applied. StreamName supports wildcard regular expressions.
Currently, CencProtectScheme only supports "cbcs" since FairPlay also supports only cbcs. There may be limited prospects for adding other schemes in the near future.
KeyId, Key, Iv and Pssh values are essential and should be provided by your DRM provider. FairPlayKeyUrl is only need for FairPlay and if you want to enable FairPlay to your stream, it is required. It will be also provided by your DRM provider.
OvenPlayer now includes DRM-related options. Enable DRM and input the License URL. Your content is now securely protected.
Delivery
HTTP/1.1 HTTP/2
Security
TLS (HTTPS)
Container
The OME Docker Launcher is a tool that simplifies the process of deploying and managing the OvenMediaEngine (OME) application using Docker containers. This tool can be used by developers and system administrators who want to quickly deploy and test the OME application in a Docker environment.
The OME Docker Launcher provides a set of commands that allow users to easily manage the OME Docker container. These commands include:
This command pulls the OME Docker image(airensoft/ovenmediaengine:latest) from the Docker registry and copies the necessary configuration files to a specified location. This command needs to be run before starting the OME Docker container.
This command creates and starts the Docker container. Once the container is started, the OME application can be accessed through a web browser using the container's IP address.
This command launches a bash shell inside the running OME Docker container, allowing users to execute commands and interact with the container.
This command displays the status of the running OME Docker container, including information such as the container name, and running status.
This command stops the running OME Docker container.
This command stops and then starts the OME Docker container.
Using the OME Docker Launcher, you can easily set up and manage an OME Docker container, without having to manually configure and manage the Docker container. This can save time and effort, especially for users who are not familiar with Docker or who do not want to spend time manually setting up and configuring the OME application.
Run the following command in your Linux shell.
Below is an example of execution:
OME Docker Launcher can be executed in the following format:
setupThe setup command pulls the OME Docker image from the Docker registry and copies the necessary configuration files to the host's /usr/share/ovenmediaengine directory. Additionally, it initializes the log path and crash dump path that will be mounted into the container when it is run.
This command prepares the host environment for running the OME Docker container and sets up the necessary directories and configurations for the container to run correctly.
If you run the "setup" command, the following files and directories will be created:
/usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf
This directory contains the OME configuration files and is mounted into the container when it is run.
/usr/share/ovenmediaengine/logs
If you want to change the configuration of OME, you can edit the /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf/Server.xml file. This file contains the server configuration settings for OME, such as the server's IP address, port, and SSL settings. Once you have made changes to this file, you will need to restart the OME Docker container for the changes to take effect. You can do this by running the restart command provided by the OME Docker Launcher.
To install a certificate in OvenMediaEngine, copy the certificate files to /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf with the following names:
If you want to change the file names, you can modify Server.xml.
startOnce the setup phase is complete, you can use the start command to run the OME Docker container. The start command creates and starts the Docker container, enabling the OME application to receive stream packets using protocols such as RTMP and SRT. Before running the start command, ensure that the necessary configuration files have been copied to the host's /usr/share/ovenmediaengine directory by running the setup command.
shThe sh command allows you to enter into the shell of the running container. You can use this command for troubleshooting purpose. Once you enter into the container's shell, you can execute any commands just like you do in a normal Linux shell. This allows you to inspect the container's internal state and debug any issues that you might be facing with the container or the application running inside it.
statusThe status command shows the current execution status of the container. If the container is running, it displays the ID and name of the container. This command helps you to verify whether the container is up and running or not. If the container is not running, you can use the start command to start the container.
stopThe stop command stops the running container and removes it from the list of Docker containers.
restartThe restart command restarts the container. This is useful when you need to apply changes to the Server.xml.
If you encounter any problems during the execution, try using the -d option in the [OPTIONS] to view detailed logs. This option shows the command sets and their results that are executed internally.
If OME terminates abnormally, providing the crash dump to the OME team can be helpful. The crash dump is stored in the /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/dumps directory, which is created during the setup phase. You can find the dump file named crash_<yyyymmdd>.dump in this directory.
Sharing those log and dump file would be greatly appreciated and helpful for the development of OME.
Request
Responses
Add an Output Profile to the Application. If this request succeeds, the application will be restarted.
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
Delete output profile settings. If this request succeeds, the Application will be restarted.
Request
Responses
<Server version="8">
<Bind>
<Publishers>
<LLHLS>
<!--
OME only supports h2, so LLHLS works over HTTP/1.1 on non-TLS ports.
LLHLS works with higher performance over HTTP/2,
so it is recommended to use a TLS port.
-->
<Port>80</Port>
<TLSPort>443</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</LLHLS>
</Publishers>
</Bind>
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Applications>
<Application>
<Publishers>
<LLHLS>
<ChunkDuration>0.2</ChunkDuration>
<SegmentDuration>6</SegmentDuration>
<SegmentCount>10</SegmentCount>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</LLHLS>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server><CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
<Url>*.airensoft.com</Url>
<Url>http://*.ovenplayer.com</Url>
<Url>https://demo.ovenplayer.com</Url>
</CrossDomains><OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles><LLHLS>
...
<DVR>
<Enable>true</Enable>
<TempStoragePath>/tmp/ome_dvr/</TempStoragePath>
<MaxDuration>3600</MaxDuration>
</DVR>
...
</LLHLS><LLHLS>
<Dumps>
<Dump>
<Enable>true</Enable>
<TargetStreamName>stream*</TargetStreamName>
<Playlists>
<Playlist>llhls.m3u8</Playlist>
<Playlist>abr.m3u8</Playlist>
</Playlists>
<OutputPath>/service/www/ome-dev.airensoft.com/html/${VHostName}_${AppName}_${StreamName}/${YYYY}_${MM}_${DD}_${hh}_${mm}_${ss}</OutputPath>
</Dump>
</Dumps>
...
</LLHLS><LLHLS>
<ChunkDuration>0.5</ChunkDuration>
<PartHoldBack>1.5</PartHoldBack>
<SegmentDuration>6</SegmentDuration>
<SegmentCount>10</SegmentCount>
<DRM>
<Enable>false</Enable>
<InfoFile>path/to/file.xml</InfoFile>
</DRM>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</LLHLS><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<DRMInfo>
<DRM>
<Name>MultiDRM</Name>
<VirtualHostName>default</VirtualHostName>
<ApplicationName>app</ApplicationName>
<StreamName>stream*</StreamName> <!-- Can be a wildcard regular expression -->
<CencProtectScheme>cbcs</CencProtectScheme> <!-- Currently supports cbcs only -->
<KeyId>572543f964e34dc68ba9ba9ef91d4xxx</KeyId> <!-- Hexadecimal -->
<Key>16cf4232a86364b519e1982a27d90xxx</Key> <!-- Hexadecimal -->
<Iv>572547f914e34dc68ba9ba9ef91d4xxx</Iv> <!-- Hexadecimal -->
<Pssh>0000003f7073736800000000edef8ba979d64acea3c827dcd51d21ed0000001f1210572547f964e34dc68ba9ba9ef91d4c4a1a05657a64726d48f3c6899xxx</Pssh> <!-- Hexadecimal, for Widevine -->
<!-- Add Pssh for FairPlay if needed -->
<FairPlayKeyUrl>skd://fiarplay_key_url</FairPlayKeyUrl> <!-- FairPlay only -->
</DRM>
<DRM>
<Name>MultiDRM2</Name>
<VirtualHostName>default</VirtualHostName>
<ApplicationName>app2</ApplicationName>
<StreamName>stream*</StreamName> <!-- Can be a wildcard regular expression -->
...........
</DRM>
</DRMInfo>This directory is the log path for OME and is mounted into the container when it is run. Log files generated by OME will be stored in this directory.
/usr/share/ovenmediaengine/dumps
This directory is the crash dump path for OME and is mounted into the container when it is run. Crash dumps generated by OME will be stored in this directory.
Certificate
cert.crt
Private Key
cert.key
CA Bundle
cert.ca-bundle
Configure output profiles to be created in Json array format.
It responds with Json array for each request.
It responds with Json array for each request.
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"default",
"audio_only"
]
}
{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}Header
Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Responses
Create a stream by pulling an external URL. External URL protocols currently support RTSP and OVT.
Request
Responses
Get detailed information of stream.
Request
Responses
Delete Stream. This terminates the ingress connection.
The sender can reconnect after the connection is terminated. To prevent reconnection, you must use AccessControl.
Request
Responses
You can set the following environment variables.
OME_HOST_IP
*
OME_ORIGIN_PORT
9000
OME_RTMP_PROV_PORT
1935
OME_SRT_PROV_PORT
9999/udp
OME_MPEGTS_PROV_PORT
4000/udp
When you need to install a certificate in OME or apply a complex configuration, you can do it by following the procedure below to modify Server.xml inside Docker.
OvenMediaEngine docker container loads configuration files from the following path.
Server.xml
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/Server.xml
Logger.xml
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/Logger.xml
Server Certificate
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/cert.crt
Server certificate file in PEM format. The intermediate certificate must not be included.
Private Key
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/cert.key
This is the private key file of the certificate.
CA Bundle
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/cert.ca-bundle
A file containing root and intermediate certificates.
There are many ways to change files inside a Docker container, but this document describes how to change them using Docker's bind mounts.
Copy your PEM certificate files to the path below if you need to enable TLS. The destination file names must match if using the default configuration. If you want to change the file name, you can do so by editing the Server.xml configuration file. See TLS Encryption for details.
The command below will make your OvenMediaEngine docker container run with $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/Server.xml and $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/Logger.xml files on your host. It will also create $OME_DOCKER_HOME/logs/ovenmediaengine.log file.
${DD}
Day
${hh}
Hour
${mm}
Minute
${ss}
Second
${S}
Timezone
${z}
UTC offset (ex: +0900)
${ISO8601}
Current time in ISO8601 format
Start recording the stream. If the requested stream does not exist on the server, this recording task is reserved. And when the stream is created, it automatically starts recording.
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
The Recording task has the state shown in the table below. You can get the state in the Start Recording and Get Recording State API response.
OvenMediaEngine provides a tester for measuring WebRTC performance called OvenRtcTester. It is developed in Go language and uses the pion/webrtc/v3 and gorilla/websocket modules. Many thanks to the pion/webrtc and gorilla/websocket teams for contributing this wonderful project.
Since OvenRtcTester is developed in Go language, Go must be installed on your system. Install Go from the following URL:
OvenRtcTester was tested with the latest version of go 1.17.
You can simply run it like this: -url is required. If the -life option is not used, it will run indefinitely until the user presses ctrl+c.
You can also use go build or go install depending on your preference.
OvenRtcTester must test OvenMediaEngine 0.12.4 or higher as the target system. OvenMediaEngine versions below 0.12.4 have a problem with incorrectly calculating the RTP timestamp, so OvenRtcTester calculates the Video Delay value incorrectly.
Linux has various tools to monitor CPU usage per thread. We will check the simplest with the top command. If you issue the top -H -p [pid] command, you will see the following screen.
You can use OvenRtcTester to test the capacity of the server as shown below. When testing the maximum performance, OvenRtcTester also uses a lot of system resources, so test it separately from the system where OvenMediaEngine is running. Also, it is recommended to test OvenRtcTester with multiple servers. For example, simulate 500 players with -n 500 on one OvenRtcTester, and simulate 2000 players with four servers.
Building and running OvenMediaEngine in debug mode results in very poor performance. Be sure to test the maximum performance using the binary generated by make release && make install .
If the OvenMediaEngine's capacity is exceeded, you will notice it in OvenRtcTester's Summary report with Avg Video Delay and Avg Audio Delay or Packet loss.
On the right side of the above capture screen, we simulate 400 players with OvenRtcTester. <Summary> of OvenRtcTester shows that Avg Video Delay and Avg Audio Delay are very high, and Avg FPS is low.
And on the left, you can check the CPU usage by thread with the top -H -p command. This confirms that the StreamWorker threads are being used at 100%, and now you can scale the server by increasing the number of StreamWorker threads. If OvenMediaEngine is not using 100% of all cores of the server, you can improve performance by .
This is the result of tuning the number of StreamWorkerCount to 8 in config. This time, we simulated 1000 players with OvenRtcTester, and you can see that it works stably.
The WorkerCount in <Bind> can set the thread responsible for sending and receiving over the socket. Publisher's AppWorkerCount allows you to set the number of threads used for per-stream processing such as RTP packaging, and StreamWorkerCount allows you to set the number of threads for per-session processing such as SRTP encryption.
With AppWorkerCount, you can set the number of threads for distributed processing of streams when hundreds of streams are created in one application. When an application is requested to create a stream, the stream is evenly attached to one of created threads. The main role of Stream is to packetize raw media packets into the media format of the protocol to be transmitted. When there are thousands of streams, it is difficult to process them in one thread. Also, if StreamWorkerCount is set to 0, AppWorkerCount is responsible for sending media packets to the session.
It is recommended that this value does not exceed the number of CPU cores.
It may be impossible to send data to thousands of viewers in one thread. StreamWorkerCount allows sessions to be distributed across multiple threads and transmitted simultaneously. This means that resources required for SRTP encryption of WebRTC or TLS encryption of HLS/DASH can be distributed and processed by multiple threads. It is recommended that this value not exceed the number of CPU cores.
If a large number of streams are created and very few viewers connect to each stream, increase AppWorkerCount and lower StreamWorkerCount as follows.
If a small number of streams are created and a very large number of viewers are connected to each stream, lower AppWorkerCount and increase StreamWorkerCount as follows.
Start push publishing the stream with SRT, RTMP or MPEG2-TS. If the requested stream does not exist on the server, this task is reserved. And when the stream is created, it automatically starts push publishing.
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
The Push Publishing task has the state shown in the table below. You can get the state in the Start Push Publishing and Get Push Publishing State API response.
SignedPolicy is a module that limits the user's privileges and time. For example, operators can distribute RTMP URLs that can be accessed for 60 seconds to authorized users, and limit RTMP transmission to 1 hour. The provided URL will be destroyed after 60 seconds, and transmission will automatically stop after 1 hour. Users who are provided with a SignedPolicy URL cannot access resources other than the provided URL. This is because the SignedPolicy URL is authenticated.
SignedPolicy URL consists of the query string of the streaming URL with Policy and Signature as shown below. If SignedPolicy is enabled in the configuration of OvenMediaEngine, access to URLs with no signature or invalid signature is not allowed. Signature uses HMAC-SHA1 to authenticate all URLs except signature.
Policy is in json format and provides the following properties.
Signature is generated by HMAC-SHA1 encoding all URLs except signature query string. The generated Signature is encoded using and included as a query string of the existing URL.
The URL entered into HMAC to generate the Signature must include :port.
When creating a signature, you cannot omit the default port such as http port 80, https port 443, or rtmp port 1935. This is because when OvenMediaEngine creates a signature for checking the signature, it is created by putting the port value.
When using SignedPolicy with SRT providers, only use the streamid portion of the URL, e.g. srt://myserver:9999?streamid=srt://myserver:9999/app/stream?policy=abc123
To enable SignedPolicy, you need to add the following <SignedPolicy> setting in Server.xml under <VirtualHost>.
We provide a script that can easily generate SignedPolicy URL. The script can be found in the path below.
Here's how to use this script:
For example, you can use it like this:
We hope to provide SignedPolicy URL Generator Library in various languages. If you have created the SignedPolicy URL Generator Library in another language, please send a Pull Request to our . Thank you for your open source contributions.
In order to include the policy in the URL, it must be encoded with .
Policy encoded with Base64URL is added as a query string to the existing streaming URL. (The query string key is set in Server.xml.)
Signature hashes the entire URL including the policy in HMAC (SHA-1) method, encodes it as Base64URL, and includes it in the query string.
Create a hash using the secret key (1kU^b6 in the example) and the URL above using HMAC-SHA1.
If you include it as a signature query string (query string key is set in Server.xml), the following SignedPolicy URL is finally generated.
Generate SignedPolicy URL with the script.
Separate the URL based on "app" as shown in the example below and enter all the parts under the stream in the Stream Key.
curl -OL 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine/master/misc/ome_docker_launcher.sh' && chmod +x ome_docker_launcher.sh$ curl -OL 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine/master/misc/ome_docker_launcher.sh' && chmod +x ome_docker_launcher.sh
$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh -h
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Usage: ./ome_docker_launcher.sh [OPTIONS] COMMAND ...
• Options:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
-v, --version Show the version and exit
-d, --debug Show debug log
-b, --hide_banner Hide the banner
-m, --monochrome Disable colors
• Commands:
setup Download the latest Docker image and setup directories for the container
start Start a docker container
sh Run a shell in the docker container
status Show the status of the docker container
stop Stop the docker container
restart Restart the docker container• Usage: ./ome_docker_launcher.sh [OPTIONS] COMMAND ...
• Options:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
-v, --version Show the version and exit
-d, --debug Show debug log
-b, --hide_banner Hide the banner
-m, --monochrome Disable colors
• Commands:
setup Download the latest Docker image and setup directories for the container
start Start a docker container
sh Run a shell in the docker container
status Show the status of the docker container
stop Stop the docker container
restart Restart the docker container$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh setup
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Creating configuration directory /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf
• Copying configuration to /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf
• Copying logs directory
• Copying crash dump directory
• OvenMediaEngine is ready to start!
If you want to change the settings, please modify /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf/Server.xml
If you want to start OvenMediaEngine, please run ./ome_docker_launcher.sh start$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh start
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Starting OvenMediaEngine...
• Obtaining the port list from /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf/Server.xml
- RTMP Provider is configured to use 1935 (Port)
- SRT Provider is configured to use 9999 (Port)
- WebRTC Provider is configured to use 3333 (Port)
- WebRTC Provider is configured to use 3334 (TLSPort)
- WebRTC Provider is configured to use 10000-10004/UDP (IceCandidate)
- WebRTC Provider is configured to use 3478 (TcpRelay)
- OVT Publisher is configured to use 9000 (Port)
- LLHLS Publisher is configured to use 3333 (Port)
- LLHLS Publisher is configured to use 3334 (TLSPort)
- WebRTC Publisher is configured to use 3333 (Port)
- WebRTC Publisher is configured to use 3334 (TLSPort)
- WebRTC Publisher is configured to use 10000-10004/UDP (IceCandidate)
- WebRTC Publisher is configured to use 3478 (TcpRelay)
• Starting a container: ovenemediaengine
docker> 7235ff9f80762b6e7b27ba3a9773f5584033d55c113340dabf0779e8f5cf53bb
• OvenMediaEngine is started successfully!$ OME_HOST_IP=1.2.3.4 ./ome_docker_launcher.sh start
...
• OvenMediaEngine is started successfully!
$ tail -f /usr/share/ovenmediaengine/logs/ovenmediaengine.log
...
[2023-11-01 00:00:00.000] I [OvenMediaEngine:1] ICE | ice_port_manager.cpp:305 | ICE candidate found: 1.2.3.4:40000
...OME_HOST_IP
OME_RTMP_PROV_PORT
OME_WEBRTC_CANDIDATE_IP
OME_WEBRTC_CANDIDATE_PORT
OME_WEBRTC_SIGNALLING_PORT
OME_WEBRTC_SIGNALLING_TLS_PORT
OME_WEBRTC_TCP_RELAY_PORT$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh sh
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Run a shell in the running container: ID: 7235ff9f8076
root@7235ff9f8076:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 10:29 ? 00:00:01 /opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/OvenMediaEngine -c origin_conf
root 53 0 0 10:44 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash
root 61 53 0 10:44 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -ef
root@7235ff9f8076:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin# top -bn1
top - 10:44:44 up 333 days, 3:33, 0 users, load average: 0.44, 0.78, 0.78
Tasks: 3 total, 1 running, 2 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 1.4 us, 0.3 sy, 0.0 ni, 98.3 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
MiB Mem : 128723.7 total, 10529.4 free, 31268.5 used, 86925.7 buff/cache
MiB Swap: 31250.0 total, 30345.8 free, 904.2 used. 96221.5 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
1 root 20 0 320136 21812 15772 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.48 OvenMediaEngine
53 root 20 0 4116 3456 2896 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.01 bash
62 root 20 0 5972 3160 2732 R 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 top
root@7235ff9f8076:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin# $ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh status
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Container is running: ID: 7235ff9f8076, name: ovenemediaengine$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh stop
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Stopping a container: ovenemediaengine
docker> ovenemediaengine
• Removing a container: ovenemediaengine
docker> ovenemediaengine
• OvenMediaEngine is stopped successfully$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh stop
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Restarting a container: ovenemediaengine
docker> ovenemediaengine$ ./ome_docker_launcher.sh -d stop
▄██████▀███▄
█████▀ ▄██████ OvenMediaEngine Launcher v0.1
███▄▄▄▄▀▀▀▀███
██████▀ ▄█████ https://github.com/AirenSoft/OvenMediaEngine
▀███▄██████▀
• Stopping a container: ovenemediaengine
┌── /usr/bin/docker stop ovenemediaengine
docker> ovenemediaengine
└── Succeeded
• Removing a container: ovenemediaengine
┌── /usr/bin/docker rm ovenemediaengine
docker> ovenemediaengine
└── Succeeded
• OvenMediaEngine is stopped successfullyAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonContent-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}[
{
"name": "bypass_profile",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}_bypass",
"encodes": {
"videos": [
{
"bypass": true
}
],
"audios": [
{
"bypass": true
}
]
}
}
]
# name (required)
The name of the output profile. cannot be duplicated
# outputStreamName (required)
The name of the output stream to be created through this profile.
# encodes (required)
encode profile list. It must have videos or audios, and must have at least one item.[
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "bypass_profile",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}_bypass",
"encodes": {
"audios": [],
"videos": [
{
"bypass": true
}
]
}
},
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
...
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Created output profile information[
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "app",
"outputProfiles": {
...
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
...
},
{
"statusCode": 409,
"message": "Conflict",
"response": {
...
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Output profile information created when statusCode is 200{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "bypass_profile2",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}_bypass"
"encodes": {
"audios": [],
"videos": [
{
"bypass": true
}
]
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Output Profile information{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
Content-Type: application/json
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>{
"name": "new_stream_name",
"urls": [
"rtsp://192.168.0.160:553/app/stream",
"url to pull the stream from - support OVT/RTSP",
"Only urls with the same scheme can be sent as a group."
],
"properties":{
"persistent": false,
"noInputFailoverTimeoutMs": 3000,
"unusedStreamDeletionTimeoutMs": 60000,
"ignoreRtcpSRTimestamp": false
}
}
# name (required)
Stream name to create
# urls (required)
A list of URLs to pull streams from, in Json array format.
All URLs must have the same scheme.
# properties (optional)
## persistent
Created as a persistent stream, not deleted until DELETE
## noInputFailoverTimeoutMs
If no data is input during this period, the stream is deleted,
but ignored if persistent is true
## unusedStreamDeletionTimeoutMs
If no data is output during this period (if there is no viewer),
the stream is deleted, but ignored if persistent is true
## ignoreRtcpSRTimestamp
No waits RTCP SR and start stream immediatelyContent-Type: application/json{
"message": "Created",
"statusCode": 201
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response codeWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"statusCode": 404,
"message": "Could not find the application: [default/non-exists] (404)"
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"input": {
"createdTime": "2021-01-11T03:45:21.879+09:00",
"sourceType": "Rtmp",
"tracks": [
{
"id": 0,
"type": "Video",
"video": {
"bitrate": "2500000",
"bypass": false,
"codec": "H264",
"framerate": 30.0,
"hasBframes": false,
"keyFrameInterval": 30,
"height": 720,
"width": 1280
}
},
{
"id": 1,
"audio": {
"bitrate": "128000",
"bypass": false,
"channel": 2,
"codec": "AAC",
"samplerate": 48000
},
"type": "Audio"
}
]
},
"name": "stream",
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stream",
"tracks": [
{
"id": 0,
"type": "Video",
"video": {
"bypass": true
}
},
{
"id": 1,
"audio": {
"bypass": true
},
"type": "Audio"
},
{
"id": 2,
"audio": {
"bitrate": "128000",
"bypass": false,
"channel": 2,
"codec": "OPUS",
"samplerate": 48000
},
"type": "Audio"
}
]
}
]
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Details of the streamkeyFrameInterval is GOP sizeWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 404,
"message": "Could not find the application or stream (404)"
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response codeWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}Content-Type: application/json{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the stream: [default/#default#app/stream] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}docker run --name ome -d -e OME_HOST_IP=Your.HOST.IP.Address \
-p 1935:1935 -p 9999:9999/udp -p 9000:9000 -p 3333:3333 -p 3478:3478 -p 10000-10009:10000-10009/udp \
airensoft/ovenmediaengine:0.16.3export OME_DOCKER_HOME=/opt/ovenmediaengine
sudo mkdir -p $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf
sudo mkdir -p $OME_DOCKER_HOME/logs
# Set permissions for the created directory if necessary.
sudo chgrp -R docker $OME_DOCKER_HOME
sudo chmod -R 775 $OME_DOCKER_HOME
# If you want to use OME_HOME permanently, add the following line to the ~/.profile file for bash, for other shells, you can do it accordingly.
echo "export OME_DOCKER_HOME=/opt/ovenmediaengine" >> ~/.profiledocker run -d --name tmp-ome airensoft/ovenmediaengine:0.16.3
docker cp tmp-ome:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/Server.xml $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf
docker cp tmp-ome:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/Logger.xml $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf
docker rm -f tmp-omecp /your/server_certificate_file.crt $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/cert.crt
cp /your/certificate_key_file.key $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/cert.key
cp /your/ca_bundle_file.ca-bundle $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/cert.ca-bundlevi $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf/Server.xmldocker run -d -it --name ome -e OME_HOST_IP=Your.HOST.IP.Address \
-v $OME_DOCKER_HOME/conf:/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf \
-v $OME_DOCKER_HOME/logs:/var/log/ovenmediaengine \
-p 1935:1935 -p 9999:9999/udp -p 9000:9000 -p 3333:3333 -p 3478:3478 \
-p 10000-10009:10000-10009/udp \
airensoft/ovenmediaengine:0.16.3tail -f $OME_DOCKER_HOME/logs/ovenmediaengine.logdocker restart omedocker stop ome
docker rm omescheme://domain.com:port/app/stream?policy=<>&signature=<>OME_LLHLS_STREAM_PORT
3333
OME_LLHLS_STREAM_TLS_PORT
3334
OME_WEBRTC_SIGNALLING_PORT
3333
OME_WEBRTC_SIGNALLING_TLS_PORT
3334
OME_WEBRTC_TCP_RELAY_PORT
3478
OME_WEBRTC_CANDIDATE_PORT
10000-10004/udp
Started
In Progress
Stopping
Is stopping
Stopped
Stopped
Error
Error
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>{
"id": "{unique_push_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"variantNames": []
},
"protocol": "srt",
"url": "srt://{host}[:port]?mode=caller&latency=120000&timeout=500000",
"streamKey": ""
}
# id (required)
unique ID to identify the task
# stream (required)
## name (required)
output stream name
## variantNames (optional)
Array of track names to publsh.
This value is Encodes.[Video|Audio|Data].Name in the OutputProfile
setting.
If empty, all tracks will be sent.
# protocol (required)
srt
# url (required)
address of destination.
options can be set in query-string format.
# streamKey (optional)
not used with mpegts{
"id": "{unique_push_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"variantNames": [ "h264_fhd", "aac" ]
},
"protocol": "rtmp",
"url":"rtmp://{host}[:port]/{app_name}",
"streamKey":"{stream_name}"
}
# id (required)
unique ID to identify the task
# stream (required)
## name (required)
output stream name
## variantNames (optional)
Array of track names to publsh.
This value is Encodes.[Video|Audio|Data].Name in the OutputProfile
setting.
If empty, The first track among video tracks (by ID) and the first
track among audio tracks (by ID) are selected automatically.
# protocol (required)
rtmp
# url (required)
address of destination
# streamKey (required)
RTMP stream key{
"id": "{unique_push_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"variantNames": []
},
"protocol": "mpegts",
"url": "udp://{host}[:port]",
"streamKey": ""
}
# id (required)
unique ID to identify the task
# stream (required)
## name (required)
output stream name
## variantNames (optional)
Array of track names to publsh.
This value is Encodes.[Video|Audio|Data].Name in the OutputProfile
setting.
If empty, all tracks will be sent.
# protocol (required)
mpegts
# url (required)
address of destination
# streamKey (optional)
not used with mpegts{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"id": "{unique_push_id}",
"state": "ready",
"vhost": "default",
"app": "app",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"trackIds": [],
"variantNames": []
},
"protocol": "rtmp",
"url": "rtmp://{host}[:port]/{app_name}",
"streamKey": "{stream_name}",
"sentBytes": 0,
"sentTime": 0,
"sequence": 0,
"totalsentBytes": 0,
"totalsentTime": 0,
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T23:02:34.371+09:00",
"startTime": "1970-01-01T09:00:00.000+09:00",
"finishTime": "1970-01-01T09:00:00.000+09:00"
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Created push publishing task informationWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>{
"id": "{unique_push_id}"
}
# id (required)
unique ID to identify the push publishing taskContent-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response codeWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>{
"id": "{unique_push_id}"
}
# id (optional)
unique ID to identify the push publishing task. If no id is given in the request, the full list is returned.Content-Type: application/json{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
{
"id": "{unique_push_id}",
"state": "started",
"vhost": "default",
"app": "app",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"trackIds": [],
"variantNames": []
},
"protocol": "rtmp",
"url": "rtmp://{host}[:port]/{app_name}",
"streamKey": "{stream_name}",
"sentBytes": 0,
"sentTime": 0,
"sequence": 0,
"totalsentBytes": 0,
"totalsentTime": 0,
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T23:02:34.371+09:00",
"startTime": "1970-01-01T09:00:00.000+09:00",
"finishTime": "1970-01-01T09:00:00.000+09:00"
},
{
"id": "4",
...
}
]
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Information of recording tasks. If there is no recording task,
response with empty array ("response": [])WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Please note that responses are incorrectly returned in Json array format for version 0.15.3 and earlier.
The response is Json array format.
Ready
Preparing to start or waiting for the stream to be created.
Started
In Progress
Stopping
Is stopping
Stopped
Stopped
Error
Error
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"id": "{unique_record_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}",
"variantNames": []
}
}
# id (required)
{
"id": "{unique_record_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}"
},
"interval": 60000,
"segmentationRule": "discontinuity"
{
"id": "{unique_record_id}",
"stream": {
"name": "{output_stream_name}"
},
"schedule" : "0 */1 *"
"segmentationRule": "continuity"
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"id": "2",
"state": "ready",
{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}<Bind><Providers><RTMP><WorkerCount>
SPMPEGTS
<Bind><Providers><MPEGTS><WorkerCount>
SPOvtPub
<Bind><Pubishers><OVT><WorkerCount>
SPSRT
<Bind><Providers><SRT><WorkerCount>
Thread name
Element in the configuration
AW-XXX
<Application><Publishers><AppWorkerCount>
StreamWorker
<Application><Publishers><StreamWorkerCount>
SPICE-XXX
<Bind><Provider><WebRTC><IceCandidates><TcpRelayWorkerCount>
<Bind><Pubishers><WebRTC><IceCandidates><TcpRelayWorkerCount>
SPRtcSignalling
<Bind><Provider><WebRTC><Signalling><WorkerCount>
<Bind><Pubishers><WebRTC><Signalling><WorkerCount>
SPSegPub
<Bind><Pubishers><HLS><WorkerCount>
<Bind><Pubishers><DASH><WorkerCount>
Type
Value
Default
1
Minimum
1
Maximum
72
Type
Value
Default
8
Minimum
0
Maximum
72
SPRTMP-XXX
<String> IPv4 CIDR
Allowed IP address range, 192.168.0.0/24
url_expire
(Required)
<Number> Milliseconds since unix epoch
The time the URL expires Reject on request after the expiration
url_activate
(Optional)
<Number> Milliseconds since unix epoch
The time the URL activates Reject on request before activation
stream_expire
(Optional)
<Number> Milliseconds since unix epoch
The time the Stream expires Transmission and playback stop when the time expires
PolicyQueryKeyName
The query string key name in the URL pointing to the policy value
SignatureQueryKeyName
The query string key name in the URL pointing to the signature value
SecretKey
The secret key used when encoding with HMAC-SHA1
Enables
List of providers and publishers to enable SignedPolicy. Currently, SignedPolicy supports rtmp among providers, and among publishers, WebRTC, LLHLS, Thumbnail are supported.
allow_ip
(Optional)
We will update this document as we gather troubleshooting examples. (Written in Nov 04, 2021)
prerequisites.sh Script FailedIf you have problems with the prerequisites.sh the script we have provided, please install it manually as follows.
systemctl start ovenmediaengine failedIf SELinux is running on your system, SELinux can deny the execution of OvenMediaEngine.
You can choose between two methods of adding a policy to SELinux or setting SELinux to permissive mode. To add a policy, you must apply the SELinux policy file for the OvenMediaEngine service to your system as follows:
Setting SELinux to permissive mode is as simple as follows. But we don't recommend this method.
WebRTC does not support b-frame of H.264. But if your encoder sends b-frames the video will be stuttered in the player. In this case, you can solve the problem by disabling the b-frame function in your encoder. For OBS, you can set bframes=0 option as below.
Or by activating the encoding options in OvenMediaEngine.
In this case, you are probably trying to stream with UDP in an environment where packet loss is high due to network performance, connection problems, etc., the interruption during stream playback may more and more worsen. This problem can be solved simply by playing with WebRTC/TCP.
If you want to monitor packet loss in your Chrome browser, you can access it by typing 'chrome://webrtc-internals' in the address bar.
Also, if the device's network speed, which is running the player, isn't fast enough to accommodate the stream's BPS, the stuttering during streaming won't resolve and will eventually drop the connection. In this case, there is no other way than to speed up your network.
If the Origin server uses excessive CPU/Memory/Network, all players may experience stuttering during streaming.
When you see Origin is CPU intensive on your Origin-Edge structure, the transcoding options in the OvenMediaEngine may be the primary cause. That is, you may have set the quality of the input stream too high, or the output stream to exceed the capabilities of your hardware significantly. In this case, it can be solved by enabling the hardware encoder in OvenMediaEngine.
If the edge server excessively uses CPU/Memory/Network, the player connected to that Edge may experience stuttering during streaming. In this case, it can be solved by expanding Edge.
When you see a specific thread overuses the CPU, the video may not stream smoothly. Please refer to the manual below for more information on this.
The Linux kernel, which is set by default, cannot handle 1Gbps output, so put it as follows:
The mobile environment used by many people uses a wireless network. It has a high network speed but, conversely, can cause high packet loss.
Look, CUBIC, the Congestion Control set by default in your Linux, adjusts the TCP Window by packet loss, so it is not suitable to provide stable streaming in such an environment.
So our suggestion is to use Google's BBR. This setting is even more important if you mainly provide WebRTC services to mobile users who use a wireless network. Change the Congestion Control from CUBIC to BBR on your Linux.
If you try to access OvenMediaEngine's WebRTC URL starting with ws:// (Non-TLS) from an HTTPS (HTTP/TLS) site, the connection may be rejected due to a mixed content problem depending on the browser.
In this case, you can solve this by installing a certificate in OvenMediaEngine and trying to connect with the wss:// (WebSocket/TLS) URL.
As of October 2021, most browsers have enforced the , and CORS errors often occur when requesting access to other domains if it is not a TLS site. In this case, you can solve the problem by installing a certificate on the site that loads the player.
At some point, when the message "Too many open files" is output in your OvenMediaEngine log, it may not be able to handle any more player connections. In this case, you can solve the problem by setting it as follows:
If you use Transcoding as Bypass in OvenMediaEngine and set a long keyframe interval in the encoder, the WebRTC player cannot start streaming until a keyframe is an input.
In this case, you can solve this by setting the keyframe interval in the encoder to 1-2 seconds,
Or by enabling the encoding options in OvenMediaEngine.
A/V may not be input evenly from the encoder. There are some encoders with policies for reliable streaming that they decide, for example, sending audio first and video very later, or video first and audio very late.
OvenMediaEngine outputs the input received from the encoder as-is for sub-second latency streaming. The WebRTC player also streams the received input as-is, so the A/V sync may not match during the initial playback due to the policy of specific encoders.
However, this can be resolved naturally as the player will sync A/V while streaming based on Timestamp. Still, if this work looks like an error, you can also solve it by enabling JitterBuffer in OvenMediaEngine.
Also, suppose you are using a transcoder in OvenMediaEngine and trying to input with b-frames of H264. Audio is encoded fast, but a video is buffered at the decoder because of b-frames. Therefore, there is a time difference at the start of each encoding, which may cause the A/V to be out of sync. Even in this case, enabling JitterBuffer will solve this problem.
There may be cases where the A/V sync is not corrected even after a certain amount of time has elapsed after playback. This problem is caused by small internal buffers in some browsers such as Firefox, which causes the player to give up calibration if the A/V sync differs too much. But this can also be solved by enabling JitterBuffer.
Nevertheless, if the A/V sync is not corrected, you should suspect an error in the original video file, which can be checked by playing as HLS.
However, if A/V sync is well during streaming with HLS, this is OvenMediaEnigne's bug. If you find any bugs, please feel free to report them to .
WebRTC supports Opus, not AAC, as an audio codec. Because RTMP and other protocols mainly use and transmit AAC as the audio codec, you may not have set up Opus, but WebRTC cannot output audio without Opus. This can be solved by setting Opus in OvenMediaEnigne.
If you are using video encoding in OME, the video bitrate may be set low. In this case, the video quality can be improved by increasing the unit of video bitrate.
However, since OvenMediaEngine has the default to the fastest encoding option for sub-second latency streaming, the video quality may not be as good as the set video bitrate. In this case, OvenMediaEngine provides an output profile preset that can control the quality, so you can choose to solve it.
Since the encoder is transmitting video to OvenMediaEngine in low quality, you can solve it by increasing the input quality in the encoder settings.
OvenMediaEngine uses WebRTC to provide sub-second latency streaming. WebRTC uses RTP for media transmission and provides various extensions.
OvenMediaEngine provides the following features:
{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [vhost/app1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}{
"id": "{unique_record_id}"
}
# id (required)
unique ID to identify the recording task{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"id": "{unique_record_id}"
}
# id (optional)
unique ID to identify the recording task. If no id is given in the request, the full list is returned.{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
{
"id": "2",
"state": "recording",
"vhost": "default",
"app": "app",
"stream": {
"name": "stream",
"trackIds": [],
"variantNames": []
},
"interval": 60000,
"segmentationRule": "discontinuity",
"createdTime": "2023-03-15T21:15:20.113+09:00",
},
{
"id": "3",
...
}
]
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Information of recording tasks. If there is no recording task,
response with empty array ("response": []){
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}$ cd OvenMediaEngine/misc/oven_rtc_tester
$ go run OvenRtcTester.go
-url parameter is required and must be vaild. (input : undefined)
-cint int
[Optional] PeerConnection connection interval (milliseconds) (default 100)
-life int
[Optional] Number of times to execute the test (seconds)
-n int
[Optional] Number of client (default 1)
-sint int
[Optional] Summary information output cycle (milliseconds) (default 5000)
-url string
[Required] OvenMediaEngine's webrtc streaming URL (default "undefined")
$ go run OvenRtcTester.go -url ws://192.168.0.160:13333/app/stream -n 5
client_0 connection state has changed checking
client_0 has started
client_1 connection state has changed checking
client_1 has started
client_0 connection state has changed connected
client_1 connection state has changed connected
client_1 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_0 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_1 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_0 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_2 connection state has changed checking
client_2 has started
client_2 connection state has changed connected
client_2 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_2 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_3 connection state has changed checking
client_3 has started
client_3 connection state has changed connected
client_3 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_3 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_4 connection state has changed checking
client_4 has started
client_4 connection state has changed connected
client_4 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_4 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
<Summary>
Running time : 5s
Number of clients : 5
ICE Connection State : New(0), Checking(0) Connected(5) Completed(0) Disconnected(0) Failed(0) Closed(0)
Avg Video Delay(54.20 ms) Max Video Delay(55.00 ms) Min Video Delay(53.00 ms)
Avg Audio Delay(37.00 ms) Max Audio Delay(55.00 ms) Min Audio Delay(26.00 ms)
Avg FPS(30.15) Max FPS(30.25) Min FPS(30.00)
Avg BPS(4.1 Mbps) Max BPS(4.1 Mbps) Min BPS(4.0 Mbps)
Total Bytes(11.6 MBytes) Avg Bytes(2.3 MBytes)
Total Packets(13897) Avg Packets(2779)
Total Packet Losses(0) Avg Packet Losses(0)
<Summary>
Running time : 10s
Number of clients : 5
ICE Connection State : New(0), Checking(0) Connected(5) Completed(0) Disconnected(0) Failed(0) Closed(0)
Avg Video Delay(43.60 ms) Max Video Delay(45.00 ms) Min Video Delay(42.00 ms)
Avg Audio Delay(36.60 ms) Max Audio Delay(55.00 ms) Min Audio Delay(25.00 ms)
Avg FPS(30.04) Max FPS(30.11) Min FPS(30.00)
Avg BPS(4.0 Mbps) Max BPS(4.0 Mbps) Min BPS(4.0 Mbps)
Total Bytes(24.3 MBytes) Avg Bytes(4.9 MBytes)
Total Packets(28832) Avg Packets(5766)
Total Packet Losses(0) Avg Packet Losses(0)
<Summary>
Running time : 15s
Number of clients : 5
ICE Connection State : New(0), Checking(0) Connected(5) Completed(0) Disconnected(0) Failed(0) Closed(0)
Avg Video Delay(36.60 ms) Max Video Delay(38.00 ms) Min Video Delay(35.00 ms)
Avg Audio Delay(49.20 ms) Max Audio Delay(68.00 ms) Min Audio Delay(38.00 ms)
Avg FPS(30.07) Max FPS(30.07) Min FPS(30.07)
Avg BPS(4.0 Mbps) Max BPS(4.0 Mbps) Min BPS(4.0 Mbps)
Total Bytes(36.8 MBytes) Avg Bytes(7.4 MBytes)
Total Packets(43717) Avg Packets(8743)
Total Packet Losses(0) Avg Packet Losses(0)
^CTest stopped by user
***************************
Reports
***************************
<Summary>
Running time : 15s
Number of clients : 5
ICE Connection State : New(0), Checking(0) Connected(5) Completed(0) Disconnected(0) Failed(0) Closed(0)
Avg Video Delay(23.60 ms) Max Video Delay(25.00 ms) Min Video Delay(22.00 ms)
Avg Audio Delay(11.20 ms) Max Audio Delay(18.00 ms) Min Audio Delay(5.00 ms)
Avg FPS(30.07) Max FPS(30.07) Min FPS(30.07)
Avg BPS(4.0 Mbps) Max BPS(4.0 Mbps) Min BPS(4.0 Mbps)
Total Bytes(38.6 MBytes) Avg Bytes(7.7 MBytes)
Total Packets(45662) Avg Packets(9132)
Total Packet Losses(0) Avg Packet Losses(0)
<Details>
[client_0]
running_time(15s) connection_state(connected) total_packets(9210) packet_loss(0)
last_video_delay (22.0 ms) last_audio_delay (52.0 ms)
total_bytes(7.8 Mbytes) avg_bps(4.0 Mbps) min_bps(3.6 Mbps) max_bps(4.3 Mbps)
total_video_frames(463) avg_fps(30.07) min_fps(28.98) max_fps(31.00)
client_0 connection state has changed closed
client_0 has stopped
[client_1]
running_time(15s) connection_state(connected) total_packets(9210) packet_loss(0)
last_video_delay (22.0 ms) last_audio_delay (52.0 ms)
total_bytes(7.8 Mbytes) avg_bps(4.0 Mbps) min_bps(3.6 Mbps) max_bps(4.3 Mbps)
total_video_frames(463) avg_fps(30.07) min_fps(28.98) max_fps(31.00)
client_1 has stopped
[client_2]
running_time(15s) connection_state(connected) total_packets(9145) packet_loss(0)
last_video_delay (23.0 ms) last_audio_delay (63.0 ms)
total_bytes(7.7 Mbytes) avg_bps(4.0 Mbps) min_bps(3.6 Mbps) max_bps(4.5 Mbps)
total_video_frames(460) avg_fps(30.07) min_fps(28.97) max_fps(31.02)
client_1 connection state has changed closed
client_2 has stopped
[client_3]
running_time(15s) connection_state(connected) total_packets(9081) packet_loss(0)
last_video_delay (25.0 ms) last_audio_delay (65.0 ms)
total_bytes(7.7 Mbytes) avg_bps(4.0 Mbps) min_bps(3.6 Mbps) max_bps(4.3 Mbps)
total_video_frames(457) avg_fps(30.07) min_fps(29.00) max_fps(31.03)
client_2 connection state has changed closed
client_3 has stopped
client_3 connection state has changed closed
[client_4]
running_time(15s) connection_state(connected) total_packets(9016) packet_loss(0)
last_video_delay (26.0 ms) last_audio_delay (36.0 ms)
total_bytes(7.6 Mbytes) avg_bps(4.0 Mbps) min_bps(3.6 Mbps) max_bps(4.3 Mbps)
total_video_frames(454) avg_fps(30.07) min_fps(28.99) max_fps(31.02)
client_4 has stopped$ go run OvenRtcTester.go -url ws://192.168.0.160:13333/app/stream -n 100
client_0 connection state has changed checking
client_0 has started
client_0 connection state has changed connected
client_0 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_0 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_1 connection state has changed checking
client_1 has started
client_1 connection state has changed connected
client_1 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_1 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_2 connection state has changed checking
client_2 has started
client_2 connection state has changed connected
client_2 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_2 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
....
client_94 connection state has changed checking
client_94 has started
client_94 connection state has changed connected
client_94 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_94 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_95 connection state has changed checking
client_95 has started
client_95 connection state has changed connected
client_95 track has started, of type 100: video/H264
client_95 track has started, of type 101: audio/OPUS
client_96 connection state has changed checking
client_96 has started
<Summary>
Running time : 10s
Number of clients : 97
ICE Connection State : New(0), Checking(1) Connected(96) Completed(0) Disconnected(0) Failed(0) Closed(0)
Avg Video Delay(13.51 ms) Max Video Delay(47.00 ms) Min Video Delay(0.00 ms)
Avg Audio Delay(22.42 ms) Max Audio Delay(67.00 ms) Min Audio Delay(0.00 ms)
Avg FPS(27.20) Max FPS(32.51) Min FPS(0.00)
Avg BPS(3.7 Mbps) Max BPS(4.6 Mbps) Min BPS(0bps)
Total Bytes(238.7 MBytes) Avg Bytes(2.5 MBytes)
Total Packets(285013) Avg Packets(2938)
Total Packet Losses(306) Avg Packet Losses(3)
<Bind>
<Providers>
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</RTMP>
...
</Providers>
...
<Publishers>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<IceCandidate>*:10000/udp</IceCandidate>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
...
</Bind>
<Application>
<Publishers>
<AppWorkerCount>1</AppWorkerCount>
<StreamWorkerCount>8</StreamWorkerCount>
</Publishers>
</Application><Publishers>
<AppWorkerCount>32</AppWorkerCount>
<StreamWorkerCount>0</StreamWorkerCount>
</Publishers><Publishers>
<AppWorkerCount>1</AppWorkerCount>
<StreamWorkerCount>32</StreamWorkerCount>
</Publishers>{
"url_activate":1399711581,
"url_expire":1399721581,
"stream_expire":1399821581,
"allow_ip":"192.168.100.5/32"
}Base64URL.Encode(
HMAC.Encrypt(
SHA1,
secret_key,
"scheme://domain.com:port/app/stream[/file]?policy='encoded policy'>"
)
)<VirtualHost>
<SignedPolicy>
<PolicyQueryKeyName>policy</PolicyQueryKeyName>
<SignatureQueryKeyName>signature</SignatureQueryKeyName>
<SecretKey>aKq#1kj</SecretKey>
<Enables>
<Providers>rtmp</Providers>
<Publishers>webrtc,llhls,thumbnail</Publishers>
</Enables>
</SignedPolicy>
</VirtualHost>/misc/signed_policy_url_generator.sh./signed_policy_generator.sh [HMAC_KEY] [BASE_URL] [SIGNATURE_QUERY_KEY_NAME] [POLICY_QUERY_KEY_NAME] [POLICY]{"url_expire":1399721581}eyJ1cmxfZXhwaXJlIjoxMzk5NzIxNTgxfQws://192.168.0.100:3333/app/stream?policy=eyJ1cmxfZXhwaXJlIjoxMzk5NzIxNTgxfQws://192.168.0.100:3333/app/stream?policy=eyJ1cmxfZXhwaXJlIjoxMzk5NzIxNTgxfQdvVdBpoxAeCPl94Kt5RoiqLI0YEws://192.168.0.100/app/stream?policy=eyJ1cmxfZXhwaXJlIjoxMzk5NzIxNTgxfQ&signature=dvVdBpoxAeCPl94Kt5RoiqLI0YEError Correction
ULPFEC (VP8, H.264), In-band FEC (Opus)
Codec
VP8, H.264, Opus
Signalling
Self-Defined Signalling Protocol and Embedded Web Socket-Based Server
If you want to use the WebRTC feature, you need to add <WebRTC> element to the <Publishers> and <Ports> in the Server.xml configuration file, as shown in the example below.
WebRTC uses ICE for connections and specifically NAT traversal. The web browser or player exchanges the Ice Candidate with each other in the Signalling phase. Therefore, OvenMediaEngine provides an ICE for WebRTC connectivity.
If you set IceCandidate to *: 10000-10005/udp, as in the example above, OvenMediaEngine automatically gets IP from the server and generates IceCandidate using UDP ports from 10000 to 10005. If you want to use a specific IP as IceCandidate, specify a specific IP. You can also use only one 10000 UDP Port, not a range, by setting it to *: 10000.
OvenMediaEngine has embedded a WebSocket-based signalling server and provides our defined signalling protocol. Also, OvenPlayer supports our signalling protocol. WebRTC requires signalling to exchange Offer SDP and Answer SDP, but this part isn't standardized. If you want to use SDP, you need to create your exchange protocol yourself.
If you want to change the signaling port, change the value of <Ports><WebRTC><Signalling>.
The Signalling protocol is defined in a simple way:
If you want to use a player other than OvenPlayer, you need to develop the signalling protocol as shown above and can integrate OvenMediaEngine.
Add WebRTC element to Publisher to provide streaming through WebRTC.
Timeout
ICE (STUN request/response) timeout as milliseconds, if there is no request or response during this time, the session is terminated.
30000
Rtx
WebRTC retransmission, a useful option in WebRTC/udp, but ineffective in WebRTC/tcp.
false
Ulpfec
WebRTC forward error correction, a useful option in WebRTC/udp, but ineffective in WebRTC/tcp.
false
WebRTC Streaming starts when a live source is inputted and a stream is created. Viewers can stream using OvenPlayer or players that have developed or applied the OvenMediaEngine Signalling protocol.
Also, the codecs supported by each browser are different, so you need to set the Transcoding profile according to the browser you want to support. For example, Safari for iOS supports H.264 but not VP8. If you want to support all browsers, please set up VP8, H.264, and Opus codecs in all transcoders.
WebRTC doesn't support AAC, so when trying to bypass transcoding RTMP input, audio must be encoded as opus. See the settings below.
If you created a stream as shown in the table above, you can play WebRTC on OvenPlayer via the following URL:
WebRTC Signalling
ws://<Server IP>[:<Signalling Port]/<Application name>/<Stream name>
Secure WebRTC Signalling
wss://<Server IP>[:<Signalling Port]/<Application name>/<Stream name>
If you use the default configuration, you can stream to the following URL:
ws://[OvenMediaEngine IP]:3333/app/stream
wss://[OvenMediaEngine IP]:3333/app/stream
We have prepared a test player to make it easy to check if OvenMediaEngine is working. Please see the Test Player chapter for more information.
OvenMediaEnigne provides adaptive bitrates streaming over WebRTC. OvenPlayer can also play and display OvenMediaEngine's WebRTC ABR URL.
You can provide ABR by creating a playlist in <OutputProfile> as shown below. The URL to play the playlist is ws[s]://domain[:port]/<app name>/<stream name>/<playlist file name>
<Playlist><Rendition><Video> and <Playlist><Rendition><Audio> can connected using <Encodes><Video><Name> or <Encodes><Audio><Name>.
It is not recommended to use a <Bypass>true</Bypass> encode item if you want a seamless transition between renditions because there is a time difference between the transcoded track and bypassed track.
If <Options><WebRtcAutoAbr> is set to true, OvenMediaEngine will measure the bandwidth of the player session and automatically switch to the appropriate rendition.
Here is an example play URL for ABR in the playlist settings below. wss://domain:13334/app/stream/abr
See the Adaptive Bitrates Streaming section for more details on how to configure renditions.
WebRTC can negotiate codecs with SDP to support more devices. Playlist can set rendition with different kinds of codec. And OvenMediaEngine includes only renditions corresponding to the negotiated codec in the playlist and provides it to the player.
If an unsupported codec is included in the Rendition, the Rendition is not used. For example, if the Rendition's Audio contains aac, WebRTC ignores the Rendition.
In the example below, it consists of renditions with H.264 and Opus codecs set and renditions with VP8 and Opus codecs set. If the player selects VP8 in the answer SDP, OvenMediaEngine creates a playlist with only renditions containing VP8 and Opus and passes it to the player.
There are environments where the network speed is fast but UDP packet loss is abnormally high. In such an environment, WebRTC may not play normally. WebRTC does not support streaming using TCP, but connections to the TURN (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8656) server support TCP. Based on these characteristics of WebRTC, OvenMediaEngine supports TCP connections from the player to OvenMediaEngine by embedding a TURN server.
You can turn on the TURN server by setting <TcpRelay> in the WebRTC Bind.
Example : <TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
OME may sometimes not be able to get the server's public IP to its local interface. (Environment like Docker or AWS) So, specify the public IP for Relay IP. If * is used, the public IP obtained from <StunServer> and all IPs obtained from the local interface are used. Port is the tcp port on which the TURN server is listening.
WebRTC players can configure the TURN server through the iceServers setting.
You can play the WebRTC stream over TCP by attaching the query transport=tcp to the existing WebRTC play URL as follows.
OvenPlayer automatically sets iceServers by obtaining TURN server information set in <TcpRelay> through signaling with OvenMediaEngine.
If you are using custom player, set iceServers like this:
When sending Request Offer in the signaling phase with OvenMediaEngine, if you send the transport=tcp query string, ice_servers information is delivered as follows. You can use this information to set iceServers.
Delivery
RTP / RTCP
Security
DTLS, SRTP
Connectivity
ICE
sudo apt install -y build-essential nasm autoconf libtool zlib1g-dev tclsh cmake curlsudo yum install -y gcc-c++ make nasm autoconf libtool zlib-devel tcl cmake# for downloading latest version of nasm (x264 needs nasm 2.13+ but centos provides 2.10 )
sudo curl -so /etc/yum.repos.d/nasm.repo https://www.nasm.us/nasm.repo
sudo yum install centos-release-scl
sudo yum install -y bc gcc-c++ cmake nasm autoconf libtool glibc-static tcl bzip2 zlib-devel devtoolset-7
source scl_source enable devtoolset-7<Bind>
<Publishers>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000-10005/udp</IceCandidate>
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<TcpForce>true</TcpForce>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Bind><Server version="7">
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Applications>
<Application>
<Publishers>
<WebRTC>
<Timeout>30000</Timeout>
<Rtx>false</Rtx>
<Ulpfec>false</Ulpfec>
<JitterBuffer>false</JitterBuffer>
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server><OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Video>
<!-- vp8, h264 -->
<Codec>vp8</Codec>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30.0</Framerate>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles><OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>default</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<Playlist>
<Name>for Webrtc</Name>
<FileName>abr</FileName>
<Options>
<WebRtcAutoAbr>false</WebRtcAutoAbr>
</Options>
<Rendition>
<Name>1080p</Name>
<Video>1080p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>480p</Name>
<Video>480p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>720p</Name>
<Video>720p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
</Playlist>
<Playlist>
<Name>for llhls</Name>
<FileName>llhls_abr</FileName>
<Rendition>
<Name>480p</Name>
<Video>480p</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>720p</Name>
<Video>720p</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
</Playlist>
<Encodes>
<Video>
<Name>bypass_video</Name>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Video>
<Name>480p</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Width>640</Width>
<Height>480</Height>
<Bitrate>500000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
</Video>
<Video>
<Name>720p</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
</Video>
<Video>
<Name>1080p</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Width>1920</Width>
<Height>1080</Height>
<Bitrate>5000000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Name>bypass_audio</Name>
<Bypass>True</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Audio>
<Name>opus</Name>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles><Playlist>
<Name>for Webrtc</Name>
<FileName>abr</FileName>
<Options>
<WebRtcAutoAbr>false</WebRtcAutoAbr>
</Options>
<Rendition>
<Name>1080p</Name>
<Video>1080p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>480p</Name>
<Video>480p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>720p</Name>
<Video>720p</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>1080pVp8</Name>
<Video>1080pVp8</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>480pVp8</Name>
<Video>480pVp8</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>720pVp8</Name>
<Video>720pVp8</Video>
<Audio>opus</Audio>
</Rendition>
</Playlist><Server version="8">
...
<StunServer>stun.l.google.com:19302</StunServer>
<Bind>
<Publishers>
<WebRTC>
...
<IceCandidates>
<!-- <TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay> -->
<TcpRelay>Relay IP:Port</TcpRelay>
<TcpForce>false</TcpForce>
<IceCandidate>*:10000-10005/udp</IceCandidate>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Bind>
...
</Server> ws(s)://host:port/app/stream?transport=tcpmyPeerConnection = new RTCPeerConnection({
iceServers: [
{
urls: "turn:Relay IP:Port?transport=tcp",
username: "ome",
credential: "airen"
}
]
});candidates: [{candidate: "candidate:0 1 UDP 50 192.168.0.200 10006 typ host", sdpMLineIndex: 0}]
code: 200
command: "offer"
ice_servers: [{credential: "airen", urls: ["turn:192.168.0.200:3478?transport=tcp"], user_name: "ome"}]
id: 506764844
peer_id: 0
sdp: {,…}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
OPENSSL_VERSION=1.1.0g && \
DIR=/tmp/openssl && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-${OPENSSL_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
./config --prefix="${PREFIX}" --openssldir="${PREFIX}" -Wl,-rpath="${PREFIX}/lib" shared no-idea no-mdc2 no-rc5 no-ec2m no-ecdh no-ecdsa no-async && \
make -j 4 && \
sudo make install_sw && \
rm -rf ${DIR} && \
sudo rm -rf ${PREFIX}/binPREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
SRTP_VERSION=2.2.0 && \
DIR=/tmp/srtp && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://github.com/cisco/libsrtp/archive/v${SRTP_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-shared --disable-static --enable-openssl --with-openssl-dir="${PREFIX}" && \
make shared_library -j 4 && \
sudo make install && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
SRT_VERSION=1.3.3 && \
DIR=/tmp/srt && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://github.com/Haivision/srt/archive/v${SRT_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
PKG_CONFIG_PATH=${PREFIX}/lib/pkgconfig:${PKG_CONFIG_PATH} ./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-shared --disable-static && \
make -j 4 && \
sudo make install && \
rm -rf ${DIR} && \
sudo rm -rf ${PREFIX}/binPREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
OPUS_VERSION=1.1.3 && \
DIR=/tmp/opus && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://archive.mozilla.org/pub/opus/opus-${OPUS_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
autoreconf -fiv && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-shared --disable-static && \
make -j 4&& \
sudo make install && \
sudo rm -rf ${PREFIX}/share && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
X264_VERSION=20190513-2245-stable && \
DIR=/tmp/x264 && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://download.videolan.org/pub/videolan/x264/snapshots/x264-snapshot-${X264_VERSION}.tar.bz2 | tar -jx --strip-components=1 && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-shared --enable-pic --disable-cli && \
make -j 4&& \
sudo make install && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
VPX_VERSION=1.7.0 && \
DIR=/tmp/vpx && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://codeload.github.com/webmproject/libvpx/tar.gz/v${VPX_VERSION} | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-vp8 --enable-pic --enable-shared --disable-static --disable-vp9 --disable-debug --disable-examples --disable-docs --disable-install-bins && \
make -j 4 && \
sudo make install && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
FDKAAC_VERSION=0.1.5 && \
DIR=/tmp/aac && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://github.com/mstorsjo/fdk-aac/archive/v${FDKAAC_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
autoreconf -fiv && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" --enable-shared --disable-static --datadir=/tmp/aac && \
make -j 4&& \
sudo make install && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
FFMPEG_VERSION=3.4 && \
DIR=/tmp/ffmpeg && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://github.com/AirenSoft/FFmpeg/archive/ome/${FFMPEG_VERSION}.tar.gz | tar -xz --strip-components=1 && \
PKG_CONFIG_PATH=${PREFIX}/lib/pkgconfig:${PKG_CONFIG_PATH} ./configure \
--prefix="${PREFIX}" \
--enable-gpl \
--enable-nonfree \
--extra-cflags="-I${PREFIX}/include" \
--extra-ldflags="-L${PREFIX}/lib -Wl,-rpath,${PREFIX}/lib" \
--extra-libs=-ldl \
--enable-shared \
--disable-static \
--disable-debug \
--disable-doc \
--disable-programs \
--disable-avdevice --disable-dct --disable-dwt --disable-error-resilience --disable-lsp --disable-lzo --disable-rdft --disable-faan --disable-pixelutils \
--disable-everything \
--enable-zlib --enable-libopus --enable-libvpx --enable-libfdk_aac --enable-libx264 \
--enable-encoder=libvpx_vp8,libvpx_vp9,libopus,libfdk_aac,libx264 \
--enable-decoder=aac,aac_latm,aac_fixed,h264 \
--enable-parser=aac,aac_latm,aac_fixed,h264 \
--enable-network --enable-protocol=tcp --enable-protocol=udp --enable-protocol=rtp --enable-demuxer=rtsp \
--enable-filter=asetnsamples,aresample,aformat,channelmap,channelsplit,scale,transpose,fps,settb,asettb && \
make && \
sudo make install && \
sudo rm -rf ${PREFIX}/share && \
rm -rf ${DIR}PREFIX=/opt/ovenmediaengine && \
JEMALLOC_VERSION=5.2.1 && \
DIR=${TEMP_PATH}/jemalloc && \
mkdir -p ${DIR} && \
cd ${DIR} && \
curl -sLf https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc/releases/download/${JEMALLOC_VERSION}/jemalloc-${JEMALLOC_VERSION}.tar.bz2 | tar -jx --strip-components=1 && \
./configure --prefix="${PREFIX}" && \
make && \
sudo make install_include install_lib && \
rm -rf ${DIR}# Example of SELinux disallow OvenMediaEngine execution
$ systemctl start ovenmediaengine
==== AUTHENTICATING FOR org.freedesktop.systemd1.manage-units ====
Authentication is required to start 'ovenmediaengine.service'.
Authenticating as: Jeheon Han (getroot)
Password:
==== AUTHENTICATION COMPLETE ====
Failed to start ovenmediaengine.service: Unit ovenmediaengine. service not found.
# Check if SELinux is enabled
$ sestatus
SELinux status: enabled
SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux
SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux
Loaded policy name: targeted
Current mode: enforcing
Mode from config file: enforcing
Policy MLS status: enabled
Policy deny_unknown status: allowed
Memory protection checking: actual (secure)
Max kernel policy version: 31
# Check if SELinux denies execution
$ sudo tail /var/log/messages
...
May 17 12:44:24 localhost audit[1]: AVC avc: denied { read } for pid=1 comm="systemd" name="ovenmediaengine.service" dev="dm-0" ino=16836708 scontext=system_u:system_r:init_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:default_t:s0 tclass=file permissive=0
May 17 12:44:24 localhost audit[1]: AVC avc: denied { read } for pid=1 comm="systemd" name="ovenmediaengine.service" dev="dm-0" ino=16836708 scontext=system_u:system_r:init_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:default_t:s0 tclass=file permissive=0$ cd <OvenMediaEngine Git Clone Root Path>
$ sudo semodule -i misc/ovenmediaengine.pp
$ sudo touch /.autorelabel
# If you add a policy to SELinux, you must reboot the system.
$ sudo reboot$ sudo setenforce 0[ec2-user@ip-172-31-56-213 ~]$ cat /etc/sysctl.conf
fs.file-max = 100000
net.core.somaxconn = 65535
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 1440000
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 15
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 324000
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
net.core.rmem_default = 16777216
net.core.wmem_default = 16777216
net.core.optmem_max = 40960
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 16777216
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 50000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 2000000
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 10
net.ipv4.tcp_slow_start_after_idle = 0
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-56-213 ~]$ cat /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 1048576
* hard nofile 1048576[ec2-user@ip-172-31-56-213 ~]$ cat /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 1048576
* hard nofile 1048576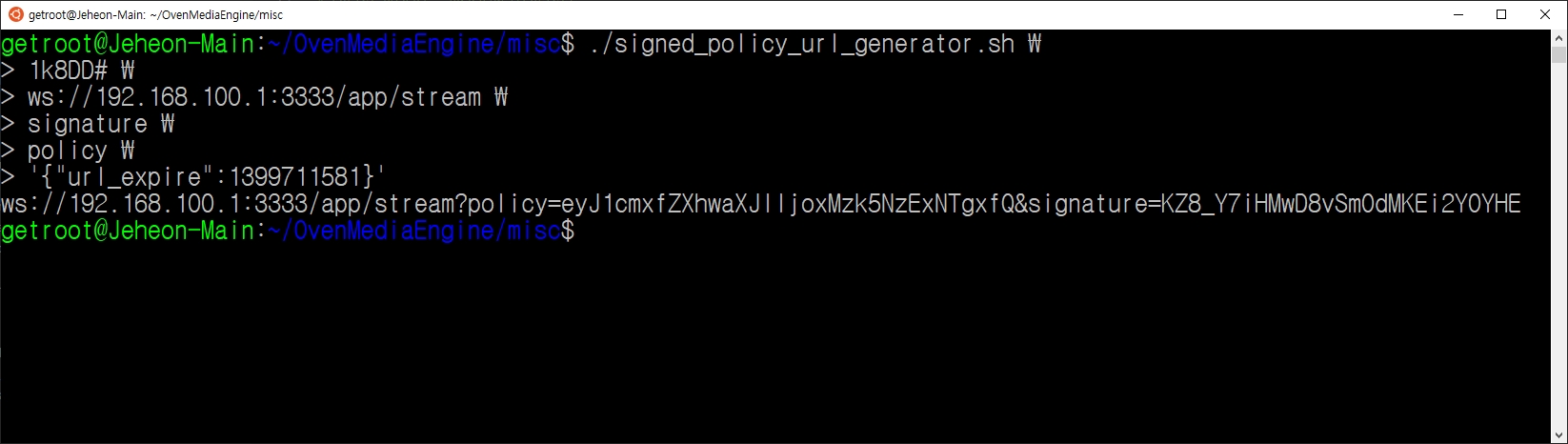
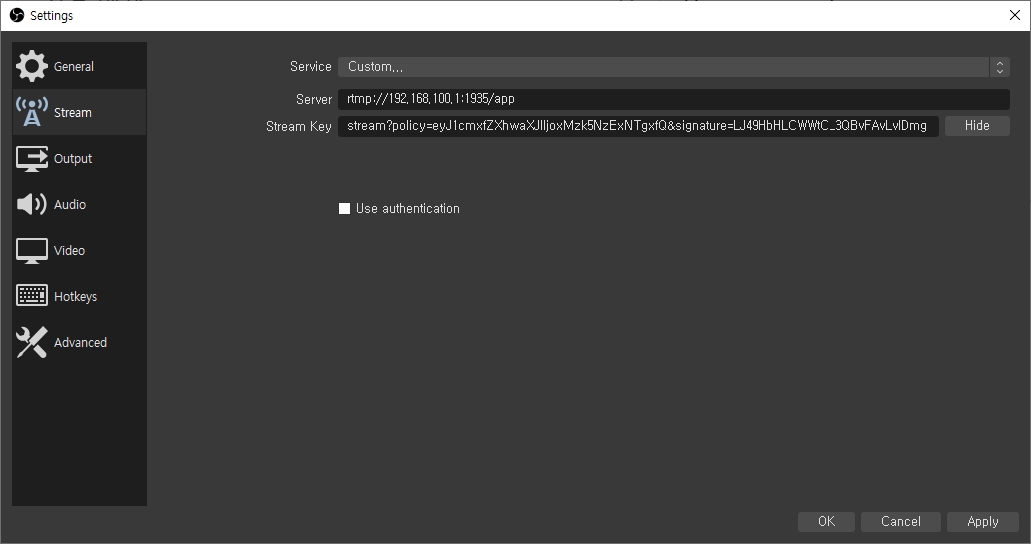

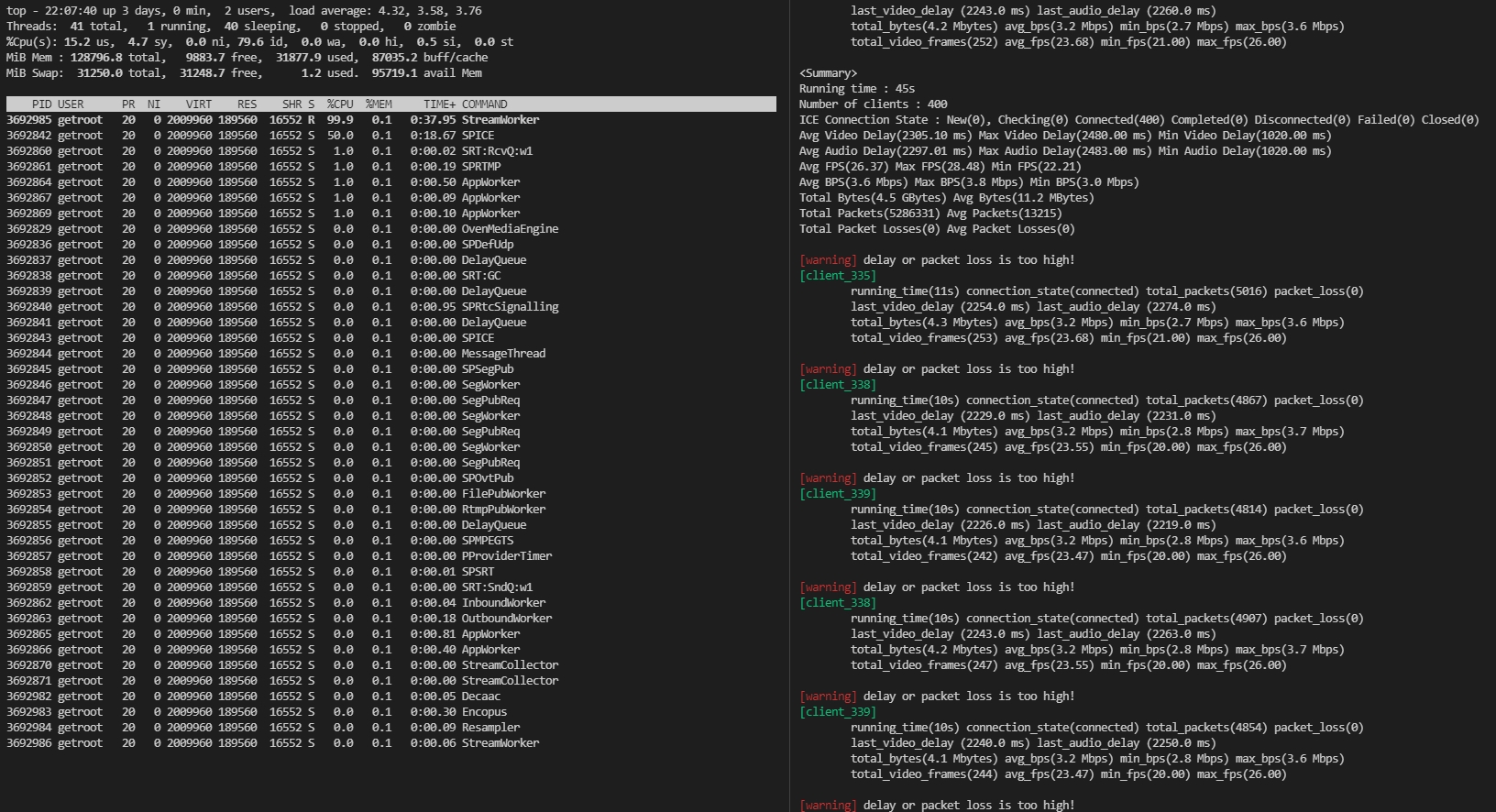
JitterBuffer
Audio and video are interleaved and output evenly, see below for details
false
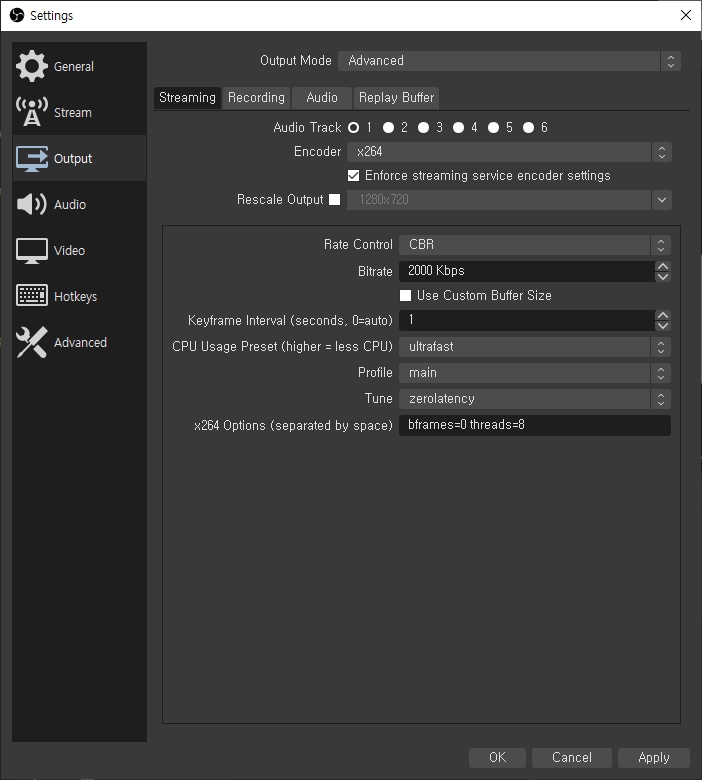
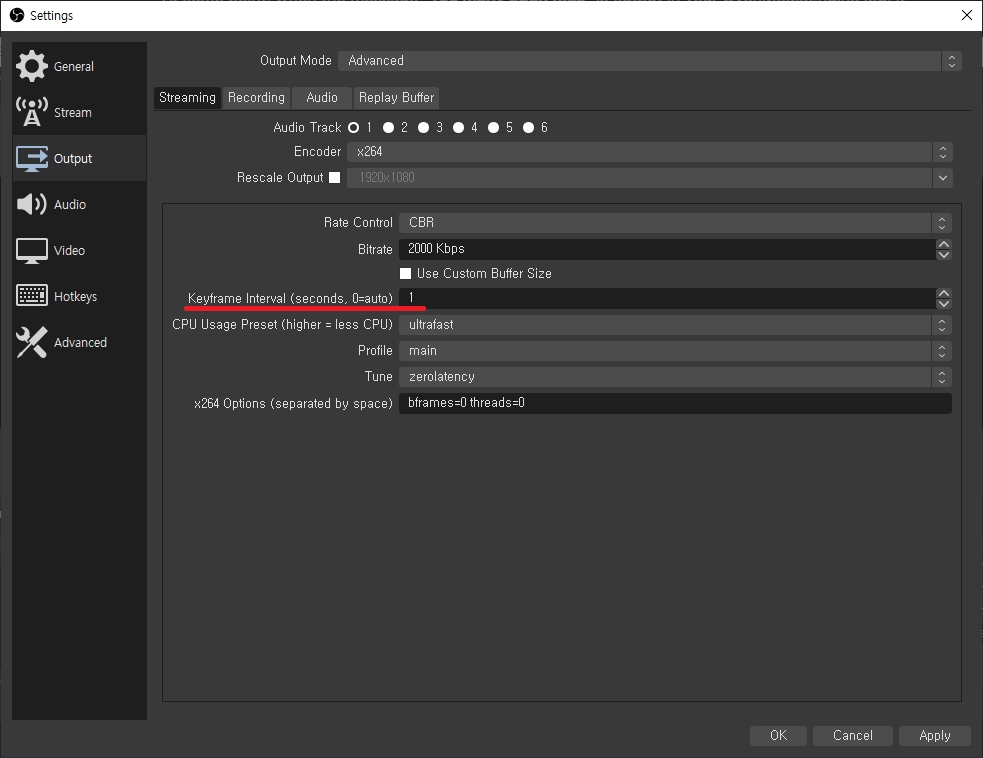
Configure virtual hosts to be created in Json array format.
It responds with Json array for each request.
It responds with Json array for each request.
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"default",
"service",
"poc"
]
{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}List all application names in the virtual host.
Request
Responses
Create application in the virtual host
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
Modify application settings. If this request succeeds, the Application will be restarted.
Request
Responses
Request
Responses
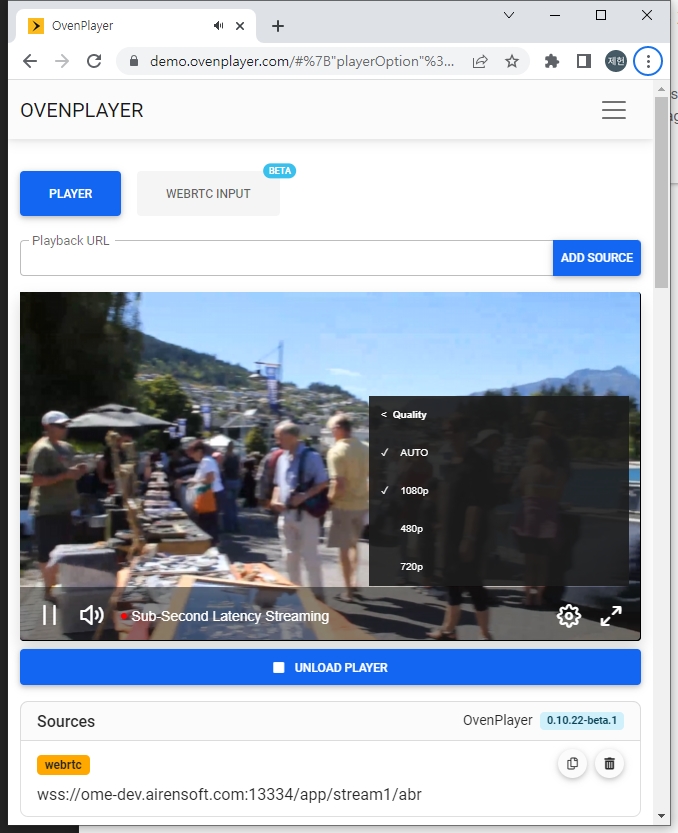
Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonContent-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the virtual host: [default1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the virtual host: [default1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Internal Server Error (500)",
"statusCode": 500
}[
{
"name": "vhost",
"host": {
"names": [
"ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"prod.airensoft.com"
],
"tls": {
"certPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.crt",
"chainCertPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.ca-bundle",
"keyPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.key"
}
},
"signedPolicy": {
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"policyQueryKeyName": "policy",
"secretKey": "aKq#1kj",
"signatureQueryKeyName": "signature"
},
"admissionWebhooks": {
"controlServerUrl": "https://control.server/admission",
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"secretKey": "",
"timeout": 3000
},
"origins": {
"origin": [
{
"location": "/app/rtsp",
"pass": {
"scheme": "rtsp",
"urls": {
"url": [
"rtsp.server:8554/ca-01"
]
}
}
}
]
},
"originMapStore": {
"originHostName": "ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"redisServer": {
"auth": "!@#ovenmediaengine",
"host": "redis.server:6379"
}
}
},
{
"name": "vhost2",
"host": {
"names": [
"ovenmediaengine.com"
],
"tls": {
"certPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.crt",
"chainCertPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.ca-bundle",
"keyPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.key"
}
}
}
]
# name (required)
The virtual host name. Cannot be duplicated.
# host (required)
## names (required)
The addresses(IP or Domain)of the host.
## tls (optional)
The certificate file path. Required if using TLS.
# signedPolicy (optional)
The SignedPolicy setting. Please refer to the manual for details.
# admissionWebhooks (optional)
The AdmissionWebhooks setting. Please refer to the manual for details.
# origins (optional)
The Origins setting. Please refer to the manual for details.
# originMapStore (optional)
The OriginMapStore setting. Please refer to the manual for details.[
{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200,
"response": {
"name": "enterprise",
"host": {
"names": [
"ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"prod.airensoft.com"
],
"tls": {
"certPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.crt",
"chainCertPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.ca-bundle",
"keyPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.key"
}
},
"signedPolicy": {
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"policyQueryKeyName": "policy",
"secretKey": "aKq#1kj",
"signatureQueryKeyName": "signature"
},
"admissionWebhooks": {
"controlServerUrl": "https://control.server/admission",
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"secretKey": "",
"timeout": 3000
},
"origins": {
"origin": [
{
"location": "/app/rtsp",
"pass": {
"scheme": "rtsp",
"urls": {
"url": [
"rtsp.server:8554/ca-01"
]
}
}
}
]
},
"originMapStore": {
"originHostName": "ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"redisServer": {
"auth": "!@#ovenmediaengine",
"host": "redis.server:6379"
}
}
}
},
{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200,
"response": {
"name": "free",
"host": {
"names": [
"ovenmediaengine.com"
],
"tls": {
"certPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.crt",
"chainCertPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.ca-bundle",
"keyPath": "/etc/pki/ovenmediaengine.com/_ovenmediaengine_com.key"
}
}
}
}
]
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Created virtual host information[
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "enterprise",
"host": {
"names": [
...
},
{
"statusCode": 409,
"message": "Conflict",
"response": {
...
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Virtual host information created when statusCode is 200{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
"response": {
"name": "default",
"distribution": "ovenServer",
"host": {
"name": "default",
"distribution": "ovenServer",
"host": {
"names": [
"ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"*"
],
"tls": {
"certPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.crt",
"chainCertPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.ca-bundle",
"keyPath": "/etc/pki/airensoft.com/_airensoft_com.key"
}
},
"signedPolicy": {
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"policyQueryKeyName": "policy",
"secretKey": "aKq#1kj",
"signatureQueryKeyName": "signature"
},
"admissionWebhooks": {
"controlServerUrl": "https://control.server/admission",
"enables": {
"providers": "rtmp,webrtc,srt",
"publishers": "webrtc,llhls"
},
"secretKey": "",
"timeout": 3000
},
"origins": {
"origin": [
{
"location": "/app/rtsp",
"pass": {
"scheme": "rtsp",
"urls": {
"url": [
"rtsp.server:8554/ca-01"
]
}
}
}
]
},
"originMapStore": {
"originHostName": "ome-dev.airensoft.com",
"redisServer": {
"auth": "!@#ovenmediaengine",
"host": "redis.server:6379"
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Virtual host information{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}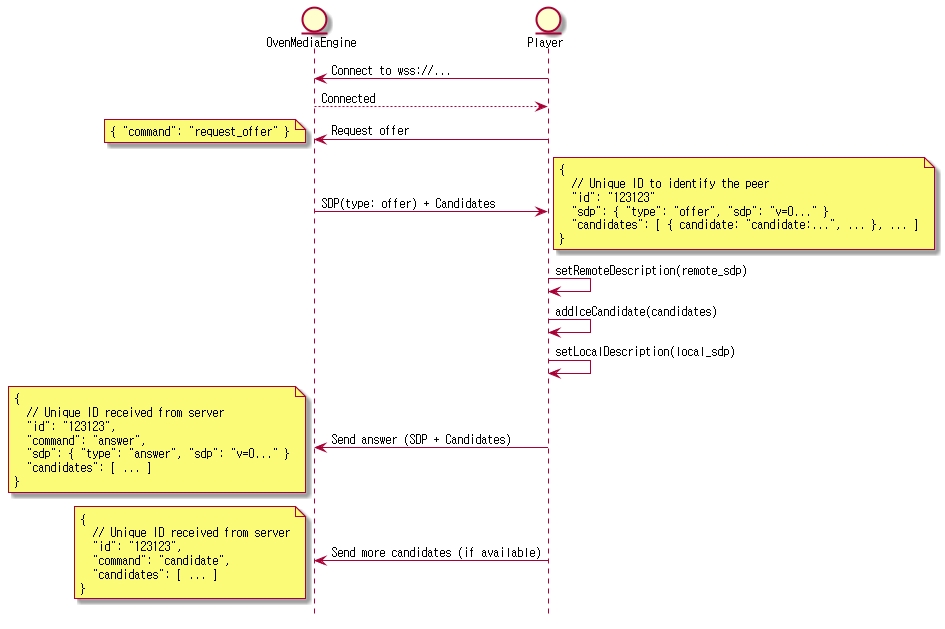
Configure applications to be created in Json array format.
It responds with Json array for each request.
It responds with Json array for each request.
Write the value you want to modify. However, name and outputProfiles cannot be modified.
Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the virtual host: [default1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": [
"app",
"app2",
"app3"
]
{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}OvenMediaEngine has a built-in live transcoder. The live transcoder can decode the incoming live source and re-encode it with the set codec or adjust the quality to encode at multiple bitrates.
The <OutputProfile> setting allows incoming streams to be re-encoded via the <Encodes> setting to create a new output stream. The name of the new output stream is determined by the rules set in <OutputStreamName>, and the newly created stream can be used according to the streaming URL format.
According to the above setting, if the incoming stream name is stream, the output stream becomes stream_bypassand the stream URL can be used as follows.
WebRTC ws://192.168.0.1:3333/app/stream_bypass
LLHLS http://192.168.0.1:8080/app/stream_bypass/llhls.m3u8
You can set the video profile as below:
The meaning of each property is as follows:
* required
Table of presets
A table in which presets provided for each codec library are mapped to OvenMediaEngine presets. Slow presets are of good quality and use a lot of resources, whereas Fast presets have lower quality and better performance. It can be set according to your own system environment and service purpose.
References
https://trac.ffmpeg.org/wiki/Encode/VP8
https://docs.nvidia.com/video-technologies/video-codec-sdk/nvenc-preset-migration-guide/
You can set the audio profile as below:
The meaning of each property is as follows:
* required
It is possible to have an audio only output profile by specifying the Audio profile and omitting a Video one.
You can set the Image profile as below:
The meaning of each property is as follows:
The image encoding profile is only used by thumbnail publishers. and, bypass option is not supported.
You can configure Video and Audio to bypass transcoding as follows:
You need to consider codec compatibility with some browsers. For example, chrome only supports OPUS codec for audio to play WebRTC stream. If you set to bypass incoming audio, it can't play on chrome.
WebRTC doesn't support AAC, so if video bypasses transcoding, audio must be encoded in OPUS.
If the codec or quality of the input stream is the same as the profile to be encoded into the output stream. there is no need to perform re-transcoding while unnecessarily consuming a lot of system resources. If the quality of the input track matches all the conditions of BypassIfMatch, it will be Pass-through without encoding
* eq: equal to / lte: less than or equal to / gte: greater than or equal to
* eq: equal to / lte: less than or equal to / gte: greater than or equal to
To support WebRTC and LLHLS, AAC and Opus codecs must be supported at the same time. Use the settings below to reduce unnecessary audio encoding.
If a video track with a lower quality than the encoding option is input, unnecessary upscaling can be prevented. SAR (Storage Aspect Ratio) is the ratio of original pixels. In the example below, even if the width and height of the original video are smaller than or equal to the width and height set in the encoding option, if the ratio is different, it means that encoding is performed without bypassing.
If you want to transcode with the same quality as the original. See the sample below for possible parameters that OME supports to keep original. If you remove the Width, Height, Framerate, Samplerate, and Channel parameters. then, It is transcoded with the same options as the original.
To change the video resolution when transcoding, use the values of width and height in the Video encode option. If you don't know the resolution of the original, it will be difficult to keep the aspect ratio after transcoding. Please use the following methods to solve these problems. For example, if you input only the Width value in the Video encoding option, the Height value is automatically generated according to the ratio of the original video.
From version 0.14.0, OvenMediaEngine can encode same source with multiple bitrates renditions and deliver it to the player.
As shown in the example configuration below, you can provide ABR by adding <Playlists> to <OutputProfile>. There can be multiple playlists, and each playlist can be accessed with <FileName>.
The method to access the playlist set through LLHLS is as follows.
http[s]://<domain>[:port]/<app>/<stream>/<FileName>.m3u8
The method to access the Playlist set through WebRTC is as follows.
ws[s]://<domain>[:port]/<app>/<stream>/<FileName>
Note that <FileName> must never contain the playlist and chunklist keywords. This is a reserved word used inside the system.
To set up <Rendition>, you need to add <Name> to the elements of <Encodes>. Connect the set <Name> into <Rendition><Video> or <Rendition><Audio>.
In the example below, three quality renditions are provided and the URL to play the abr playlist as LLHLS is https://domain:port/app/stream/abr.m3u8 and The WebRTC playback URL is wss://domain:port/app/stream/abr
Even if you set up multiple codecs, there is a codec that matches each streaming protocol supported by OME, so it can automatically select and stream codecs that match the protocol. However, if you don't set a codec that matches the streaming protocol you want to use, it won't be streamed.
The following is a list of codecs that match each streaming protocol:
Therefore, you set it up as shown in the table. If you want to stream using LLHLS, you need to set up H.264 and AAC, and if you want to stream using WebRTC, you need to set up Opus.
Also, if you are going to use WebRTC on all platforms, you need to configure both VP8 and H.264. This is because different codecs are supported for each browser, for example, VP8 only, H264 only, or both.
However, don't worry. If you set the codecs correctly, OME automatically sends the stream of codecs requested by the browser.
Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonContent-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the virtual host: [default1] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [default/app2] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/json{
"message": "[HTTP] Cannot change [name] using this API (400)",
"statusCode": 400
}WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [default/app2] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}Authorization: Basic {credentials}
# Authorization
Credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication created with <AccessToken>Content-Type: application/jsonWWW-Authenticate: Basic realm=”OvenMediaEngine”{
"message": "[HTTP] Could not find the application: [default/app2] (404)",
"statusCode": 404
}{
"message": "[HTTP] Internal Server Error (500)",
"statusCode": 500
}[
{
"name": "app",
"type": "live",
"outputProfiles": {
"outputProfile": [
{
"name": "default",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}",
"encodes": {
"audios": [
{
"name": "opus",
"codec": "opus",
"samplerate": 48000,
"bitrate": 128000,
"channel": 2,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
}
},
{
"name": "aac",
"codec": "aac",
"samplerate": 48000,
"bitrate": 128000,
"channel": 2,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
}
}
],
"videos": [
{
"name": "bypass_video",
"bypass": true
}
]
}
}
]
},
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
"rtspPull": {},
"srt": {},
"webrtc": {}
},
"publishers": {
"llhls": {},
"ovt": {},
"webrtc": {}
}
}
]
# name (required)
Application name to create
# type (required)
live - currently only support live
# outputProfiles (optional)
Set OutputProfile for Transcoding. See the ABR and Transcoding chapter for more details. If no outputProfiles are present in the request, a default outputProfile as above is configured.
# providers (optional)
Configure providers. See the Live Source chapter for details. If providers are not present in the request, they are configured with default providers as above.
# publishers (optional)
Configure publishers. See the Streaming chapter for details. If publishers are not present in the request, they are configured with default publishers as above.[
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "app",
"outputProfiles": {
...
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
...
},
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
...
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Created application information[
{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"name": "app",
"outputProfiles": {
...
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
...
},
{
"statusCode": 409,
"message": "Conflict",
"response": {
...
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Application information created when statusCode is 200{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"dynamic": false,
"name": "app",
"type": "live",
"outputProfiles": {
"outputProfile": [
{
"encodes": {
"audios": [
{
"bitrate": 128000,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
},
"channel": 2,
"codec": "opus",
"name": "opus",
"samplerate": 48000
},
{
"bitrate": 128000,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
},
"channel": 2,
"codec": "aac",
"name": "aac",
"samplerate": 48000
}
],
"videos": [
{
"bypass": true,
"name": "bypass_video"
}
]
},
"name": "bypass",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}"
}
]
},
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
"rtspPull": {},
"srt": {},
"webrtc": {}
},
"publishers": {
"llhls": {},
"ovt": {},
"webrtc": {}
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Application information{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"providers": {
"webrtc": {
"timeout": 60000
}
}
}{
"statusCode": 200,
"message": "OK",
"response": {
"dynamic": false,
"name": "app",
"type": "live",
"outputProfiles": {
"outputProfile": [
{
"encodes": {
"audios": [
{
"bitrate": 128000,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
},
"channel": 2,
"codec": "opus",
"name": "opus",
"samplerate": 48000
},
{
"bitrate": 128000,
"bypassIfMatch": {
"codec": "eq"
},
"channel": 2,
"codec": "aac",
"name": "aac",
"samplerate": 48000
}
],
"videos": [
{
"bypass": true,
"name": "bypass_video"
}
]
},
"name": "bypass",
"outputStreamName": "${OriginStreamName}"
}
]
},
"providers": {
"ovt": {},
"rtmp": {},
"rtspPull": {},
"srt": {},
"webrtc": {
"timeout": 60000
}
},
"publishers": {
"llhls": {},
"ovt": {},
"webrtc": {}
}
}
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code
# response
Mofified application information{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}{
"message": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
}
# statusCode
Same as HTTP Status Code
# message
A human-readable description of the response code{
"message": "[HTTP] Authorization header is required to call API (401)",
"statusCode": 401
}h264_nvenc
h264_qsv
h264_beamr (Enterprise Only)
Audio
AAC
aac
Opus
opus
Image
JPEG
jpeg
PNG
png
Framerate
Frames per second
KeyFrameInterval
Number of frames between two keyframes (0~600) default is framerate (i.e. 1 second)
BFrames
Number of B-frame (0~16) default is 0
Profile
H264 only encoding profile (baseline, main, high)
Preset
Presets of encoding quality and performance
ThreadCount
Number of threads in encoding
best
medium
QP (24-51)
p5
No Support
good
fast
QP (32-51)
p4
No Support
realtime
faster
QP (40-51)
p3
No Support
realtime
eq
Compare ratio of video resolution
Video
VP8, H.264
Audio
AAC, Opus
Video
VP8
vp8
H.264
h264 (Automatic Codec Selection)
h264_openh264
Codec*
Specifies the vp8 or h264 codec to use
Bitrate*
Bit per second
Name
Encode name for Renditions
Width
Width of resolution
Height
Height of resolution
slower
QP( 10-39)
p7
No Support
best
slow
QP (16-45)
p6
Codec*
Specifies the opus or aac codec to use
Bitrate*
Bits per second
Name
Encode name for Renditions
Samplerate
Samples per second
Channel
The number of audio channels
Codec
Specifies the jpeg or png codec to use
Width
Width of resolution
Height
Height of resolution
Framerate
Frames per second
Codec (Optional)
eq
Compare video codecs
Width (Optional)
eq, lte, gte
Compare horizontal pixel of video resolution
Height (Optional)
eq, lte, gte
Compare vertical pixel of video resolution
Codec (Optional)
eq
Compare audio codecs
Samplerate (Optional)
eq, lte, gte
Compare sampling rate of audio
Channel (Optional)
eq, lte, gte
Compare number of channels in audio
WebRTC
VP8, H.264, Opus
LLHLS
H.264, AAC
No Support
SAR (Optional)
<OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}_bypass</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles><Encodes>
<Video>
<Name>h264_hd</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30.0</Framerate>
<KeyFrameInterval>30</KeyFrameInterval>
<BFrames>0</BFrames>
<Preset>fast</Preset>
<ThreadCount>4</ThreadCount>
</Video>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Audio>
<Name>opus_128</Name>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Image>
<Codec>jpeg</Codec>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Framerate>1</Framerate>
</Image>
</Encodes><Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio><Encodes>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Name>cond_audio_aac</Name>
<Codec>aac</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
<BypassIfMatch>
<Codec>eq</Codec>
<Samplerate>lte</Samplerate>
<Channel>eq</Channel>
</BypassIfMatch>
</Audio>
<Audio>
<Name>cond_audio_opus</Name>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
<BypassIfMatch>
<Codec>eq</Codec>
<Samplerate>lte</Samplerate>
<Channel>eq</Channel>
</BypassIfMatch>
</Audio>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Video>
<Name>prevent_upscaling_video</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Bitrate>2048000</Bitrate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
<BypassIfMatch>
<Codec>eq</Codec>
<Width>lte</Width>
<Height>lte</Height>
<SAR>eq</SAR>
</BypassIfMatch>
</Video>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Video>
<Codec>vp8</Codec>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
</Audio>
<Image>
<Codec>jpeg</Codec>
</Image>
</Encodes><Encodes>
<Video>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<!-- Height is automatically calculated as the original video ratio -->
<Framerate>30.0</Framerate>
</Video>
<Video>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Bitrate>2000000</Bitrate>
<!-- Width is automatically calculated as the original video ratio -->
<Height>720</Height>
<Framerate>30.0</Framerate>
</Video>
</Encodes><OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<!--LLHLS URL : https://domain/app/stream/abr.m3u8 -->
<Playlist>
<Name>For LLHLS</Name>
<FileName>abr</FileName>
<Options> <!-- Optinal -->
<!--
Automatically switch rendition in WebRTC ABR
[Default] : true
-->
<WebRtcAutoAbr>true</WebRtcAutoAbr>
</Options>
<Rendition>
<Name>Bypass</Name>
<Video>bypass_video</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>FHD</Name>
<Video>video_1280</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
<Rendition>
<Name>HD</Name>
<Video>video_720</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
</Playlist>
<!--LLHLS URL : https://domain/app/stream/llhls.m3u8 -->
<Playlist>
<Name>Change Default</Name>
<FileName>llhls</FileName>
<Rendition>
<Name>HD</Name>
<Video>video_720</Video>
<Audio>bypass_audio</Audio>
</Rendition>
</Playlist>
<Encodes>
<Audio>
<Name>bypass_audio</Name>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Name>bypass_video</Name>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Name>video_1280</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Bitrate>5024000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
<Width>1920</Width>
<Height>1280</Height>
<Preset>faster</Preset>
</Video>
<Video>
<Name>video_720</Name>
<Codec>h264</Codec>
<Bitrate>2024000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Preset>faster</Preset>
</Video>
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>OvenMediaEngine has an XML configuration file. If you start OvenMediaEngine with systemctl start ovenmediaengine, the config file is loaded from the following path.
If you run it directly from the command line, it loads the configuration file from:
If you run it in Docker container, the path to the configuration file is:
The Server is the root element of the configuration file. The versionattribute indicates the version of the configuration file. OvenMediaEngine uses this version information to check if the config file is a compatible version.
The IP address is OvenMediaEngine will bind to. If you set *, all IP addresses of the system are used. If you enter a specific IP, the Host uses that IP only.
PrivacyProtection is an option to comply with GDPR, PIPEDA, CCPA, LGPD, etc. by deleting the client's personal information (IP, Port) from all records. When this option is turned on, the client's IP and Port are converted to xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xxx in all logs and REST APIs.
OvenMediaEngine needs to know its public IP in order to connect to the player through WebRTC. The server must inform the player of the IceCandidates and TURN server addresses when signaling, and this information must be the IP the player can connect to. However, in environments such as Docker or AWS, public IP cannot be obtained through a local interface, so a method of obtaining public IP using stun server is provided (available from version 0.11.1).
If OvenMediaEngine obtains the public IP through communication with the set stun server, you can set the public IP by using * or ${PublicIP} in IceCandidate and TcpRelay.
The Bind is the configuration for the server port that will be used. Bind consists of Providers and Publishers. The Providers are the server for stream input, and the Publishers are the server for streaming.
The meaning of each element is shown in the following table:
VirtualHosts are a way to run more than one streaming server on a single machine. OvenMediaEngine supports IP-based virtual host and Domain-based virtual host. "IP-based" means that you can separate streaming servers into multiples by setting different IP addresses, and "Domain-based" means that even if the streaming servers use the same IP address, you can split the streaming servers into multiples by setting different domain names.
VirtualHostsconsist of Name, Host, Origins, SignedPolicy, and Applications.
The Domain has Names and TLS. Names can be either a domain address or an IP address. Setting * means it allows all domains and IP addresses.
SignedPolicy is a module that limits the user's privileges and time. For example, operators can distribute RTMP URLs that can be accessed for 60 seconds to authorized users, and limit RTMP transmission to 1 hour. The provided URL will be destroyed after 60 seconds, and transmission will automatically stop after 1 hour. Users who are provided with a SingedPolicy URL cannot access resources other than the provided URL. This is because the SignedPolicy URL is authenticated. See the chapter for more information.
Origins (also we called OriginMap) are a feature to pull streams from external servers. It now supports OVT and RTSP for the pulling protocols. OVT is a protocol defined by OvenMediaEngine for Origin-Edge communication. It allows OvenMediaEngine to relay a stream from other OvenMediaEngines that have OVP Publisher turned on. Using RTSP, OvenMediaEngine pulls a stream from an RTSP server and creates a stream. RTSP stream from external servers can stream by WebRTC, HLS, and MPEG-DASH.
The Origin has Location and Pass elements. Location is a URI pattern for incoming requests. If the incoming URL request matches Location, OvenMediaEngine pulls the stream according to a Pass element. In the Pass element, you can set the origin stream's protocol and URLs.
To run the Edge server, Origin creates application and stream if there isn't those when user request. For more learn about Origin-Edge, see the chapter.
<Application> consists of various elements that can define the operation of the stream, including Stream input, Encoding, and Stream output. In other words, you can create as many <Application> as you like and build various streaming environments.
<Application> needs to set <Name> and <Type> as follows:
<Name> is used to configure the Streaming URL.
<Type> defines the operation of <Application>. Currently, there is only a live type.
<OutputProfile> is a configuration that creates an output stream. Output stream name can be set with <OutputStreamName>, and transcoding properties can be set through <Encodes>. If you want to stream one input to multiple output streams, you can set multiple <OutputProfile>.
For more information about the OutputProfiles, please see the chapter.
Providers ingest streams that come from a media source.
If you want to get more information about the <Providers>, please refer to the chapter.
You can configure the Output Stream operation in <Publishers>. <ThreadCount> is the number of threads used by each component responsible for the <Publishers> protocol.
OvenMediaEngine currently supports WebRTC, Low-Latency DASH, MEPG-DASH, and HLS. If you don't want to use any protocol then you can delete that protocol setting, the component for that protocol isn't initialized. As a result, you can save system resources by deleting the settings of unused protocol components.
If you want to learn more about WebRTC, visit the chapter. And if you want to get more information on Low-Latency DASH, MPEG-DASH, and HLS, refer to the chapter on .
Finally, Server.xml is configured as follows:
/usr/share/ovenmediaengine/conf/Server.xml/<OvenMediaEngine Binary Path>/conf/Server.xml# For Origin mode
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/origin_conf/Server.xml
# For Edge mode
/opt/ovenmediaengine/bin/edge_conf/Server.xmlOVT port for an origin server.
OVT is a protocol defined by OvenMediaEngine for Origin-Edge communication. For more information about Origin-Edge, see the chapter.
LLHLS
HTTP(s) port for LLHLS streaming.
<Managers><API>
REST API Server port
RTMP
RTMP port for incoming RTMP stream.
SRT
SRT port for incoming SRT stream
MPEG-TS
MPEGTS ports for incoming MPEGTS/UDP stream.
WebRTC
Port for WebRTC. If you want more information on the WebRTC port, see the WebRTC Ingest and WebRTC Streaming chapters.
OVT
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<IP>*</IP>
<PrivacyProtection>false</PrivacyProtection>
<StunServer>stun.l.google.com:19302</StunServer>
<Bind>...</Bind>
<VirtualHosts>...</VirtualHosts>
</Server> <IP>*</IP><StunServer>stun.l.google.com:19302</StunServer><!-- Settings for the ports to bind -->
<Bind>
<!-- Enable this configuration if you want to use API Server -->
<!--
<Managers>
<API>
<Port>8081</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</API>
</Managers>
-->
<Providers>
<!-- Pull providers -->
<RTSPC>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</RTSPC>
<OVT>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</OVT>
<!-- Push providers -->
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</RTMP>
<SRT>
<Port>9999</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</SRT>
<MPEGTS>
<!--
Listen on port 4000~4005 (<Port>4000-4004,4005/udp</Port>)
This is just a demonstration to show that you can configure the port in several ways
-->
<Port>4000/udp</Port>
</MPEGTS>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000/udp</IceCandidate>
<!--
If you want to stream WebRTC over TCP, specify IP:Port for TURN server.
This uses the TURN protocol, which delivers the stream from the built-in TURN server to the player's TURN client over TCP.
For detailed information, refer https://airensoft.gitbook.io/ovenmediaengine/streaming/webrtc-publishing#webrtc-over-tcp
-->
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<!-- TcpForce is an option to force the use of TCP rather than UDP in WebRTC streaming. (You can omit ?transport=tcp accordingly.) If <TcpRelay> is not set, playback may fail. -->
<TcpForce>true</TcpForce>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Providers>
<Publishers>
<OVT>
<Port>9000</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</OVT>
<LLHLS>
<!--
OME only supports h2, so LLHLS works over HTTP/1.1 on non-TLS ports.
LLHLS works with higher performance over HTTP/2,
so it is recommended to use a TLS port.
-->
<Port>3333</Port>
<!-- If you want to use TLS, specify the TLS port -->
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</LLHLS>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000-10005/udp</IceCandidate>
<!--
If you want to stream WebRTC over TCP, specify IP:Port for TURN server.
This uses the TURN protocol, which delivers the stream from the built-in TURN server to the player's TURN client over TCP.
For detailed information, refer https://airensoft.gitbook.io/ovenmediaengine/streaming/webrtc-publishing#webrtc-over-tcp
-->
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<!-- TcpForce is an option to force the use of TCP rather than UDP in WebRTC streaming. (You can omit ?transport=tcp accordingly.) If <TcpRelay> is not set, playback may fail. -->
<TcpForce>true</TcpForce>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Bind><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<VirtualHosts>
<VirtualHost>
<Name>default</Name>
<Host>
...
</Host>
<Origins>
...
</Origins>
<SignedPolicy>
...
</SignedPolicy>
<Applications>
...
</Applications>
</Host>
</Hosts>
</Server><Host>
<Names>
<!-- Domain names
<Name>stream1.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>stream2.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>*.sub.airensoft.com</Name>
-->
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<TLS>
<CertPath>path/to/file.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>path/to/file.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>path/to/file.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
</Host><Origins>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/stream</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/stream_720p</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/rtsp/stream</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>rtsp</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>rtsp-server.com:554/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin2.com:9000/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
</Origins><VirtualHost>
...
<Applications>
<Application>
...
</Application>
<Application>
...
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost><Application>
<Name>app</Name>
<Type>live</Type>
<OutputProfiles> ... </OutputProfiles>
<Providers> ... </Providers>
<Publishers> ... </Publishers>
</Application><Application>
<OutputProfiles>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
<!--
<Video>
<Codec>vp8</Codec>
<Bitrate>1024000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
</Video>
-->
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles>
</Application><Application>
<Providers>
<RTMP/>
<WebRTC/>
<SRT/>
<RTSPPull/>
<OVT/>
<MPEGTS>
<StreamMap>
...
</StreamMap>
</MPEGTS>
</Providers>
</Application><Application>
<Publishers>
<OVT />
<HLS />
<DASH />
<LLDASH />
<WebRTC />
</Publishers>
</Application><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server version="8">
<Name>OvenMediaEngine</Name>
<!-- Host type (origin/edge) -->
<Type>origin</Type>
<!-- Specify IP address to bind (* means all IPs) -->
<IP>*</IP>
<PrivacyProtection>false</PrivacyProtection>
<!--
To get the public IP address(mapped address of stun) of the local server.
This is useful when OME cannot obtain a public IP from an interface, such as AWS or docker environment.
If this is successful, you can use ${PublicIP} in your settings.
-->
<StunServer>stun.l.google.com:19302</StunServer>
<Modules>
<!--
Currently OME only supports h2 like all browsers do. Therefore, HTTP/2 only works on TLS ports.
-->
<HTTP2>
<Enable>true</Enable>
</HTTP2>
<LLHLS>
<Enable>true</Enable>
</LLHLS>
<!-- P2P works only in WebRTC and is experiment feature -->
<P2P>
<!-- disabled by default -->
<Enable>false</Enable>
<MaxClientPeersPerHostPeer>2</MaxClientPeersPerHostPeer>
</P2P>
</Modules>
<!-- Settings for the ports to bind -->
<Bind>
<!-- Enable this configuration if you want to use API Server -->
<!--
<Managers>
<API>
<Port>8081</Port>
<TLSPort>8082</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</API>
</Managers>
-->
<Providers>
<!-- Pull providers -->
<RTSPC>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</RTSPC>
<OVT>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</OVT>
<!-- Push providers -->
<RTMP>
<Port>1935</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</RTMP>
<SRT>
<Port>9999</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</SRT>
<MPEGTS>
<!--
Listen on port 4000~4005 (<Port>4000-4004,4005/udp</Port>)
This is just a demonstration to show that you can configure the port in several ways
-->
<Port>4000/udp</Port>
</MPEGTS>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000/udp</IceCandidate>
<!--
If you want to stream WebRTC over TCP, specify IP:Port for TURN server.
This uses the TURN protocol, which delivers the stream from the built-in TURN server to the player's TURN client over TCP.
For detailed information, refer https://airensoft.gitbook.io/ovenmediaengine/streaming/webrtc-publishing#webrtc-over-tcp
-->
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<!-- TcpForce is an option to force the use of TCP rather than UDP in WebRTC streaming. (You can omit ?transport=tcp accordingly.) If <TcpRelay> is not set, playback may fail. -->
<TcpForce>true</TcpForce>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Providers>
<Publishers>
<OVT>
<Port>9000</Port>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</OVT>
<LLHLS>
<!--
OME only supports h2, so LLHLS works over HTTP/1.1 on non-TLS ports.
LLHLS works with higher performance over HTTP/2,
so it is recommended to use a TLS port.
-->
<Port>3333</Port>
<!-- If you want to use TLS, specify the TLS port -->
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</LLHLS>
<WebRTC>
<Signalling>
<Port>3333</Port>
<TLSPort>3334</TLSPort>
<WorkerCount>1</WorkerCount>
</Signalling>
<IceCandidates>
<IceCandidate>*:10000-10005/udp</IceCandidate>
<!--
If you want to stream WebRTC over TCP, specify IP:Port for TURN server.
This uses the TURN protocol, which delivers the stream from the built-in TURN server to the player's TURN client over TCP.
For detailed information, refer https://airensoft.gitbook.io/ovenmediaengine/streaming/webrtc-publishing#webrtc-over-tcp
-->
<TcpRelay>*:3478</TcpRelay>
<!-- TcpForce is an option to force the use of TCP rather than UDP in WebRTC streaming. (You can omit ?transport=tcp accordingly.) If <TcpRelay> is not set, playback may fail. -->
<TcpForce>true</TcpForce>
<TcpRelayWorkerCount>1</TcpRelayWorkerCount>
</IceCandidates>
</WebRTC>
</Publishers>
</Bind>
<!--
Enable this configuration if you want to use API Server
<AccessToken> is a token for authentication, and when you invoke the API, you must put "Basic base64encode(<AccessToken>)" in the "Authorization" header of HTTP request.
For example, if you set <AccessToken> to "ome-access-token", you must set "Basic b21lLWFjY2Vzcy10b2tlbg==" in the "Authorization" header.
-->
<!--
<Managers>
<Host>
<Names>
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<TLS>
<CertPath>path/to/file.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>path/to/file.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>path/to/file.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
</Host>
<API>
<AccessToken>ome-access-token</AccessToken>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*.airensoft.com</Url>
<Url>http://*.sub-domain.airensoft.com</Url>
<Url>http?://airensoft.*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</API>
</Managers>
-->
<VirtualHosts>
<!-- You can use wildcard like this to include multiple XMLs -->
<VirtualHost include="VHost*.xml" />
<VirtualHost>
<Name>default</Name>
<!--Distribution is a value that can be used when grouping the same vhost distributed across multiple servers. This value is output to the events log, so you can use it to aggregate statistics. -->
<Distribution>ovenmediaengine.com</Distribution>
<!-- Settings for multi ip/domain and TLS -->
<Host>
<Names>
<!-- Host names
<Name>stream1.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>stream2.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>*.sub.airensoft.com</Name>
<Name>192.168.0.1</Name>
-->
<Name>*</Name>
</Names>
<!--
<TLS>
<CertPath>path/to/file.crt</CertPath>
<KeyPath>path/to/file.key</KeyPath>
<ChainCertPath>path/to/file.crt</ChainCertPath>
</TLS>
-->
</Host>
<!--
Refer https://airensoft.gitbook.io/ovenmediaengine/signedpolicy
<SignedPolicy>
<PolicyQueryKeyName>policy</PolicyQueryKeyName>
<SignatureQueryKeyName>signature</SignatureQueryKeyName>
<SecretKey>aKq#1kj</SecretKey>
<Enables>
<Providers>rtmp,webrtc,srt</Providers>
<Publishers>webrtc,hls,llhls,dash,lldash</Publishers>
</Enables>
</SignedPolicy>
-->
<!--
<AdmissionWebhooks>
<ControlServerUrl></ControlServerUrl>
<SecretKey></SecretKey>
<Timeout>3000</Timeout>
<Enables>
<Providers>rtmp,webrtc,srt</Providers>
<Publishers>webrtc,hls,llhls,dash,lldash</Publishers>
</Enables>
</AdmissionWebhooks>
-->
<!-- <Origins>
<Properties>
<NoInputFailoverTimeout>3000</NoInputFailoverTimeout>
<UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout>60000</UnusedStreamDeletionTimeout>
</Properties>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/stream</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/stream_720p</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
<ForwardQueryParams>false</ForwardQueryParams>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/app/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
<Origin>
<Location>/edge/</Location>
<Pass>
<Scheme>ovt</Scheme>
<Urls><Url>origin.com:9000/app/</Url></Urls>
</Pass>
</Origin>
</Origins> -->
<!-- Settings for applications -->
<Applications>
<Application>
<Name>app</Name>
<!-- Application type (live/vod) -->
<Type>live</Type>
<OutputProfiles>
<!-- Enable this configuration if you want to hardware acceleration using GPU -->
<HardwareAcceleration>false</HardwareAcceleration>
<OutputProfile>
<Name>bypass_stream</Name>
<OutputStreamName>${OriginStreamName}</OutputStreamName>
<Encodes>
<Audio>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Audio>
<Video>
<Bypass>true</Bypass>
</Video>
<Audio>
<Codec>opus</Codec>
<Bitrate>128000</Bitrate>
<Samplerate>48000</Samplerate>
<Channel>2</Channel>
</Audio>
<!--
<Video>
<Codec>vp8</Codec>
<Bitrate>1024000</Bitrate>
<Framerate>30</Framerate>
<Width>1280</Width>
<Height>720</Height>
<Preset>faster</Preset>
</Video>
-->
</Encodes>
</OutputProfile>
</OutputProfiles>
<Providers>
<OVT />
<WebRTC />
<RTMP />
<SRT />
<MPEGTS>
<StreamMap>
<!--
Set the stream name of the client connected to the port to "stream_${Port}"
For example, if a client connects to port 4000, OME creates a "stream_4000" stream
<Stream>
<Name>stream_${Port}</Name>
<Port>4000,4001-4004</Port>
</Stream>
<Stream>
<Name>stream_4005</Name>
<Port>4005</Port>
</Stream>
-->
<Stream>
<Name>stream_${Port}</Name>
<Port>4000</Port>
</Stream>
</StreamMap>
</MPEGTS>
<RTSPPull />
<WebRTC>
<Timeout>30000</Timeout>
</WebRTC>
</Providers>
<Publishers>
<AppWorkerCount>1</AppWorkerCount>
<StreamWorkerCount>8</StreamWorkerCount>
<OVT />
<WebRTC>
<Timeout>30000</Timeout>
<Rtx>false</Rtx>
<Ulpfec>false</Ulpfec>
<JitterBuffer>false</JitterBuffer>
</WebRTC>
<LLHLS>
<ChunkDuration>0.2</ChunkDuration>
<SegmentDuration>6</SegmentDuration>
<SegmentCount>10</SegmentCount>
<CrossDomains>
<Url>*</Url>
</CrossDomains>
</LLHLS>
</Publishers>
</Application>
</Applications>
</VirtualHost>
</VirtualHosts>
</Server>